* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces and Motion
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
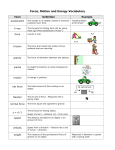
Name Date Forces and Motion Complete. acceleration gravity mass speed work balance inertia momentum spring scale force joule motion velocity friction magnetism newton weight Matching Match each definition with a word. 1. A device used for measuring mass. 2. A measure of the force of gravity on an object. 3. A measure of how fast something moves over a distance. 4. A change in the position or place of something over time in comparison to a reference point. 5. The amount of matter that an object has. 6. A measurement of the motion of something. This is equal to the product of the moving object's mass times its velocity. 7. A measure of both the speed and direction of a moving object. 8. A force that pulls objects towards each other. 9. Energy in the form of a push or a pull. 10. A device used for measuring weight. Multiple Choice Select the definition that most nearly defines the given word. 11. force A. A measurement of the motion of something. This is equal to the product of the moving object's mass times its velocity. B. Energy in the form of a push or a pull. 12. mass A. The amount of matter that an object has. B. The rate at which velocity changes. 13. acceleration A. The rate at which velocity changes. B. A measure of how fast something moves over a distance. Name Date 14. newton A. A unit that is a measure of force. B. A force that pulls objects towards each other. 15. motion A. A unit that is a measure of force. B. A change in the position or place of something over time in comparison to a reference point. 16. magnetism A. The natural force produced by a magnetic field. B. A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are touching. 17. velocity A. The amount of matter that an object has. B. A measure of both the speed and direction of a moving object. 18. work A. The natural force produced by a magnetic field. B. A measure of the amount of force needed to move an object a certain distance. 19. inertia A. Energy in the form of a push or a pull. B. The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion. 20. weight A. A measure of the force of gravity on an object. B. A change in the position or place of something over time in comparison to a reference point. Review 21. The handlebar of a bicycle is an example of using a wheel and axle to reduce the amount of force a rider needs to turn the front wheel. A. False B. True 22. Which law of motion demolished the idea that a moving object needs a push or a pull to keep its motion? A. The law of inertia B. The law of gravitation C. The second law of motion D. The law of conservation of momentum 23. A fingernail clipper is a compound machine made up of a pair of levers and a pair of wedges. A. True B. False 24. Inertia is the force that keeps an object moving in a circle. A. True B. False Name Date 25. Which type of simple machine should you use if you do NOT want to increase force? A. A fixed pulley B. A wheel and axle C. An inclined plane D. A lever 26. Which of the following statements is NOT true? A. Mass is the resistance of an object to a change in its motion. B. Weight is the gravitational force between an object and Earth. C. Friction is a natural force that can slow down a motion. D. Speed measures how fast an object is moving and in what direction the object is moving towards. 27. The greater the mechanical advantage, the more work that is done by the machine itself. A. True B. False 28. Which law of motion says that forces of action and reaction are always equal in size but opposite in direction? A. The first law of motion B. The second law of motion C. The third law of motion D. None of the above 29. Each of the following is an example of a first-class lever EXCEPT ____. A. A plier B. A crowbar C. A bottle opener 30. If a machine reduces the force you must use to move an object, the machine increases the distance through which you must apply that force. A. True B. False Answer Key 1. balance 2. weight 3. speed 4. motion 5. mass 6. momentum 7. velocity 8. gravity 9. force 10. spring scale 11. B 12. A 13. A 14. A 15. B 16. A 17. B 18. B 19. B 20. A 21. (B) 22. (A) 23. (A) 24. (B) 25. (A) 26. (D) 27. (A) 28. (C) 29. (C) 30. (A)