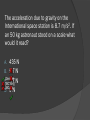* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inverse Square Law
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
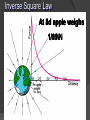
Gravity Sucks! The acceleration due to gravity on the International space station is 8.7 m/s2. If an 50 kg astronaut stood on a scale what would it read? 435 N B. 5.7 N [Default] C. [MC.17 Any] N [MC All] D. 0 N A. The “Discovery” of Gravity We’ve all heard the story… an apple fell on Newton’s head and he discovered gravity. Most scholars believe that Newton did see an apple fall and it got him wondering about the rules for falling objects. He wondered if the force that pulled the apple down also affected the Moon. Remember Newton’s 1st Law He had already explained that straight-line motion was perfectly natural and moving in a circle required a force Johannes Kepler had shown that planets and moons moved in an ellipse. Newton wanted to understand what made them move that way. His breakthrough was to explain how the same rules apply to little things like apples and big things like the moon. Making sense of one force and two very different results We already learned that the apple will accelerate at about 9.8 m/s2 downward Newton also knew that the moon accelerates toward the Earth at 0.00272 m/s2 Distance is only part of the story Distance has a large effect on the force of gravity (we’ll explore this more in a minute) Remember, though F = m • a The force of gravity is also affected by the mass or more correctly, both masses Gravitational Force Gravitational Force is the mutual force of attraction between particles of matter This force always exists between two masses, regardless of the medium that separates them It is not just between large masses, like the sun and the Earth. The chair you are sitting on is attracted to the person next to you. However, the force of friction between the chair and the carpet is so great that you don’t move. m1m2 Fg G 2 r Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation is an example of an inverse-square law This is because the force decreases the further the two objects get from each other. The distance is measured from the center of each mass. Remember, the Force of gravity (Fgrav) that acts on an object is the same as that object’s weight (in Newtons) Inverse Square Law 4 1/4 9 1/9 16 1/16 Inverse Square Law At 4d 3d 2d 5d apple weighs 1/9 1/25 1/4 1/16NN If a large meteor hits the moon, causing it to get closer to the earth. If the moon’s orbits the earth at half of its original radius, would its force be? Double the original force [Default] B. Half the original force [MC Any] [MC C. All] Four times the original force D. One fourth the original force A. Connecting the two formulas Example #1 Find the force of gravity between a 30 kg girl and her 10 kg cat if they are 2 meters apart. m1 = 30 kg m1m m 2 kg = 10 2 Fg G 2 G = 6.67 r x 10-11 N·m2/kg2 r = 2m Fg 6.67 x10 11 30kg 10kg 2 (2m ) 9 Fg 5.0025 x10 N Example #2 Find the distance between a 0.300 kg billiard ball and a 0.400 kg billiard ball if the magnitude of the gravitational force is 8.92 x 10-11 N. m1 m2 m1 = 0.3 kg Fg G m2 = 0.4 kg r2 -11 N = 8.92 x 10 r 2 Fg G Fm m g1 2 r = ? m m 2 r2 G 1 Fg m1 m2 r G Fg 6.67 x10 11 0.300 0.400 8.92 x10 11 r 0.2996 m about 30cm Determine the magnitude of the gravitational force between a baseball player with a mass of 100 kg and Earth (5.98 X 1024 kg), if they are separated by a distance of 5.38 X 106 m. [Default] [MC Any] [MC All] [Option 1] B. [Option 2] C. [Option 3] D. [Option 4] A. Tides Newton also used the inverse square law to explain the tides. People had known for centuries that the moon affects the tides. No one until Newton knew how it did this. d-R d d+R Which of the two forces: moon on left mass (m) or moon on right mass (m) is stronger and why? Fd-R Tidal Bulges Ocean tides are the alternate rising and falling of the surface of the ocean that usually occurs in two intervals everyday, between the hours of 7a.m. to 7p.m. It is caused by the gravitational attraction of the moon occurring unequally on different parts of the earth.