* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download L06 - Fetal Circulation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
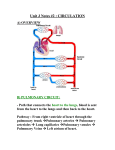
L06 - Fetal Circulation Thursday, April 16, 2015 11:17 AM Fetal circulation is modified to - Maximizes gas/nutrient exchange between mother and fetus VIA PLACENTA - Provides more O2/Nutrients to developing organs with high metabolic need and bypassing low metabolic need VIA SHUNTS ○ Heart/Brian vs Lungs/kidneys - By early 4th week, embryo's future heart cells becomes contractile to move blood Circulation moves from higher pressure to lower pressure - In adults, HIGH Pressure is Left side of heart (Systemic circulation) and LOW pressure is right side (Pulmonary) - In fetus, HIGH pressure is pulmonary because collapsed lungs with fluid built up causing constricted arterioles => high resistance ○ LOW pressure is systemic as blood goes from aorta -> placenta Prenate vs Neonatal circulation - Differences are due to 3 factors ○ Gas exchange in fetus occurs at Placenta, NOT lungs ○ Fetus obtains nutrients via Placenta, NOT GI Tract ○ Fluid excretion and ion regulation via Placenta, NOT kidneys - Primary circulatory organs in fetus are Lungs, Heart, Liver, and Umbilical vessels ○ Umbilical cord has 3 vessels: 2 umbilical arteries and 1 Umbilical Vein Arteries because DEOXYGENATED blood AWAY from fetal heart Vein because OXYGENATED blood TOWARDS fetal heart from placenta Wharton's Jelly composes space between vessels Torsion of umbilical cord may compromise blood flow - Ductus Arteriosus ○ Fetal artery that carries blood from pulmonary trunk to arch of aorta ○ 90% of blood passes through FO and DA ○ Pulmonary Hypoxic Vasoconstriction = hypoxic conditions causes constriction of pulmonary arterioles -> increases resistance of flow into lungs => forces blood into Ductus Arteriosus - Foramen Ovale ○ Opening between right and left atria (interatrial septum) to get to aorta faster so that the partially oxygenated blood can get to rest of body ○ 90% of fetal blood passes through FO and DA - Ductus venosus ○ Shunt that carries blood from umbilical vein to inferior vena cava and mostly bypassing liver ○ Causes mixing of Oxygenated and Deoxygenated blood Placenta - Placenta contains 3 general portions ○ Chorionic Plate (Fetal) ○ Basal plate (maternal) ○ Intervilus space (combined) - Deoxygenated/Nutrient poor blood travels via Umbilical artery to Fetal Capillaries within Chorionic villi -> Intervillus space -> UTERINE Vein - Oxygenated/Nutrient rich blood travels from Maternal UTERINE Artery into Intervilus space immediately next to Fetal Capillaries -> Umbilical Vein Remember that fetal Hb has higher affinity for O2 than Adult Hb Physio Page 1 ○ Remember that fetal Hb has higher affinity for O2 than Adult Hb Parturition (Birth) - Several stimuli causes first breath in newborn ○ Physical stress of birth ○ Sudden exposure to lower temp ○ Post-birth hypoxia and hypercapnia due to severed connection with placenta => Stimulates CNS breathing center - Changes in Pulmonary resistance ○ First breath Lungs take in air -> pushes fluid out of alveoli -> arterioles dilate -> decrease resistance ○ Placenta expelled Leads to Decrease PG concentration => Causes DUCTUS ARTERIOSIS CLOSURE - Changes in Systemic Resistance ○ Placenta Expelled Leads to Increased resistance in Umbilical artery causing sudden increase in aortic/systemic pressure ○ Left Atrial pressure increase at birth causes closure of Foramen Ovale and forms Fossa Ovalis Right atrium has less pressure and blood cannot flow directly from Right atrium to Left atrium ○ Cutting/Closure of Umbilical vessels causes systemic FLOW to decrease => Increases systemic RESISTANCE => increases pressure in left side of heart - Anatomical Changes ○ Ductus Arteriosus closes Closure of DA due to O2 increase and PG decrease leads to formation of Ligamentum Arteriosum ○ Foramen Ovale closes due to increase in Left Atrial Pressure -> Fossa Ovalis formed ○ Ductus venosus closes forming Ligamentum Venosum ○ Umbilical vein closes to form ligamentum teres hepatis ○ Umbilical artery closes to form medial umbilical ligaments ○ Due to temperature change, Wharton's Jelly contracts and "clamps" umbilical structures ~5 minutes after birth Umbilical Cord Pathologies - Nuchal Cord = 1+ loops of umbilical cord are wrapped around fetal neck - True Umbilical Cord Knot - Umbilical cord pseudoknot = not true knot, just exaggerated loop of umbilical artery because it is longer than vein Patent Ductus Arteriosus - Occurs when DA fails to close at birth -> Blood flows through PDA and INCREASES Pulmonary pressure while allowing Oxygenated and Deoxygenated blood to mix - Presentation ○ No early symptoms ○ Aortic pressure increases with age resulting in greater flow through PDA into pulmonary vessels Pressure increase due to body/heart not getting enough O2 ○ Cyanosis ○ Worsens as PDA increases in diameter Physio Page 2