* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interactions Slideshow Lecture Notes Page
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
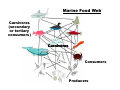
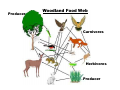
Epiphytes Bromeliad Orchid Warning Coloration Skunk Poison Dart Frogs Milk Snake - Mimic Coral Snake - Toxic Monarch - Toxic Viceroy - Mimic Chemical Defenses – Warning Coloration Predators must have (–) experience w/ prey before learning to associate pain OR palatability w/ color or pattern Blue jay eats a monarch that had fed on poisonous milkweed Later - blue jay vomits Following the episode, blue jay refused to eat any monarchs Energy Flow Through Ecosystems •Ecosystems require a constant supply of Energy •Stored in large organic molecules (contain carbon) of carbs, fats, proteins •Producers (plants, etc.): trap solar ENERGY (photosynthesis) & make Energy available to ecosystem •Each step in the flow of Energy thru ecosystem is known as trophic level Food Chain: Marine Simple connections between trophic levels Woodland Top Consumer (Carnivore) ↑ Secondary Consumer ↑ Primary Consumer (Herbivore) ↑ Primary Producer Decomposer – recycles all trophic levels Decomposers: break down ALL Food Webs: Complex feeding relationships between Trophic levels Marine Food Web Carnivores (secondary or tertiary consumers) Carnivores Consumers Producers Producer Woodland Food Web Carnivores Herbivores Producer Trophic Levels: Community organization based on Feeding or Energy Transfer 0.1 kg. 10 kg. 100 kg. 1,000 kg. 10,000 kg. Keystone Species: Their presence contributes to a diversity of life & their absence leads to extinction of other species •Help support their ecosystem Ochre Sea Star Sea Otter Black-tailed Prairie Dog Sea Urchin (Otter prey)