* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Plant Kingdom - Junta de Andalucía
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
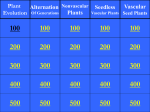
TABLA DE IDENTIFICACIÓN DE LA TAREA TÍTULO THE PLANT KINGDOM IDIOMA Inglés ÁREA/ MATERIA Ciencias de la Naturaleza NÚCLEO TEMÁTICO Los Seres Vivos GUÍON TEMÁTICO Conocer el Reino Plantas, tanto sus características propias como su clasificación más general. Además, reconocer los distintos órganos de una planta y su función. Por último, completar el estudio del reino con las funciones de nutrición y reproducción. CORRESPONDENCIA CURRICULAR (etapa, curso) 1º de Educación Secundaria AUTORÍA Mª Encarnación Femenía Ríos TEMPORALIZACIÓN APROXIMADA 6 sesiones (2 semanas) Conocimiento e interacción con el medio físico. Conociendo las distintas especies vegetales del entorno. Matemática. Gracias al estudio de las partes de una planta y las etapas de sus procesos reproductivos. COMPETENCIAS BÁSICAS Tratamiento de la información y competencia digital. A través de la elaboración de la tarea principal. Cultural y artística. También mediante la preparación de la tarea principal. Aprender a Aprender. Con la conexión conceptual de las diferentes parte de la secuencia didáctica. OBSERVACIONES 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom La competencia en comunicación lingüística es una competencia tratada de forma continuada tanto en inglés como en español. 2 TABLA DE PROGRAMACIÓN DE LA TAREA TEMA O SUBTEMA OBJETIVOS Interpretar y producir con propiedad, autonomía y creatividad mensajes que utilicen códigos artísticos, científicos y técnicos. Bloque 4. Los seres vivos y su diversidad. Reconocer las características propias de las especies del Reino Plantas. Entender cómo se nutren las plantas. Describir las etapas de la reproducción en angiospermas. Desarrollo de una actitud favorable a la conservación de la biodiversidad. 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom CONTENIDOS DEL ÁREA CONTENIDOS LINGÜÍSTICOS TAREAS FUNCIONES: Realizar comparaciones. Reconocer y describir las características de las plantas a partir de fotografías y dibujos. Describir procesos. El Reino Plantas. Las plantas sin flores. Las plantas con flores. Hacer generalizaciones. ESTRUCTURAS: Did you find …? Look for information … Can you spell …? Las hojas, el tallo y la raíz. May I …? La nutrición de las plantas. Complete this chart with La relación de las plantas. Find this concept La reproducción de las plantas. In my opinión … Can you repeat …? Connect with linkers LÉXICO: Angiosperm, dispersal, ferns, fertilisation, germination, gymnosperm, mosses, pollination, stomata, transpiration, vascular. CRITERIOS DE EVALUACIÓN Ejercicios de vocabulario específico con definiciones monolingües. Preparar presentaciones para el resto de los compañeros en formato digital. Exponer al resto de los compañeros las presentaciones elaboradas. Clasificar plantas utilizando claves sencillas. Describir los órganos y partes de una planta y explicar su función. Describir el proceso de nutrición de las plantas, explicando el papel de la fotosíntesis Describir el proceso de reproducción de las angiospermas, explicando el papel que desempeñan las flores, frutos y las semillas. 3 UNIT 6. THE PLANT KINGDOM TASK: MAKE YOUR OWN INVE^TIGATION Work in groups of four. Choose a plant of your area (for example, pine tree), and investigate about its classification, its way of carry out nutrition, its types of interaction with the environment and its reproduction. After this, elaborate a digital presentation and explain it to the rest of the class. 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom 4 UNIT 6. THE PLANT KINGDOM INTRODUCTION 1. Work in pairs. Look at the pictures. Do you know which of them represent plants? Talk to your partner about what they all have in common, and the differences between them. Expressions to use: The picture …. is …. The main differences between plants and animals are… The characteristics that all plants have are … What’s different is… 2. Match the word with its definition. Root The main organ of photosynthesis and transpiration in higher plants. Stems Living beings that have many different cells. Leaves Cells which have a nucleus. Multicellullar Pigment that absorbs the Sun’s energy to elaborate organic matter during photosynthesis. Eukaryotic cells The organ of a higher plant that anchors the rest of the plant in the ground and absorbs water and mineral salts from the soil. Chlorophyll Living beings that produce the organic substances which they need from inorganic substances. Photosynthesis The main axis of a plant, which bears the leaves and flowers. Autotrophic The synthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide and water (with the release of oxygen) using light energy absorbed by chlorophyll. 