* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cp23
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
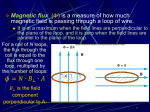
Lesson 23 (1) For the surface in a magnetic field with the normal chosen, find 1. the normal component of the magnetic field 2. the magnetic flux (2) A rectangular wire frame of dimensions 10cm×20cm is in a uniform magnetic field of 4.00G in the x-direction. Find the magnetic flux if the normal vector is ˆ i (a) (b) ĵ ˆ ˆ i j (c) 2 (3) Find the magnetic flux through the triangle abc where the magnetic field is 2.0T in the +z direction. (4) A circular wire of radius 0.6m and resistance 50Ω is on a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. The magnetic field increases from 1.0T to 3.0T in 5.0ms. Choosing the normal parallel to the magnetic field, find 1. the change of magnetic flux through the wire loop 2. the magnitude and direction of the averaged induced emf 3. the averaged current through the wire 4. the electric field inside the wire (5) The loop of the previous problem is flipped through 180° in 2.0s while the magnetic field stays contant at 1.0T. Find 1. the averaged induced emf 2. the total charge that has circulated through the loop during this time. (6) The magnetic flux through a coil rotating in a magnetic field is given by 1 jm = cos100p t Wb 50p where t is in seconds. Find the induced emf at t=0.005s. (7) A metal ring is falling away from a magnet. When viewed from the bottom as shown, is the induced current clockwise or counter-clockwise? (8) A small circular loop is concentric with a large circular loop. A current flows in the large loop in the counterclockwise direction, and is diminishing. Use Lenz law to determine the direction of the induced current in the small loop. (9) Refer to the previous problem. The radius of the large loop is 50cm and that of the small loop is 1.0 cm. The current in the large loop reduces from 10.0A to 4.0A in a 30ms interval. What is the induced emf in the small loop during this time interval? (Hint: the magnetic field due to the large loop at the small loop can be considered uniform)