* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 17. Pituitary and Adrenal Glands
Cryptorchidism wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Bovine somatotropin wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
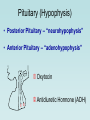
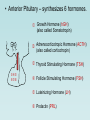
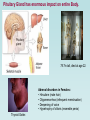
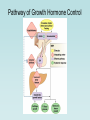
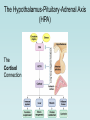
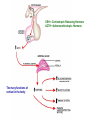
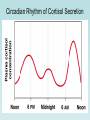
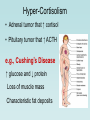
The Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus significantly influences the pituitary gland Posterior pituitary Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones are delivered to the anterior pituitary The hypothalamus makes and releases the hormones of the posterior pituitary Pituitary (Hypophysis) • Posterior Pituitary – “neurohypophysis” • Anterior Pituitary – “adenohypophysis” Oxytocin Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) • Anterior Pituitary – synthesizes 6 hormones. Growth Hormone (hGH) (also called Somatotropin) Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) (also called corticotropin) Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Prolactin (PRL) hGH – is the primary hormone that regulates overall body growth, also important in general metabolism. ACTH – stimulates cortisol secretion from the adrenal cortex (the stress hormone!). Also promotes growth of adrenal cortex. TSH – stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone and the growth of the thyroid gland. Important regulator of metabolic activity in the body. FSH – a) in females: stimulates growth and development of ovarian follicles, and promotes estrogen secretion. b) in males: it is required for sperm production. LH – a) in females: responsible for ovulation and for luteinization. Regulates estrogen and progesterone. b) in males: stimulates interstitial cells (in testes) to secrete testosterone. * called interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) PRL – enhances breast development and milk production in females. Pituitary Gland has enormous impact on entire Body. 7ft 7in tall, died at age 22. Adrenal disorders in Females: • Hirsutism (male hair) • Oligomenorrhea (infrequent menstruation) • Deepening of voice • Hypertrophy of clitoris (resemble penis) Thyroid Goiter. Negative Feedback Loop of Hypothalmic-Adenohypophysis and the Thyroid Gland Normal Growth • Growth hormone and other hormones • An adequate diet • Absence of stress • Genetics Acetyl CoA Hydroxymethyl Glutaric Acid (HMG-CoA) Statin = HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors Mevolaonate Mevolaonate Pyrophosphate Isopentenyl Pyrophosphate Geranyl Pyrophosphate Famesyl Pyrophosphate Squalene Ubiquinone (CoQ10) Cholesterol Dolichol Cholesterol Vitamin D Cortisone Glucocorticoids Mineralcorticoids Steroid Hormones (testosterone, estrogen, progesterone) Bile Salts Wow, what a “Life Saver”. Growth Hormone • Severe hGH deficiency leads to dwarfism • Over secretion of hGH in children leads to gigantism • Over secretion of hGH in adults leads to acromegaly Pathway of Growth Hormone Control The Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis (HPA) The Cortisol Connection CRH = Corticotropin Releasing Hormone ACTH = Adrenocorticotropic Hormone The many functions of cortisol in the body: Cortisol • Promotes gluconeogenesis • Breakdown of skeletal muscle proteins • Enhances lipolysis (prevents glucose use) • Permissive – needed for NE vasoconstriction • Suppresses the immune system • Response to stressors – protective? Circadian Rhythm of Cortisol Secretion Hyper-Cortisolism • Adrenal tumor that ↑ cortisol • Pituitary tumor that ↑ ACTH e.g., Cushing’s Disease ↑ glucose and ↓ protein Loss of muscle mass Characteristic fat deposits Normal Hyper-Cortisolism "Moon" face, "Buffalo" hump Protruding abdomen High Blood Pressure Weakness, Acne, Backache Excessive thirst & urination Easy Bruising Hypo-Cortisolism • Under secretion of adrenal steroid hormones • Autoimmune destruction of adrenal cortex e.g. Addison’s Disease ↓ glucose (hypoglycemia) Poor response to stress Lack of vasoconstriction (permissive NE action) Symptoms and Clinical Signs Fatigue and muscle weakness. Low Blood Pressure (Orthostatic Hypotension). Headache, sweating, joint and muscle pains. Increased Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH). Growth Hormone