* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Roman Republic
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Roman consul wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman emperor wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
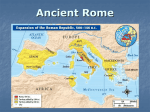
Name Date REVIEW CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARD 6.7 The Roman Republic OVERALL OBJECTIVE: Analyze the geographic, political, economic, religious, and social structures during the development of Rome. Read the summary to answer questions on the next page. The Founding of Rome, 753 B.C.: According to legend, Romulus founded Rome near the Tiber River. The early Romans were ruled by Etruscan kings. In 509 B.C., the Romans overthrew the Etruscan rule and founded a republic. The Roman Republic: The new republic consisted of the powerful patricians, or nobles, and the plebeians, or common people. In time, the plebeians won the right to elect representatives called tribunes. They also had their own assembly. The Twelve Tables, the law code written in 451 B.C. protected the rights of all citizens. Three Branches of Government: • Executive Branch—Two consuls were elected for one year. They were chief executives of the government and commanders-in-chief of the military. • Legislative Branch—A senate of 300 was chosen from the aristocracy. Copyright © McDougal Littell/Houghton Mifflin Company • Judicial Branch—Eight judges, or praetors, were chosen for one year. End of the Republic, 46 B.C.: During a civil war, Julius Caesar, a Roman general, won great popularity among the people. He ended the war and was named dictator for life. He was an absolute ruler, expanded the senate, enforced laws against crime, and created jobs for the poor. He was assassinated by senators who feared his growing power. The Roman Empire, 27 B.C.: Caesar’s great nephew, Augustus, became Rome’s first emperor. Augustus had absolute power but retained the senate, consuls, and tribunes. Under his rule, Rome expanded and enjoyed a period of peace and prosperity. The Roots of Christianity, A.D. 6: The Romans made the Jewish kingdom of Judea, Jesus’s birthplace, a Roman province. Both a Jew and a Roman subject, Jesus preached justice and compassion. Jesus’s success and popularity made enemies of the Roman officials. As a result, he was put to death. After Jesus’s death, his disciples, or followers, continued preaching his message. CSS Overall Objective 6.7: Review 29 wh07ec.PG017–030.indd 29 2/11/05 2:50:15 PM Name Date PRACTICE CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARD 6.7 The Roman Republic DIRECTIONS: Choose the letter of the best answer. 1 Which event marked the beginning of the Roman Republic? 3 In what way were Augustus and Julius Caesar similar? A the assassination of Julius Caesar A Both upheld republican ideals. B the overthrow of Etruscan rule B Both held the title of emperor. C established the Twelve Tables C Both had absolute power. D Both expanded the government. 2 Why was the consuls’ term of office limited to one year? A to allow as many people as possible to be consuls B to prevent them from gaining too much power C because the first consuls only served a year D because the consuls then became the commanders-in-chief of the army • • • • The Arts Epic poetry Arch and dome Mosaics and frescoes Sculpture Use the chart below to answer question 4. 4 Based on the chart, what are some contributions of the Roman Empire to future civilizations? A architecture, language, law, religion B technology, law, mathematics C architecture, medicine, law, language D language, astronomy, art, medicine Legacies of Ancient Rome Technology Government • Legal systems • Use of concrete in engineering • Republican forms • System of roads • Aqueducts Culture • Spread of Christianity • Influence of Latin on Romance languages Copyright © McDougal Littell/Houghton Mifflin Company D the rise of Augustus 30 CSS Overall Objective 6.7: Practice wh07ec.PG017–030.indd 30 2/11/05 2:50:16 PM