* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download psych therapies
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
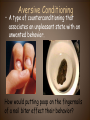
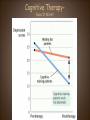
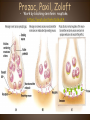
Psychological Therapies example crash course "Bring Me To Life"-therapy; start @ 24:24 Philippe Pinel • French doctor who was the first to take the chains off and declare that these people are sick and “a cure must be found!!!” • Dorethea Dix- American reformer! Two Types of Therapy Psychological Therapies • Structured interactions between a trained professional and a client • AKA – Psychotherapy; many types • Most influential: – – – – Psychoanalysis Humanistic Therapy Behavioral Therapy Cognitive Therapy Biomedical Therapies • Therapies that act directly on a client’s nervous system • AKA – Somatic Therapy • Emphasizes Psychopharmacology Psychoanalytic Therapy crash course who? • Psychoanalysis (childhood experiences…. hypnosis , free association, dream interpretation • 15 min (dream interpretation) • Unconscious • Transference • Catharsis • Fried Green Tomatoes Resistance/Transference Resistance • The blocking from consciousness of anxiety causing material Transference • In psychoanalysis, the patient’s transfer to the analyst of emotions linked with other relationships. • Example: • Sheldon's psychotherapy Humanistic Therapy start @ 4:29 • Client-Centered Therapy by Carl Rogers • These are non-directive therapies and use active listening. • Self-actualization, freewill and unconditional positive regard. • Gestalt Therapy by Fritz Perls encourage clients to get in touch with whole self. Client (Person) Centered Therapy • Developed by Carl Rogers • Therapist uses genuineness, acceptance, and empathy, showing unconditional positive regard. • Goal – Clients deepen self understanding and self acceptance BEHAVIORAL THERAPY START @ 6:06 • B.F. Skinner and other behaviorists question the effectiveness/value of “talk” therapies. • Therapy that applies learning principles to the elimination of unwanted behaviors. • The behaviors are the problems - so we must change the behaviors. • Counterconditioning – Based on Classical Conditioning – i.e. • Aversive Conditioning • Systematic Desensitization • Flooding • Operant Conditioning • Token Economy Behavior Therapy Systematic Desensitization Systematic Desensitization example • A type of counterconditioning that associates a pleasant relaxed state with gradually increasing anxietytriggering stimuli. How would you use systematic desensitization to reduce the fear of dentists? ANXIETY HIERARCHY USED IN SYSTEMATC DESENSITIZATION Flooding Virtual Technology / Exposure Therapy example Aversive Conditioning Aversive Conditioning • A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state with an unwanted behavior. How would putting poop on the fingernails of a nail biter effect their behavior? Aversive Conditioning • Associating unpleasant state /stimuli with an unwanted behavior • Using aversive conditioning, what are some ways you can change the behavior of your friends who bite their fingernails? Operant Conditioning Token Economy: an operant conditioning procedure that rewards a desired behavior. A patient exchanges a token of some sort, earned for exhibiting the desired behavior, for various privileges or treats. Cognitive Therapy 8:20 • Change the way we think(change our schemas) • Aaron Beck • Albert Ellis and Rational Emotive Therapy Cognitive Therapy Cognitive Therapy • Cognitive Therapists try to teach people new, more constructive ways of thinking. Is .300 a good or bad batting average? Cognitive Therapies Cognitive Therapies Cognitive Therapies Cognitive Therapies Cognitive Therapies Cognitive Therapies Aaron Beck and his view of Depression • Noticed that depressed people were similar in the way they viewed the world. • Used cognitive therapy get people to take off the “dark sunglasses” in which they view their surroundings Cognitive TherapyDoes It Work? Group Therapy START @ 9:56 Eclectic Approach • the most “popular” approach to therapy; combining different techniques from the various approaches to psychotherapy How effective is Psychotherapy? • Depends on the measure… – Client Perceptions? Yes… – Clinician Perceptions? Yes… – Scientific Research? • Eysenck’s challenge in 1950’s – noted little differences in treated vs. nontreated • Meta-Analysis ( statistically combining the results of many different studies) offer different conclusions… Comparison of Psychotherapies http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4uA0DHzoPpY Comparison of Psychotherapies Comparison of Psychotherapies Comparison of Psychotherapies Comparison of Psychotherapies Comparison of Psychotherapies Somatic Therapies START @ 4:56 (psychiatrist or clinical psychologist?) Psychopharmacology • Antipsychotics (thorazine, haldol) • Anti-anxiety (valium, barbiturates, Xanax) • Mood Disorders (serotonin reuptake inhibitors-SRI) • Bipolar (lithium) Psychopharmacology • The study of the effects of drugs on mind and behavior. Antianxiety Drugs • i.e. - Valium ,Xanax, Ativan • like alcohol, they depress nervous system activity • may lead to psychological dependence Mood Stabilizers • Lithium aka - Lithium Carbonate a cheap salt that provides effective drug therapy for the mood swings of bipolar (manic-depressive) disorder • Depakote originally used to treat seizures also used in treatment of bipolar disorder Antidepressant Drugs • Lift you up out of depression. Most increase the neurotransmitter norepinephrine and serotonin. Antipsychotics start @ 5:23 • i.e. - Thorazine, Clozaril • dampen responsiveness to irrelevant stimuli • typically work by blocking the neurotransmitter dopamine (antagonist) • side effects are common (sluggishness, tremors, twitches) • most helpful in reducing positive symptoms of schizophrenia Prozac, Paxil, Zoloft • Work by blocking serotonin reuptake. https://youtu.be/twhvtzd6gXA • http://youtu.be/twhvtzd6gXA Somatic Therapy • Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)- for depression • Psychosurgury lobotomy Transcranial Brain Stimulation (treatment for depression) SAD Light therapy Drugs and Hospitalization Deinstitutionalization Mental Health Professionals Type Description Clinical Psychologist Ph.D. in Psychology, specializing in research, assessment, & therapy with supervised internship. Some work in agencies/institutions, some in private practice. Clinical or Psychiatric Social Workers M.S. in Social Work; NASW certification Counselors Varying degrees (perhaps just a B.S. or B.A.); often provide simple verbal advice and assistance rather than formal therapy Psychiatrists M.D., specializing in treatment of Psych Disorders; may or may not offer psychotherapy; can prescribe meds; often have their own medical practices Important People • • • • • • • A. Beck A. Ellis S. Freud M. C. Jones C. Rogers B.F. Skinner J. Wolpe • Behaviorist; would argue that therapy should focus on abnormal behaviors rather than their “roots/causes” • Client-centered therapy; humanistic psychology • Psychoanalysis • Behaviorist; Rational Emotive (Behavioral) Therapy • Amongst the first to use counterconditioning; experiment w/ boy afraid of rabbits; “mother of behavioral therapy” • Cognitive therapy; worked with depressed patients; take off “dark sunglasses” • Refined / published the work of M.C. Jones