* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INSOMNIA EVALUATION MAJOR CATEGORIES OF SLEEP
Combat stress reaction wikipedia , lookup
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorders and memory wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Factitious disorder imposed on another wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Treatment of bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Munchausen by Internet wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
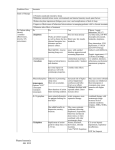
INSOMNIA EVALUATION Type Characteristic Sleep-onset insomnia Sleep maintenance insomnia Sleep offset insomnia Nonrestorative sleep duration Difficulty falling asleep Frequent or sustained awakenings Early morning awakenings Persistent sleepiness despite sleep of adequate duration Insomnia Duration Characteristic Transient Insomnia complaint lasting one to several nights within a s ingle episode (eg, acute illness, jet lag, shift changes) Insomnia lasting from a few days to 3 weeks (eg, associated with a longer duration of stress such as grief, stress, short-term illness) Insomnia lasting for months or years, often waxing and waning (eg, due to medical or psychiatric diseases, chronic stress, bereavement, primary sleep disorders) Short-term Long-term or chronic REFERENCES Adapted from: Czeisler CA, et al, Sleep Disorders. In: Kasper DL et al. Harrison’s Textbook of Internal Medicine 16th ed. New York, NY; McGraw-Hill Professional: 2004;153–162. (Rev. 12/2005) MAJOR CATEGORIES OF SLEEP DISORDERS Description Type PRIMARY SLEEP DISORDERS Sleep disorders thought to arise from endogenous abnormalities Dyssomnias—characterized by abnormalities in the amount, in sleep-wake generating or timing mechanisms, often quality, or timing of sleep. complicated by conditioning factors. Parasomnias—characterized by abnormal behavior or physiologic events occurring in association with sleep. MENTAL DISORDER-RELATED SLEEP DISORDER Presence of either insomnia or hypersomnia thought to be related to another mental disorder (eg, major depressive d isorder, dysthymic disorder, mood disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, adjustment disorders, somatoform disorders, personality disorders). Diagnosis of insomnia or hypersomnia due to another mental disorder should be made only when symptoms are severe and are an independent focus of clinical attention; the sleep disturbance may be one of the earliest symptoms in persons who subsequently develop an associated mental disorder. GENERAL MEDICAL CONDITION RELATED SLEEP DISORDER Prominent disturbance in sleep due to a general medical condition and severe enough to warrant independent clinical attention. History, physical exam, and lab findings suggest that the sleep disturbance is the direct physiologic consequence of a medical condition; the disturbance is not due to another medical disorder (eg, an adjustment disorder) and does not occur only during a delirium; breathing related sleep disorder or narcolepsy can be ruled out. SUBSTANCE-INDUCED SLEEP DISORDER Prominent disturbance in sleep, thought to be due to direct physiologic effects of a substance (eg, drugs of abuse, medication, a toxin) or withdrawal from such a substance. One of the 4 types of sleep disturbance seen: insomnia, hypersomnia, parasomnia, mixed-type insomnia. REFERENCES Adapted from: American Psychiatric Assn. Diagnosis and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed, Text Revision. Washington DC; Amer Psych Assn; 2000; 597–607. (Rev. 12/2005)