* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I. Whole Number Multiplication Multiplication is repeated addition
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Section 2.4 Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers
I. Whole Number Multiplication
Multiplication is repeated addition.
vs.
3⋅4 =
Example: 4⋅3 =
Help students by reading “4 of 3” and “3 of 4”
Definition: Multiplication of Whole Numbers as
Repeated Addition: The product of a and b,
writtena ⋅b , is defined by a ⋅b = b
+ b +
...+b and 0⋅b = 0 .
a addends
Also write: a ⋅b = a×b = a*b = ab = a(b) = (a)b = (a)(b) .
Words to know:
1) a and b are factors, a ⋅b is the product.
2) Multiplication is a binary operation.
Properties of Whole Number Multiplication
Closure Property: If a and b are any whole numbers,
then a ⋅b is a unique whole number.
Commutative Property: If a and b are any whole
numbers, then a ⋅b = b⋅a .
Associative Property: If a, b, and c are any whole
numbers, then a(bc) = (ab)c .
Multiplicative Identity Property of One: If a is a
whole number, then a ⋅1=1⋅a = a .
1
Section 2.4 Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers
Multiplication, Repeated Addition Context, Set
Model
Example: Jamie is buying boxes of 3 chocolate eggs
each. She buys 4 boxes. If she gives each friend one
egg, to how many friends can she give eggs?
?
***
***
***
***
4⋅3 = 3+ 3+ 3+ 3 =12
Multiplication, Repeated Addition Context, Number
line Model
Example: Sue hiked 2 miles each day for 3 days. How
far did she hike in all?
2
0
1
2
2
3
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
3⋅2 = 2 + 2 + 2 = 6
2
Section 2.4 Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers
Array Context – Set Model (horizontal rows,
vertical columns)
Example: Jim plants 2 rows of three bean seeds. How
many seeds did he plant?
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
2 rows of 3
2 ⋅3
vs.
*
*
*
3 rows of 2
3⋅2
Rectangular Area Context – Number Line Model
Example: How many tiles are needed to tile a 2 feet by
3 feet area with 1 square foot tiles?
2
1
0
1
2
3
4
row × column = 2 × 3
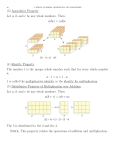
Example: Use C-rods to show 5 × 3 with a repeated
addition context. Use C-rods to show 5 × 3 with a
rectangle context.
Use C-rods and an area model to illustrate (4+2)(3+5).
3
Section 2.4 Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers
Cartesian Product Model
The Cartesian Product of sets A and B, written A× B ,
is the set of all ordered pairs whose first coordinate is
an element of the set A and second coordinate is an
element of B: {(a,b)| a∈ A and b∈B}.
Example: Find the Cartesian product of the sets
A = {r, y, b} and B = {+, –,×, /}
How many members in the Cartesian Product A× B ?
Tree Diagram Model (See Figure 2.21, page 123)
A = {r, y, b} and B = {+, –,×, /}
4
Section 2.4 Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers
II. Whole Number Division
Definition: Division of Whole Numbers
If a and b ≠ 0 are whole numbers, their quotient,
writtena ÷b , is the unique whole number c such
thata = b⋅c . That is, a ÷b = c if and only if there is a
whole number c such that a = b⋅c .
Vocabulary to know:
1) a is the dividend, b is the divisor, c is the quotient.
2) Division is a binary operation.
Properties of Whole Number Division?
If a, b, and c are any whole numbers, then
Closure Property?
Commutative Property?
Associative Property?
Identity property of 1?
5
Division: Repeated Subtraction (Measurement)
Context with Set Model
Example: Mr. Milton puts 15 students into groups of
3. How many groups of 3 will he have?
***
***
***
***
***
15 ÷ 3 = 5 groups
Division: The Partition (Fair Share) Context
Example: Mr. Milton has 3 sets of blocks with 15
students. How many students are assigned to each set
of blocks if he wants equal size groups?
1 set 2 set 3 set
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
15 ÷ 3 = 5 students in one group
6
Section 2.4 Multiplication and Division of Whole Numbers
Repeated Subtraction Context with Number Line
Model
Example: Ruby has 15 yards of ribbon with which to
make bows. Each bow requires 3 yards of ribbon.
How many bows can she make?
Fact Families – Write the fact family for3⋅4 =12 .
Division with zero:
0÷2 = ?
2 ÷0 = ?
0 ÷0 = ?
Theorem: The Division Algorithm If a and b ≠ 0 are
whole numbers, there is a unique whole number q called
the quotient and a unique whole number called the
remainder such that a = q ⋅b + r, 0 ≤ r < b .
Example: Use repeated subtraction to divide 43 by 9.
Use long division to divide 403 by 9.
Definition: The Power Operation for Whole Numbers:
If a and m are whole numbers the exponential
expression am or a to the mth power is given by
am = a ⋅a ⋅a
⋅...⋅a ⋅a . Number a is the base; m is the
m times
exponent.
7