* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
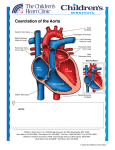
Lecture 16 • Blood vessels are lined by a layer known as endothelium. • The large body cavities: pericardial, peritoneal, pleural. • Mesothelium = lining of large body cavities. • Angiogenic cells are formed in the yolk sac, they form a thin layer of blood vessel (endothelial layer). Afterwards the other layers are formed, tunica.. • The two heart tubes in the splachnopleuric mesoderm...remaining area of the mesoderm above the pericardial sac = septum transversum. Some tube in front of pericardial sac. Some portion of the heart tube is also in the septum transversum. When it folds, the septum transversum • The heart tubes invaginate the pericardial sac, the sac completely surrounds it, heart tubes attached by a fold of the sac called dorsal-mesocardium. This later degenerates. • This splachnopleuric mesoderm becomes thick; forms the myoepicardial mantle. Forms the musculature of the heart – myocardium as well as form the visceral layer of the pericardium. The outer most layer , parietal layer, is derived from somatopleuric intraembryonic mesoderm. • The heart tubes has got an arterial end and a venous end. Venous end is cranial and arterial end is down before folding. After folding, venous end is down and arterial end is cranial. • Venous end slowly gets released, comes out of septum transversum, becomes folded and comes to the cranial part. • The fetal circulation: lungs not completely working/functional. The source of oxygenation is the placenta . Opening between the two atriums = known as the foramen ovale. Oxygenated blood from the placenta goes to the right atrium from the inferior vena cava. Liver is forming in between. From the placenta, the oxygenated blood first goes to the liver, from there it will go the inferior vena cava. But some amount of blood is bypassed. Bypassing the liver from placenta to inferior vena cava = this is called ductus venosus. • As blood enters, 90% of the blood is directed towards the opening between right and left atrium and then goes to the left ventricle and enters the aorta. • Deoxygenated blood comes from the superior vena cava comes to right ventricle and goes to the lungs. Lungs are not established properly. It has to go to lungs by pulmonary trunk. There is a trunk between pulmonary trunk and aorta = this is known as ductus arteriosus. • Beyond the junction of ductus arteriosis to aorta, there is a mix of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. • The blood coming out before the junction will supply oxygenated blood to the head region. • The aorta coming down carrying both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood and becomes the umbilical arteries which goes the placenta for oxygenation. Once it is oxygenated blood, it is taken up by the umbilical vein to the liver and to the inferior vena cava. Soem doesn’t enter live, bypass and goes to directly to IVC = ductus venosus. • After birth, the first to be obliterated is the umbilical artery (they will close), no more blood goes to the placenta from the fetus. After some time, the umbilical vein will also get obliterated. Pulmonary vasculature gets established as the baby tries to breathe on its own. More blood comes to left atrium and there is a rise in the left atrial pressure, since theres an increase in pressure the valve attaches to the flap. The foramen ovale is closed. Even the ductus arteriosus constricts and gets obliterated. • Anomalies: Foramen ovale is open after birth. Patent ductus arteriosus = you can hear the murmur. One condition known as coarctation of aorta (narrowing of the aorta). The intima layer of the ductus arteriosus proliferates and completely blocks the ductus arteriosus. Thats how it gets obliterated. The ductus arteriosus proliferation can sometimes extend into the aorta and the aorta can get narrowed. Preductal coarctation and postductual coarctation. • Preductal coarctation: upper extremities are under high pressure, these patients will have high blood pressure in upper but not lower limb. • Umbilical vein becomes the ligamentum teres of the liver. In the adult life, it remains as ligamentum teres (this is the remnants of the LEFT umbilical vein, the one the right degenerates). • The ductus venosus forms the ligamentum venosum. • Ductus arteriosus becomes the ligamentum arteriosum. • Umbilical arteries become the medial umbilical ligaments.