* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atrial fibrillation is a heart condition that causes an irregular and
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
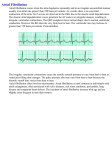
Atrial fibrillation is a heart condition that causes an irregular and often abnormally fast heart rate. CSF026 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION A normal heart rate should be between 60 and 100 beats a minute when you're resting, and is regular. You can measure your heart rate by feeling the pulse in your wrist or neck. In atrial fibrillation, the heart rate may be over 140 beats a minute, although it can be any speed. The main difference between a normal rhythm and atrial fibrillation is that you are unable to predict when the next heart beat will come along, as heart rate is irregular. This may lead to a number of problems, including dizziness and shortness of breath. You may also be aware of a fast and irregular heartbeat (palpitations) and feel very tired. Read more about the symptoms of atrial fibrillation. Some people with atrial fibrillation have no symptoms and are completely unaware that their heart rate is not regular. When to see your GP Make an appointment to see your GP if: you notice a sudden change in your heartbeat your heart rate is consistently lower than 60 or above 100 - especially if you are experiencing other symptoms of atrial fibrillation See your GP as soon as possible if you have chest pain. What happens in atrial fibrillation? When the heart beats normally, its muscular walls contract (tighten and squeeze) to force blood out and around the body. They then relax, so the heart can fill with blood again. This process is repeated every time the heart beats. In atrial fibrillation, the upper chambers of the heart, called the atria, contract randomly and sometimes so fast that the heart muscle cannot relax properly between contractions. This reduces the heart's efficiency and performance. Why it happens Atrial fibrillation occurs when abnormal electrical impulses suddenly start firing in the atria. These impulses override the heart's natural pacemaker, which can no longer control the rhythm of the heart. This causes you to have a highly irregular pulse rate. The cause is not fully understood, but it tends to occur in certain groups of people (see below) and may be triggered by certain situations, such as drinking excessive amounts of alcohol or smoking. Read more about the causes of atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation may be defined in various ways, depending on the degree to which it affects you: Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation - this comes and goes and usually stops within 48 hours without any treatment. Persistent atrial fibrillation - this lasts for longer than seven days (or less when it is treated). Longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation - this means you have had continuous atrial fibrillation for a year or longer. Permanent atrial fibrillation - atrial fibrillation is present all the time and no more attempts to restore normal heart rhythm will be made. Who is affected? Atrial fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disturbance and affects up to 800,000 people in the UK. Atrial fibrillation can affect adults of any age. However, it affects more men than women and becomes more common the older you get. It affects about 10% of people over 75. Atrial fibrillation is more likely to occur in people with other conditions, such as high blood pressure or atherosclerosis. It's uncommon in younger people, but may be slightly more common in people with another heart condition, such as a heart valve problem. Treating atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation is generally not life threatening, but it can be uncomfortable and often needs treatment. Treatment may involve: medication to prevent a stroke medication to control the heart rate or rhythm cardioversion, where the heart is given a controlled electric shock to restore normal rhythm cather ablation, to prevent atrial fibrillation from occurring having a pacemaker fitted to help your heart beat regularly