* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrocardiographs ECG
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
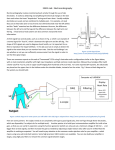
Electrocardiographs ECG OUTLINES : Introducing what is meant by Biopotential signals. what is Electrocardiograph (ECG). The conduction system. The standard Lead system. The ECG machine Construction. Introduction to Biopotential Signals I Electrocardiograph (ECG). I The ECG is a graph showing the electrical activity due to the systole and diastole of the heart muscle Which Records : 1-Amount of electrical activity of the heart. 2-The time required for the electrical activity to travel through the heart . 3-The rate and rhythm of the heart. The heart acts as a blood pump. Heart contracts generating action potential. This potential creates electrical currents that spread from the heart throughout the body. The spreading electrical currents create potentials differences which can be detected through surface electrodes The waveform produced is called the electrocardiogram (ECG) Electrocardiogram (ECG) Is a recording of electrical activity of heart conducted through ions in body to surface 13-60 ECG Graph Paper • Runs at a paper speed of 25 mm/sec • Each small block of ECG paper is 1 mm2 • At a paper speed of 25 mm/s, one small block equals 0.04 s • Five small blocks make up 1 large block which translates into 0.20 s (200 msec) • Hence, there are 5 large blocks per second • Voltage: 1 mm = 0.1 mV between each individual block vertically (SA node) (AV node) Normal conduction pathway: SA node -> atrial muscle -> AV node -> bundle of His -> Left and Right Bundle Branches -> Ventricular muscle Recording of the ECG: Leads used: • Limb leads are I, II, II. • Each of the leads are bipolar; i.e., it requires two sensors on the skin to make a lead. • If one connects a line between two sensors, one has a vector. • There will be a positive end at one electrode and negative at the other. • The positioning for leads I, II, and • III were first given by Einthoven. • Form the basis of Einthoven’s triangle. Types of ECG Recordings Bipolar leads record voltage between electrodes placed on wrists & legs (right leg is ground) Lead I records between right arm & left arm Lead II: right arm & left leg Lead III: left arm & left leg 13-61 ECG 3 distinct waves are produced during cardiac cycle P wave caused by atrial depolarization QRS complex caused by ventricular depolarization T wave results from ventricular repolarization 13-63 Normal ECG Waveform ECG Readout devices 1- Medical Oscilloscope: vertical output is severely limited. CRT persistence is very long . ECG use a horizontal sweep speed 25 mm/s. 2- strip chart recorder (speed 25 mm/s) and has a grid pattern that is 50 mm wide. The small grid are 1 mm apart. The vertical scale is calibrated at 0.1 mV/mm