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom 5 3. What’s the difference? Root – leaves Multicellular – unicellular Eukaryotic – prokaryotic Autotrophic -heterotrophic The most interesting difference between ... and ... is ... By the way, don’t forget that ... In my opinion you’re right but it’s more important to emphasize that ... I think they are similar but with a little difference that is ... I agree with you, but I don’t think we need to write about it because it’s obvious that ... I disagree with you because ... HOW ARE PLANTS CLASSIFIED? 4. Listening: complete the text. Plants are classified in two groups: non-flowering and flowering. Non-flowering ________ are simple plants without __________ or seeds. Mosses. They are small, and non-vascular: they have no conductor vessels. Ferns. They are bigger than mosses. They are vascular: they have conductor vessels to distribute water and nutrients. ___________ plants are more complex, with flowers or ________. Gymnosperms. They have seeds inside a false fruit, like a pinecone. Angiosperms. They have seeds inside a real fruit. 5. Test your partner. Ask questions. Which plants have flowers? Which plants do not have seeds? Which plants ……..? 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom 6 6. Working in groups of four, classify the following sentences into mosses, ferns, gymnosperms and angiosperms. Angiosperms are flowering plants. Ferns are non-flowering plants. Mosses are very small, non-vascular plants. Gymnosperms’ seeds are not protected by a fruit. Ferns reproduce by spores. The mature spores are dispersed by the wind. The spores germinate and produce new ferns. Instead of leaves, mosses have small laminas called phyllodes. Angiosperms’ seeds are enclosed by a fruit. The fruit protects the seeds. It also enables them to be dispersed more easily. Ferns’ leaves are large, and are called fronds. Mosses don’t have true roots, stems or leaves. They fix themselves to the ground by rhizoids. Most of gymnosperms are evergreens, like pine trees and sequoias. They have leaves all year. The leaves are normally shaped like needles. Ferns develop clusters of spores called sorus on the underside of the fronds. Mosses produce spores inside capsules at the end of filaments. Many angiosperms are deciduous, for example, oak trees. They lose their leaves in winter. Ferns have roots, stems and leaves. The stem, called a rhizome, grows horizontally in the ground. Gymnosperms are flowering plants. Mosses reproduce by spores. The mature spores are dispersed by the wind. The spores germinate and produce new mosses. Angiosperms have brightly coloured flowers. The flowers attract animals and facilitate polinisation. Ferns are vascular plants. They can be very large. Gymnosperms have small, insignificant flowers. These group together into inflorescens or cones. These cones are male and female. Mosses are non-flowering plants. Now, each of you chooses a different group of plants, and develops its definition using the information from the sentences above and the appropriate linking words from the box on the right. Type of plant: ………………. Linking words Sequencing: first, second, … Adding: also, too, … Contrasting: however, although, …. Finally, each of you reads aloud your definition and the others copy down what you say. 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom 7 PLANT NUTRITION – FUNCTIONS OF LEAVES, STEMS AND ROOTS 7. Work in pairs. Take turns to read. Then classify the sentences and write the numbers. 1. Plants have three main organs: leaves, stems and roots. 2. Mosses belong to this group. 3. They reproduce by spores which are dispersed by the wind. 4. They grow seeds in order to reproduce. 5. These keep the plant upright and conduct nutrients from the roots to the leaves. 6. Raw sap is transformed in the leaves into elaborated sap through photosynthesis. 7. Angiosperms are deciduous and have brightly coloured flowers. 8. The stem of the fern, which grows horizontally in the ground, is called rhizome. 9. When mineral salts dissolve in the water absorbed by plant roots, raw sap is produced. 10. Oxygen goes into the leaves as excess water is expelled through the stomata as water vapour. 11. Gymnosperms have small, insignificant flowers grouped together into inflorescens. 