* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inverse Square Law - Hutto High School
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
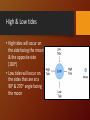
This week in Physics • 3/02 Monday – Universal Gravitation Lecture (notes) • 3/03 Tuesday – Computer Lab 9-121 • 3/04 Wednesday – Universal Gravitation Lecture (as needed) Worksheet • 3/05 Thursday – Universal Gravitation • 3/06 Friday – Individual Review – Review Sheets • Progress Reports due • 3-09 Monday – Class Review • 3/10 Tuesday – Rotational Motion, Torque & Universal Gravitation Exam MOST COMMON QUIZ MISTAKES -2.5 Incorrect or no Unit! Frequency = 1/sec =Hertz Period = sec/1 = seconds Velocity = m/s Acceleration = m/s2 Force = N Torque = N-m Using t (time) instead of T (period)in formula for Velocityc = 2πr T USE WTF!!!! set your problem up, then plug in numbers March 2: Pioneer 10 • Launched In 1972 • It passed close by Jupiter and Neptune • 1st man-made object to leave the Solar System and travel on a flight path into interstellar space. • Heading in the direction of the red star Aldeberan. • That's the main star seen as the eye of The Bull in the constellation Taurus in Earth's night sky. • Aldebaran is about 68 light years away. • Pioneer 10 should arrive at Aldeberan in 2 million years. Where is Pioneer 10 today? Law of Universal Gravitation Newton's Discovery Newton explains gravity • Remember• Law of Inertia: An object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an outside force • Also applied to objects traveling in a circular motion • So… His breakthrough was to explain how the same rules apply to little things like apples and big things like the moon. Gravitational Force • the mutual force of attraction between particles of matter. • always exists between two masses, regardless of what separates them. • It is between all objects. • you are pulled to the object, & the object is pulled to you. What Newton knew… • An apple will accelerate at about 10.0 m/s2 downward. • The moon accelerates toward the Earth at 0.00272 m/s2. Gravity of Moon = 0.00272 m/s2 = 1 =1 Gravity of Apple 10 m/s2 3600 602 • The moon is 60 times further from the center of the earth than an apple on the surface of the earth. Gravitational Relationship Gravity of the apple 10 m/s2 Gravity of the moon 0.00272 m/s2 Radius of Moon to Earth 60 x Radius of Apple to Earth Fgrav ~ 1/d2 Fgrav represents the force of gravity between 2 objects ~ means “proportional to” d = distance separating 2 objects Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation • Distance and mass, of both objects effect the force of gravity • Inverse Square Law (Example) • As distance increases , Force decreases m1m2 Fg G 2 r Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation • Radius, r, is the distance between the center of gravity in one object to the center of gravity in the other object. • g = 10 m/s2 • On Earth • G= 6.67 x 10-11 m/s2 • Universal Gravitation Constant* * Newton calculated the constant mathematically, not until 1798 when Henry Cavendish built a torsion balance and was able to observe masses pulling toward each other. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation & Tides • Newton used Universal gravitation to explain the tides. • Caused by the gravitational attraction of the Sun and moon occurring unequally on different parts of the earth. • The moon is the main cause of the tides because it has a stronger gravitational pull, and it is closer to the Earth than the Sun. Tides High & Low tides • High tides will occur on the side facing the moon & the opposite side (180o) • Low tides will occur on the sides that are at a 90o & 270o angle facing the moon Spring & Neap Tides • Spring tides are tides that are even higher than high tides caused by the alignment of the sun & the moon • Neap tides are lower than the normal high tide & higher than the normal low tide, not much change between high & low in other words. Practice: Example #1 m1m2 Fg G 2 r • Find the force of gravity between a 30 kg girl and her 10 kg cat if they are 2 meters apart. Practice: Example #1 m1m2 Fg G 2 r • Find the distance between a 0.300 kg billiard ball and a 0.400 kg billiard ball if the magnitude of the gravitational force is 8.92 x 10-11 N.