* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PBS Lesson 4.1 Review
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
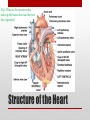
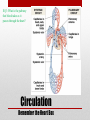
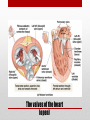
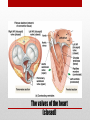
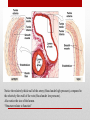
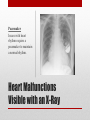
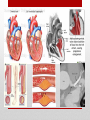
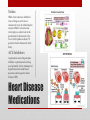
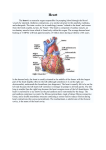
Heart Structure PBS Lesson 4.1 EQ1: What are the structures that make up the human heart and how are they organized? Structure of the Heart • Upper Chambers are called atria. • Lower Chambers are called ventricles. • Left side is Oxygenated. • Right side is DEoxygenated. Chambers of the Heart EQ2: How do the heart and lungs work together to pick up and deliver oxygen to the cells? • The cardiovascular system is responsible for carrying oxygen and nutrients to the body and carrying away carbon dioxide and other wastes. • The pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs to unload CO2 and pick up O2. • The systemic circulation carries blood throughout the body. Lungs = Pulmonary Heart = Cardiac Body = Systemic • In the lungs, the blood picks up Oxygen. • The blood then flows to the heart, which pumps the Oxygen rich blood to the whole body. • The body tissues uses the Oxygen and dumps Carbon Dioxide back into the blood. • This Oxygen Poor blood now flows back to the other side of the heart. • The heart pumps this Oxygen poor blood to the lungs, which infuse it with Oxygen again. • The cycle begins again. EQ3: What is the pathway that blood takes as it passes through the heart? Circulation Remember the Heart Box EQ4: What is the function of valves in the heart? Function is to prevent the backflow of blood. • The atrioventricular (AV) valves prevent backflow of blood into the atria. • Tricuspid- Right atrium to right ventricle. • Mitral (Bicuspid)- Left atrium to left ventricle. • The semilunar valves prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles. • Aortic- Left ventricle to aorta. • Pulmonary- Right ventricle to pulmonary artery. Valves The valves of the heart (open) The valves of the heart (closed) EQ5: How does the structure of arteries and veins relate to their functions? • Arteries carry blood away from the heart. • High Pressure • Pulmonary trunk to lungs • Aorta to whole body • Microcirculation is where exchange occurs. • Arterioles feed the capillaries. • Capillaries exchange with the tissues. • Venules receive capillary blood. • Veins bring it back to the heart. • Low pressure Veins vs. Arteries Notice the relatively thick wall of the artery (blood under high pressure), compared to the relatively thin wall of the vein (blood under low pressure). Also notice the size of the lumen. “Structure relates to function” • Superior Vena Cava (Vein): Upper body to heart, deoxygenated. • Inferior Vena Cava (Vein): Lower body to heart, deoxygenated. • Pulmonary Veins: Lungs to heart, oxygenated. • Aorta (Artery): Heart to body, oxygenated. • Pulmonary Arteries: Heart to lungs, deoxygenated. Major Vessels • Poor Anna! Autopsy Report Pacemaker Issues with heart rhythm require a pacemaker to maintain a normal rhythm. Heart Malfunctions Visible with an X-Ray • Enlarged Heart (Concentric Left Ventricular Hypertrophy) • • • • L.V. works too hard and becomes overly thick. Due to high blood pressure and obesity. Coronary arteries can cut off the blood supply to the heart. Linked to heart attacks, arrhythmias, and heart failure. Internal Heart Malfunctions • Mitral Valve Prolapse • Mitral valve doesn’t close properly. • Can lead to mitral valve regurgitation (some blood flows back into the L.A.). • Complications include arrhythmias and heart valve infection (endocarditis) Internal Heart Malfunctions • Stent in Left Anterior Descending Coronary Artery • Coronary arteries are blocked ; stent opens up the vessels to allow for blood flow. • Atherosclerosis • The formation of plaques on the inside of vessels. • Excess of cholesterol deposited on the inside of arteries supplying both the heart and the brain. • Complications include heart attack and stroke. • Peripheral Vascular Disease • Plaques are beginning to form in the vessels of the legs. Internal Heart Malfunctions Statins HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: class of drugs used to lower cholesterol levels by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of cholesterol in the liver, which produces about 70 percent of total cholesterol in the body. ACE Inhibitors Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor: a pharmaceutical drug used primarily for the treatment of hypertension (elevated blood pressure) and congestive heart failure (CHF). Heart Disease Medications