* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Terms and Abbreviations
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Protective relay wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
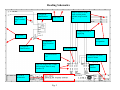
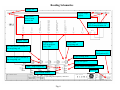
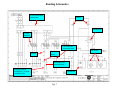
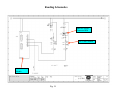
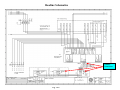
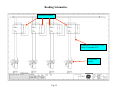
Terms and Abbreviations A – Ampere – unit of measure for electrical current - (schematic abbreviations) A1 - Schematic abbreviation - Axis Box 1 - (schematic abbreviations) A2 - Schematic abbreviation - Axis Box 2 - (schematic abbreviations) A3 - Schematic abbreviation - Axis Box 3 - (schematic abbreviations) AI - Analog Input Analog signal - A signal that attains an infinite number of different amplitude levels. AO - Analog Output Apparent Power - The power value obtained by multiplying the current by the voltage (P = I X E). 9. Axial dimension - This term is used for the measurement of the coupler distance during the generator coupler alignment procedure. 10. CB - Circuit breaker - provides power to individual circuits – also circuit protection. 11. Contactor – Is a signal actuated switch used for supplying of higher three phase voltages, usually a motor, heater etc… 12. CT - Current Transformer – used by measuring circuits in the main controller and SEG converter. 13. DE – Drive end 14. DI - Digital Input, high or low state (with the Bachmann system - 0 or 24Vdc) 15. Digital signal - A signal having an integral number of discrete levels or values. (1’s and 0’s) (24Vdc or 0Vdc). 16. DO - Digital Output – Bachmann M1 system uses outputs of 0 or 24Vdc 17. E - Voltage in Volts – U is voltage on 1.5 Schematics 18. EOC – Electrical to Optical Converter- used for converting electrical signals to light signals 19. E-Stop - Emergency stop 20. Feedback signal – signal sent back to the processor indicating the status of a component (usually 0 or 24Vdc . 21. GE – Schematic abbreviation – Generator 22. Grid voltage – See Utility 23. GT – Schematic abbreviation - Gearbox 24. I - Current in Amperes – L is current on 1.5 Schematics 25. Inductive sensor/proximity switch - Senses changes in the magnetic inductance, outputs pulses 26. K – kilo = 1000 27. LS – Schematic abbreviation - Control Cabinet (Hub) 28. LVMD - Low Voltage Main Distribution (ABB Cabinet) 29. mA - mili amp – unit of measure for electrical current 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 30. MFR 2U1 - Multifunction relay Mains Supervision/fault relay/current measuring. 31. Motherboard – (backplane) The interface between circuit boards or control modules. 32. Motor protection /thermal overload – operates with heat, contacts open at a desired current setting – used for motor and circuit protection 33. Nacelle – is the whole WTG as a unit with enclosures. 34. Nacelle Bottom – bottom enclosure 35. Nacelle Top – top enclosure 36. NC - Normally Closed – indicates the status of a relay or switch contact 37. NDE – Non-Drive End 38. NO - Normally open – indicates the status of a relay or switch contact 39. NS – Schematic abbreviation - Low Voltage Main Distribution Cabinet 40. PF- Power Factor 41. Ph - Phase 42. PLC - Program Logic Control 43. Power factor - In an alternating current circuit, the ratio of true power to apparent power – it is equal to the cosine of the phase angle, expressed in either decimal or percentage 44. Primary - The input winding of a transformer 45. Program Logic Controller (PLC) – Control system that is programmable. 46. Proximity Switch – Inductive Sensor used for counting Yaw position, Rotor rpm, and Generator rpm. 47. PT 100 - Resistive thermometer, sensor (100 Ohms at 0ºC) – used for Temperature Supervision 48. Reactive Current – the component of alternating current that is not in phase with the voltage 49. Reactive Power - is the product of kilovolts and amperes in a reactive component of a circuit. 50. Relay – A signal actuated switching device. 51. rpm - Revolutions Per Minute 52. Secondary - The output winding of a transformer 53. SR – Schematic abbreviation – Slip ring 54. SS – Schematic abbreviation - Main Controller Cabinet 55. SUB – Service Update Bulletin 56. Synchronization - The coincidence of one process or operation to another. 57. TB – Schematic abbreviation - Top Box or Terminal Block 58. Thermal Overload - Motor protection – provides adjustable circuit and motor protection, manual re-settable. 59. Transformer - A device using electromagnetic induction to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another. 60. True Power – in an ac circuit, the power actually dissipated in the resistive component, the reactive component consumes no power 61. Turns ratio - The ratio of the number of turns in the primary to the number of turns in the secondary 62. ua - micro amp 63. UPS – Un-interruptable Power supply provides power after grid loss, used for supplying power to various circuits in case of grid loss. Indicated as USV in 1.5 schematics. 