* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sheep Heart Dissection Powerpoint
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
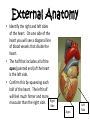
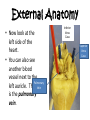
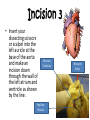
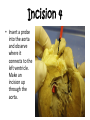
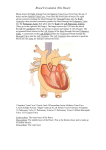
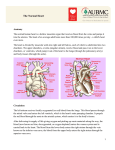
Sheep Heart Dissection Objectives By the end of this lesson, students will be able to: • Demonstrate proper dissection safety techniques • Identify the right and left sides of the heart • Identify the parts of the heart: auricles, superior vena cava, pulmonary vein, aorta, left ventricle, pulmonary artery, bicuspid and tricuspid valve. • Measure the diameter of the aorta, pulmonary trunk, left atrium, left ventricle and right ventricle. • Compare and contrast the structure of a sheep heart to a human heart External Anatomy • Identify the right and left sides of the heart. On one side of the heart you will see a diagonal line of blood vessels that divide the heart. • The half that includes all of the apex (pointed end) of the heart is the left side. • Confirm this by squeezing each half of the heart. The left half will feel much firmer and more muscular than the right side. Right Side Apex Left Side External Anatomy • Turn the heart so that the right side is on your right, as if it were in your body. This will mean that you are now looking at the back or posterior surface of the heart. • Examine the flaps of darker tissue on the top of the heart. • These ear-like flaps are called auricles. Auricle External Anatomy • Find the large opening at the top of the heart next to the right auricle. • This is the opening to the superior vena cava. • Stick a probe down the vessel. You should feel it open into the right atrium. Superior Vena Cava Auricle External Anatomy • A little down and to the left of the superior vena cava, there is another blood vessel opening. • Insert your probe into this. It should also lead to the right atrium. This is the inferior vena cava. Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava External Anatomy • Now look at the left side of the heart. • You can also see another blood vessel next to the Pulmonary left auricle. This Vein is the pulmonary vein. Inferior Vena Cava Superior Vena Cava External Anatomy • Sticking straight up from the center of the heart is the largest blood vessel you will see. This is the aorta. The aorta takes oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body. Aorta Left Ventricle External Anatomy • Behind and to the left of the aorta there is another large vessel. This is the pulmonary artery. • Answer the questions on your lab WS: External Anatomy. • You should also check all structures with teacher before making ANY incisions. Pulmonary Artery Incision 1 • Insert your dissecting scissors or scalpel into the superior vena cava and make an incision down through the wall of the right atrium and ventricle, as shown by the dotted line in the picture. Chordae Tendonae Tricuspid Valve Papillary Muscle Incision 2 • Insert your probe into the pulmonary artery and see it come through the right ventricle. Make an incision down through this artery. Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Semilunar Valve Observe and Measure • Observe the right half of the heart. • Identify the following: – – – – Tricuspid valve Pulmonary semilunar valve Papillary muscles Chordae Tendonae • Measure the following: – Diameter of the right atrium and ventricle – Wall thickness of the right atrium and ventricle – Diameter of the aorta and pulmonary trunk Observe • Try to find the three layers of the heart wall: endocardium, myocardium and epicardium • You may need to use the dissecting needle to lift the endocardium or epicardium Incision 3 • Insert your dissecting scissors or scalpel into the left auricle at the base of the aorta and make an incision down through the wall of the left atrium and ventricle as shown by the line. Chordae Tendinae Papillary Muscle Bicuspid Valve Incision 4 • Insert a probe into the aorta and observe where it connects to the left ventricle. Make an incision up through the aorta. Observation • Observe the left side of the heart. • Identify the following: – – – – Mitral or Bicuspid valve Aortic Semilunar valve Papillary muscles Chordae tendonae • Measure the following: – Diameter of the left atrium and ventricle – Wall thickness of the left atrium and ventricle. Clean Up • Place all dissecting specimens and parts into approved container provided by the instructor. • Wash dissecting equipment and trays in dilute bleach solution provided by the instructor. • Dry equipment thoroughly to prevent rusting. • Clean table tops with dilute bleach solution provided by the instructor. • Wash hands thoroughly before leaving the classroom. Resources Color Me Heart www.childrenheartinstitute.org/kidsonly/h eartflw.htm Heart House www.childrenheartinstitute.org/kidsonly/h earthse.htm Heart Dissection Lab www.hometrainingtools.com/articles/heart -dissection-project.html Heart Anatomy www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/anat omy/heart labelinterior/label.shtml Resources Heart Lessons http://www.smmm.org/heart/lessons/ heartDiagram.htm Animations/Interactives http://www.smm.org/heart/heart/top. html Heart Diagram http://classroom.kidshealth.org/classro om/6yo8/body/systems/cardiovascul ar_handout1.pdf Color Heart Diagram www.heartfoundation.org.au/documen t/NHF/heartimage.pdf