* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter-7-Lecture
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Teen dating violence wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
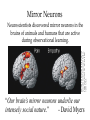
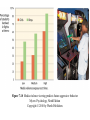
Observational Learning Chapter 7, Lecture 4 “Children need models more than they need critics.” - Joseph Joubert Learning by Observation ©Herb Terrace The monkey on the right imitates the monkey on the left in touching the pictures in a certain order to obtain a reward. © Herb Terrace Higher animals, especially humans, learn through observing and imitating others. Mirror Neurons Reprinted with permission from the American Association for the Advancement of Science, Subiaul et al., Science 305: 407-410 (2004) © 2004 AAAS. Neuroscientists discovered mirror neurons in the brains of animals and humans that are active during observational learning. “Our brain’s mirror neurons underlie our intensely social nature.” - David Myers Learning by observation begins early in life. This 14-month-old child imitates the adult on TV in pulling a toy apart. Meltzoff, A.N. (1998). Imitation of televised models by infants. Child Development, 59 1221-1229. Photos Courtesy of A.N. Meltzoff and M. Hanuk. Imitation Onset Bandura's Bobo doll study (1961) indicated that individuals (children) learn through imitating others who receive rewards and punishments. Courtesy of Albert Bandura, Stanford University Bandura's Experiments Applications of Observational Learning Unfortunately, Bandura’s studies show that antisocial models (family, neighborhood or TV) may have antisocial effects. Positive Observational Learning Bob Daemmrich/ The Image Works Fortunately, prosocial (positive, helpful) models may have prosocial effects. Gentile et al., (2004) shows that children in elementary school who are exposed to violent television, videos, and video games express increased aggression. Ron Chapple/ Taxi/ Getty Images Television and Observational Learning Modeling Violence Children modeling after pro wrestlers Glassman/ The Image Works Bob Daemmrich/ The Image Works Research shows that viewing media violence leads to an increased expression of aggression. Figure 7.18 Media violence viewing predicts future aggressive behavior Myers: Psychology, Ninth Edition Copyright © 2010 by Worth Publishers Modeling Violence Research shows that viewing media violence leads to an increased expression of aggression. “…an evil psychologist could hardly imagine a better way to make people indifferent to brutality than to expose them to a graded series of scenes, from fights to killings to the mutilations in slasher movies. Watching cruelty fosters indifference.” - David Myers Homework Study! “Television viewers are learning about life from a rather peculiar storyteller, one that reflects the culture’s mythology but not its reality.” - David Myers