64. Utility – power supplied from the local utility company 65. VisuPro – is the program that allows communication between Bachmann control system and the turbine PC for viewing/recording data and turbine control (SCADA) 66. WTG – Wind Turbine Generator 67. YC Coil – Closing Coil for the Main Switch (CB1) 68. YU Coil – Under voltage or low voltage coil for the Main Switch (CB1) Figure 3 Reading Schematics Sheets affected Description of change Current Revision 1.02 Section Date of drawing Latest Revision or current revision and date of revision Figure 4 Section Designation Sheet 0 Reading Schematics Component Map Location A2 Component Identification Map Scale Maps to sheet 4 of the same section (main cabinet) map location 1A Voltage this wire is supplying Map Scale Component Identification Wire designation Component Map Location C2 Pin Number Terminal Block X5 This wire maps to the LVMD (NS) section, Sheet 4, map location 3E Section in Schematics Fig. 5 SS identifier for Main Control Cabinet Sheet Number Reading Schematics Supply line Digital output supply Comes from sheet 13 map location 8A Supply line continues on to sheet 19-map location 1A Module 18A1 A1 is the positive terminal of the energizing coil Relay 18K6 energizing coil Digital output 24Vdc energizes relay 18K6 Section Designation (SS) Light emitting diode A2 is the negative terminal of the energizing coil Relay description Relay contact configuration Sheet 7 map location 3B Sheet 18 Map location number Fig. 6 Reading Schematics Power Distribution Transformer Fuses Thermostat Circuit Breaker A dot indicates connecting lines Switch Fan motor Terminal Block 2 Pin numbers of terminal block 2 Mapped position from sheet 3 of main controller (SS) Thermostat Fig. 7 Reading Schematics Uninterruptable power supply line Dotted box indicates external switch Power supply 120 to 24 Contact Terminal block X25 Contact 33/34 Contact 23/24 of relay 12K2 Contact 23/24 X20 pin 6 Terminal block pin 5 Terminal block X20 Maps to slipring section sheet 1 location 3C Fig. 8 Top Box section designation (TB) Reading Schematics Uninterruptable power supply line Dotted box indicates external switch Power supply 120 to 24 Contact Terminal block X25 Contact 33/34 Contact 23/24 of relay 12K2 Contact 23/24 X20 pin 6 Terminal block pin 5 Terminal block X20 Maps to slipring section sheet 1 location 3C Fig. 8 Top Box section designation (TB) Reading Schematics 24V power supply Component label number Feedback - In series with other Overvoltage protection circuits Part of motor protection circuit Contact 13/14 of relay 12K2 Solenoid Valve Relays Figure 10 Reading Schematics Digital output Description Digital output 11.19 Contact 33/34 of 12K2 Relay 26K2 Figure 11 Reading Schematics Analog Inputs 26A1 26A2 Isolation Amplifier Terminal Block in SEG Converter Figure 12 Reading Schematics PT 100 X17 X17 Terminal Block Figure 13 X17 Reading Schematics PT 100 Temperature Sensors Filter Switch Figure 14 Reading Schematics Motor Protection Circuit Overspeed Guard Relay Contact Internal Relays Resistor Switch Contact Capacitor Inductive Sensor To Main Cabinet To Gearbox Fig. 15 Relay Energizing Coil Reading Schematics Circuit Breaker Feedback Contacts Digital Inputs Relay Description Contact Configurations Digital Input Descriptions Fig. 16 Reading Schematics Power from Uninterruptable Power Supply Power Supply 120Vac to 24Vdc 24Vdc Supply Line Overvoltage Protection Contact Configuration Switch Contacts Map Location Ground Reference Fig. 17 Reading Schematics Generator Position Encoder Mounted to Rear of Generator Terminal Block in SEG Converter Fig. 18 Reading Schematics Inductive Sensor Generator RPM RC Time Constant 16A1 Counter Module Fig. 19 Reading Schematics Test Terminal block for isolating a single phase from the MFR Thermal Overload CT Inputs Mains Voltage Fault Relays MFR 13 (Multifunction Relay) Grid Monitoring Non Can Bus 0-20mA Outputs Fig. 20 To Analog Inputs Reading Schematics CanBuss Connections Fig. 20A Reading Schematics CanBuss Communications Fig. 20B Reading Schematics Thermistor Switches Feedback to 17A1 DI 11.3 Yaw Motor Temperature PTC Temperature Sensor Fig. 21 Reading Schematics Power Supply 120Vac to 24Vdc UNIOP interface on Top Box door Used for Wind Speed and Automatic Tracking of Wind To brush wear switches in slip ring compartment of generator Supply voltage Supply voltage Controls Yaw Fig. 22 Reading Schematics Inductive Sensors (proximity switch) Counts Yaw Position Fig. 23 Reading Schematics Uninterruptable Power Supply (UPS) or (USV) 120Vac Supply Line Uninterruptable Power Supply Line UPS Feedback Signals Switch 120Vac Power Receptacles Fig. 24