12. The function of plant roots is to fix the plant to the ground and absorb water and minerals. Flowering plants Non-flowering plants Function of roots, stems and leaves Plant nutrition 8. Draw a simple diagram to explain plant nutrition. 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom 8 PLANTS’ REACTION 9. Read the text and answer the questions. Plant reactions There are two types of plant reaction: permanent – related to growth and temporary – caused by stimuli in the habitat. For example, if you place a plant horizontally, the stem will grow and curve towards the light and the roots will grow down into the soil. This is a permanent reaction. In temporary reactions, the plant returns to its initial state when the stimulus stops. For example, the stems, leaves and flowers of sunflowers turn with the Sun as it moves across the sky. Plants also react to classical music: they open their leaves and flowers and bend towards the source of the music. They grow much faster if music is played to them every day. However, they do not like rock music, and absolutely hate heavy metal! They will bend away from this type of music, and if it does not stop, they usually die within two weeks. What is the difference between permanent and temporary reactions? Describe one temporary and one permanent reaction in plants. What kind of music do plants prefer? PLANTS’ REPRODUCTION 10. Listening: complete the text. Asexual ……………….. Only one plant is involved. …………… reproduction. Sexual cells from two different plants join together to produce a new plant. ………………… plants have sexual ………………. Main parts of a flower Flowers are the reproductive ………………… of angiosperms and ………………… Flowers have two ………….: the reproductive part and the protective part. ……………… parts: the stamen (male ………… part) and the pistil (…….. part). The ovules are found inside the ovary. During ……………., the ovules come into contact with the pollen, which is produced in the stamen. ……………. parts: the petals, which make up the corolla, and the sepals, which make up the calyx. 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom 9 11. Complete the word map with the main parts of the flower’s reproductive organs. Use the words in the box. stamen pistil filament stigma pollen grains ovules style anther ovary Parts of the flower Male Female 12. Match the words with the descriptions below. Then put the stages of reproduction in the correct order. Germination Fertilization Fruit and seed Formation Pollination Dispersal ____________: pollen reaches the stigma, penetrates it and fertilizes the ovules inside the ovary. ____________: the seeds fall on the ground and germinate. A small root and shoot grow. ____________: the ripe fruit falls off the plant or releases the seeds. ____________: the fertilized flower is transformed. The corolla and the calyx dry up. The ovary changes into the fruit. ____________: pollen from one flower’s anther reaches the stigma of another flower. 13. Answer the questions in pairs. a) Name two kinds of animal that help plants pollinate. b) What are the functions of fruit? c) Name some ways in which seeds are dispersed. 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom 10 UNIT 6. THE PLANT KINGDOM POST-TASK: QUIZ SHOW We’re going to play Jeopardy. This is a quiz where you are given the answer and you have to say what the question was. A. Preparing the cards for the quiz. 1. The class will be divided into 4 groups, each one will write sixteen answers (and questions) related to the following categories: a. b. c. d. Classification of plants. Plants’ nutrition. Plants’ reproduction. Plants’ reaction. 2. The Answer-questions must be written down on cards. The teacher must keep the cards in a box until the quiz starts. a. Levels of Difficulty we need: 4 very easy (score 2 points). 4 easy (score 4 points) 4 soft difficult (score 6 points) 4 difficult (score 8 points) b. Use the internet to help you. c. Write your questions in the boxes below. Very easy 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom Easy Soft difficult Difficult 11 TABLA DE AUTOEVALUACIÓN AFTER THIS UNIT…. I CAN… Identify plants YES NO Analyze the characteristics of a particular plant YES NO Give examples of each type of plant YES NO Use English to learn and communicate YES NO YES NO YES NO YES NO YES NO YES NO YES NO The functions of a plant The general classification of plants The parts of a flowering plant I KNOW… How the nutrition is carried out in plants How the reproduction is carried out in plants How plants can react 1º de ESO: The Plant Kingdom NOT YET NOT YET NOT YET NOT YET NOT YET NOT YET NOT YET NOT YET NOT YET NOT YET 12