* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Health Unit 5 Vocabulary Chapter 7:
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Acquired characteristic wikipedia , lookup
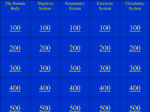
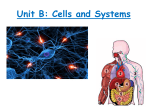
Health Unit 5 Vocabulary Chapter 7: Lesson 1: Cells – the basic building blocks of life Tissues – groups of similar cells that do the same kind of work Organs – structures made up of different types of tissues that all work together Body systems – groups of organs that perform a body function Lesson 2: Skeletal system – a body system consisting of bones and the tissues connecting them Joints– places where one bone meets another Muscle system – all the muscles in your body Lesson 3: Digestion – the process by which your body breaks down food into small nutrient particles Digestive system – the body system that controls the digestion process Excretory system – gets rid of the wastes your body produces and also maintains fluid balance Lesson 4: Circulatory system – allows the body to move blood to and from tissues Heart – the muscle that acts as the pump for the circulatory system Blood pressure – force of blood pushing against the blood vessel walls Respiratory system – enables you to breathe Lungs – the main organs of the respiratory system Diaphragm – a large muscle at the bottom of the chest Nervous system – the control and communication system of the body Neurons – cells that carry electrical messages Spinal cord – a tube of neurons that runs along the spine Health Unit 5 Vocabulary Chapter 8: Lesson 1: Adolescence – the period between childhood and adulthood Endocrine system – a body system containing glands that regulate growth and other important activities Puberty – the time when you start developing physical characteristics of adults of your gender Lesson 2: Reproductive system – a body system that makes it possible to create offspring Egg cell– the female reproductive cell Fertilization – the joining of a female egg cell with a male reproductive cell Menstruation – blood, tissue and the unfertilized egg flow out of the body Sperm – the male reproductive cells Lesson 3: Chromosomes – tiny strands of matter that carry the codes for inherited traits Genes – the basic units of heredity Fetus – a developing, unborn baby from the eighth week until birth Prenatal care – special care to ensure that the mother and her baby remain healthy