* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Suzy Mathis - Bridging Ex. - Cardiovascular System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
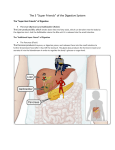
Carl Christensen PhD Chapter 24 - Digestive System Bio 2304 - Human Anatomy 1. ________________ is the muscular movement of the gut wall leading to the breakdown, mixing, and passage of ingested nutrients, then elimination of wastes. 2. What are 4 overall functions of the digestive system? 3. What are the two types of digestion? 4. What does g.i. tract stand for? 5. What are the 4 major layers of the g.i. tract and what types(s) of tissue are they composed of? layer tissue type(s) 6. What are the 3 sublayers of the mucosa? What type of tissue is each composed of? sublayer tissue type 7. ____________ _____________ are specialized columnar epithelial cells that secrete mucous. 8. The internal cavity of the g.i. tract is called the _____________. 9. How is the surface epithelium of the oral cavity, pharynx, and esophagus different from the rest of the g.i. tract? Why is it different? 1 10. What layer of the mucosa can you not see on our slides of the g.i. tract? 11. What is the function of the muscularis externa? 12. The muscularis externa consists of what 2 sublayers? 13. When the circular smooth muscle layer contracts what effect does this have on the g.i. tract? 14. When the longitudinal smooth muscle layer contracts what effect does this have on the g.i. tract? 15. How is the muscularis externa of the pharynx and esophagus different from the rest of the g.i. tract? 16. How is the muscularis externa of the stomach different from the rest of the g.i. tract? 17. How is the muscularis externa of the colon different from the rest of the g.i. tract? 18. What is another name for the serosa that covers the organs of the abdominopelvic cavity? 19. What is another name for the serosa that lines the walls of the abdominopelvic cavity? 20. What are the functions of the mesenteries? (there are 3) 21. Explain the difference between intraperitoneal and retroperitoneal. Which is the stomach & liver? Which is the duodenum & most of the pancreas? 22. The oral cavity is involved in what type(s) of digestion? (mechanical &/or chemical) 23. Chemical digestion in the oral cavity involves what enzyme? 24. Mechanical digestion in the oral cavity involves what 2 structures? 2 25. Name 6 components of saliva & describe the function of each. component function 26. What enzyme is secreted by the salivary glands and is activated by hydrochloric acid in the stomach? 27. What is the function of the pharynx and the esophagus? 28. What sphincter is associated with the lower esophagus? Why is this sphincter called a physiological sphincter? What is its function? 29. What are the 3 functions of the stomach? (peristalsis, digestion, absorption, secretion) 30. The stomach is associated with what type(s) of digestion? (chemical and/or mechanical) 31. Chemical digestion of what organic molecules occurs in the stomach? (carbohydrate, protein, lipid, nucleic acid) 32. What allows the stomach to churn and mix food (mechanical digestion)? 33. _______________ are ridges in the stomach wall that allow for distention. 34. What 2 sphincters are associated with the stomach? 35. The contents of the stomach are referred to as . 36. What are the 3 regions of the small intestine? (from beginning to end) 37. The mucosa and submucosa of the small intestine are deeply folded to form the ____________ _____________. The mucosa is further folded into projections called _____________. The cell membranes of columnar epithelial cells are further folded to form __________. What is the function of all of this folding? 3 38. What are the functions of the small intestine? (peristalsis, digestion, secretion, absorption) 39. The small intestine is involved in what type(s) of digestion? (mechanical &/or chemical) 40. Chemical digestion in the small intestine involves secretions from what 3 organs? 41. Where does most water and mineral ion absorption take place in the g.i. tract? 42. Substances transported into small intestine villi capillaries are transported to the liver via the ________________ _____________ ________________. 43. Where does carbohydrate digestion begin? 44. Where does protein digestion begin? 45. Where does lipid digestion begin? Where is it completed? Where is it completed? Where is it completed? 46. What happen to large lipid globules before digestive enzymes can go to work? 47. Where does nucleic acid digestion begin? Where is it completed? 48. Bile from the common bile duct and pancreatic enzymes from the pancreatic duct enter the _________________ of the small intestine through the ________________________ _________________. 49. There are 2 openings into the duodenum. The superior one is for the _________________ _________________ ___________; the inferior one is for the ______________________ ____________________. 50. What duct is associated with the gall bladder? 51. What ducts deliver bile from liver cells? vein. A 52. Six-sided hepatic lobules are arranged around a is located at each corner of the hepatic lobule. A portal triad is composed of a ,a , and a . Leaky capillaries called allow the blood to percolate through the liver. 53. T or F The function of the gall bladder is bile production. 54. What is bile composed of? What is the function of bile? 4 55. What is bilirubin & where does it come from? 56. What symptom would be an indication that the liver is not functioning properly? 57. Bile is necessary for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as __________________. 58. The liver contains macrophages called _______________ that remove microbes and worn-out blood cells. 59. The liver metabolizes toxic ________________ into urea to be excreted by the kidneys. 60. Explain how the liver, kidneys, and skin are involved in the synthesis of calcitriol. What is the target organ of calcitriol and what is the effect of this hormone? 61. What vitamins and minerals are stored by the liver? 62. Even if you ate a “no cholesterol diet” your body would still make cholesterol. What organ does this? 63. What molecules are responsible for the transport of cholesterol in the blood? 64. High levels of ________ are good. This indicates that a lot of cholesterol is being transported to the liver to be disposed of in bile. 65. High levels of ________ are bad. This indicates that a lot of cholesterol is being transported to body cells. The chance is high that fatty substances will be deposited on arterial walls leading to ____________________________. 66. Your overall cholesterol level should be less than ________________. 67. Your HDL level should be greater than _________. 68. In liver cells glucose is stored as _______________. What hormone is involved in this process? 69. In liver cells glycogen is broken down into _______________. What hormone is involved in this process? 70. What is the exocrine function of the pancreas? 71. What is the endocrine function of the pancreas? 72. What cells produce hormones in the pancreas? 73. What cells produce digestive enzymes in the pancreas? 74. T or F The pancreatic and accessory pancreatic ducts deliver hormone and digestive enzymes to the small intestine. 5 75. Why do the pancreas produce an alkaline secretion to be delivered to the small intestine? 76. Which hormone decreases blood glucose levels? 77. Which hormone increases blood glucose levels? 78. Name the 7 regions of the large intestine. 79. What is another name for the large intestine? 80. T or F Most of nutrient and water absorption occurs in the colon. 81. What produces the gas associated with the lower bowel? 82. The appendix is attached to the _______________. What is its function? 83. What is lactose intolerance caused by? 84. What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic salivary glands? 85. Name the 3 types of intrinsic salivary glands. 86. Name the 3 types of extrinsic salivary glands. 87. Baby teeth are called _____________ teeth. There are _______ in number. 88. Name the 4 types of permanent teeth & the function of each. Type Function 89. How are teeth held in the alveoli? 90. Most of the tooth is composed of a hard, yellowish connective tissue called . 91. What is the difference between enamel and cementum? 92. Name 4 sphincters/valves associated with the g.i. tract. 6