* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes: Human Systems, Homeostasis and Feedback Inhibition
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
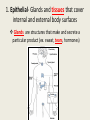
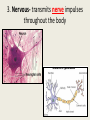
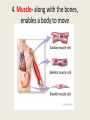
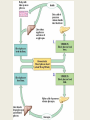
Notes: Human Systems, Homeostasis and Feedback Inhibition EQ: How does the body regulate the activities that allow it to live? Human Systems • Every cell in your body is both an independent unit and an interdependent part of a larger community (the entire organism) Independent- not influenced or controlled by others Interdependent- to rely or depend on something else Human Systems • The broadest levels of organization within multicellular organisms are cells, tissues, organ, and organ systems Human Systems • The eleven organ systems of the human body work together to maintain homeostasis in the body as a whole – Integumentary (skin) – Muscular – Skeletal – Respiratory – Circulatory —Reproductive —Endocrine —Excretory —Digestive —Nervous —Lymphatic Human Systems • There are four types of tissue in the human body: 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Connective Nervous Muscle 1. Epithelial- Glands and tissues that cover internal and external body surfaces Glands are structures that make and secrete a particular product (ex. sweat, tears, hormones) 2. Connective- provide support for the body and connects its parts 3. Nervous- transmits nerve impulses throughout the body 4. Muscle- along with the bones, enables a body to move Homeostasis • Homeostasis is the process where the body keeps internal conditions relatively constant despite changes in external conditions Homeostasis • A nonliving example of this is the heating system of a house – When the temperature drops below a set point the thermostat turns the furnace on and then when the temperature rises above the set point the furnace turns off – The furnace only runs when needed – this is an example of feedback inhibition. Feedback Inhibition (Negative Feedback) • Feedback inhibition (negative feedback) – a process in which a stimulus produces a response that opposes the original stimulus. Feedback Inhibition (negative feedback) • Systems controlled by feedback inhibition are generally fully automated and very stable. • Feedback inhibition is what biological systems (like the human body) use to achieve homeostasis. Feedback Inhibition (negative feedback) • The cellular environment responds to feedback from its own activities by switching on and off as needed. • The part of the brain that works like a thermostat to regulate and maintain a stable body temperature is the hypothalamus . Feedback Inhibition (negative feedback) • The hypothalamus does this by sending chemical messages that either speed up or slow down cellular activity. Positive feedback is a process in which the effects of a small stimulus in a system includes an increase in the magnitude of the stimulus. Examples of positive feedback in the body are blood clotting and childbirth. What body systems is this rock climber using?