* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation1
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
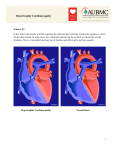
Cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease", is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium (i.e., the actual heart muscle) for any reason Cardiomyopathies can generally be categorized into two groups, based on WHO guidelines: extrinsic cardiomyopathies and intrinsic cardiomyopathies primary pathology is outside the myocardium itself. Most cardiomyopathies are extrinsic, because by far the most common cause of a cardiomyopathy is ischemia Causes of Extrinsic CMP: •Coronary artery disease •Congenital heart disease •Nutritional diseases as deficiency of thiamin (vitamin B-1), selenium, calcium and magnesium •Hypertensive cardiomyopathy •Valvular cardiomyopathy •Inflammatory cardiomyopathy • CMP secondary to a systemic metabolic disease like diabetes, hyperthyroidism, lysosomal storage diseases and the muscular dystrophies ,hemochromatosis ,amyloidosis •Alcohol cardiomyopathy •Chronic rapid heart rate (TICMP) Intrinsic cardiomyopathies An intrinsic cardiomyopathy is weakness in the muscle of the heart that is not due to an identifiable external cause intrinsic cardiomyopathies are generally classified into four types: •Dilated cardiomyopathy DCM •Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM or HOCM) •Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) •Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) •Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), the most common form, and one of the leading indications for Heart transplantation. In DCM the heart (especially the LV) is enlarged and the pumping function is diminished. It can affect people of all ages, it occurs most often in middle-aged people, and is more likely to affect men. Some people with dilated cardiomyopathy may have a family history of the condition. Approximately 40% of cases are familial, but the genetics are poorly understood compared with HCM. In some cases it manifests as peripartum CMP(nigros,multiparous,obeise), and in other cases it may be associated with alcoholism. Symptoms of DCM S&S of heart failure Fatigue, shortness of breath, edema ,nocturia ,orthopnea ,pedal edema .Arrhythmia are common(AF,PVC s and VT). Stagnated blood my complicate by DVT,PTE and stroke raised JVP, displaced apex beat,S3 g ,S4 ,systolic Murmur of functional MR and TR Treatment: antifailure ACEi,Ald,B2B,L.diuretics,anticoagulant, transplantation , LV assist device (LVADs),stem cell therapy •Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in this condition, the muscle mass of the left ventricle enlarges or "hypertrophies." In one form of the disease, the IV septum becomes enlarged and obstructs the blood flow from the left ventricle. the thickened wall sometimes distorts one leaflet of the mitral valve, causing it to leak. HCM is known as hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (H.O.C.M.) or asymmetric septal hypertrophy (A.S.H.). It's also called idiopathic hypertrophic sub aortic stenosis (I.H.S.S.). Rare type known as Yamagoshi syndrome (HCM in Japanis) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common inherited heart defect, occurring in one of 500 individuals caused by various mutations in genes encoding sarcomeric proteins β-myosin heavy chain and Troponin T. Close blood relatives (parents, children or siblings) of such persons often have enlarged septums, although they may have no symptoms. This disease is most common in young adults. The symptoms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy include shortness of breath on exertion, dizziness, fainting and angina pectoris The obstruction to blood flow from the left ventricle increases the ventricle's work, and a heart murmur may be heard(systolic murmur at the left sternal border, the pulses are jerky, the apex is not displaced but feel of double apical paradoxical impulses Some people have cardiac arrhythmias. in some cases can lead to sudden death. Often an implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is needed to shock the heart to restart a normal heart rhythm and prevent sudden death ,beta blocker (such as propranolol) or a calcium channel blocker. Surgical treatment of the obstructive form is possible in some cases if the drug treatment fails. Alcohol septal ablation is a type of nonsurgical treatment for hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy. It involves injecting alcohol down a small branch of one of the coronaries to deaden the extra heart muscle. This allows the extra heart muscle to thin out without having to cut it out surgically(myomectomy). Restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM) is an uncommon cardiomyopathy. The walls of the ventricles are stiff, but may not be thickened, and resist the normal filling of the heart with blood .the person with restrictive cardiomyopathy often complains of being tired, may have edema of hands and feet, and may have difficulty breathing on exertion. This type of cardiomyopathy can occur at any age, it most often seen in the elderly It's the least common type of cardiomyopathy and can occur for no known reason (idiopathic). The condition may also be caused by diseases elsewhere in the body that affect the heart, such as amyloidosis This disease mimic constrictive pericarditis and often difficult to differentiate The only effective therapy is transplantation!