* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Formulae and Data Booklet - SCSA
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
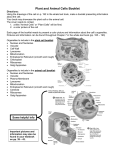
PHYSICS ATAR COURSE YEAR 12 FORMULAE AND DATA BOOKLET 2017 Copyright © School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2016 This document – apart from any third party copyright material contained in it – may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that it is not changed and that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner, and that the Authority’s moral rights are not infringed. Copying or communication for any other purpose can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with prior written permission of the School Curriculum and Standards Authority. Copying or communication of any third party copyright material can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with permission of the copyright owners. Any content in this document that has been derived from the Australian Curriculum may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY) licence. This document is valid for teaching and examining until 31 December 2017. 2016/ Physics Year 12 Formulae and Data Booklet February 2017 Physics YEAr 12 2 Formulae and data Booklet Gravity and motion Average velocity vav = ts Equations of motion v = u + at Force Fnet = ma Weight force F = mg Kinetic energy Ek = ½ mv2 Gravitational potential energy Ep = m g Δh Work done W = Fs = ΔE Equations of circular motion v = 2� r T s = ut + ½ at 2 v 2 = u 2 + 2as 2 ac = vr mv 2 Fc = mac = r m1m2 r2 Newton’s law of universal gravitation F= G Kepler's 3rd law T2 = Gravitational field strength M g = G r2 Moment of a force (force at angle θ to lever arm) τ = r Fsinθ 4�2 3 r GM Note: the variable t refers to the 'time taken', sometimes referred to as the 'change in time' or Δt. Wave particle duality and the quantum theory Wave period T = 1f Wave equation c = fλ Energy of photon E=hf Energy transitions ΔE = E2 − E1 = h f Photoelectric effect Ek = h f − W De Broglie wavelength h λ= p See next page Formulae and data booklet Electromagnetism 3 Physics year 12 1 q1q2 4�ε0 r 2 Coulomb's law F= Electric field strength E = qF = V Magnetic field strength B= Magnetic force on a charged particle F = q v B where v ┴ B Magnetic force on a current-carrying conductor F = I ℓ B where ℓ ┴ B Particle motion in a magnetic field r= Torque on a coil τ=rF Magnetic flux Ф = B A┴ Electromagnetic induction induced emf = d µ0 I 2� r m v q B ℓ v B induced emf = –N where v ┴ B Δ(B A┴) (Ф2 − Ф1) = –N ΔФ = –N t t t emfrms= AC generator emfmax = 2NℓvB = 2�NBA┴ f V = IR Ohm’s law Electric current Ideal transformer turns ratio q I= t Vp Vs = Np Ns Work and energy w = vq Power P = VI Special relativity Relativistic effects ℓ = ℓ0 u= Relativistic momentum pv = 1– v + u′ v u′ 1+ 2 c m v 1– Mass-energy equivalence v2 c2 v2 c2 E = m c2 v2 1– 2 c See next page t= t0 1– u′ = v2 c2 u–v vu 1– 2 c emfmax √2 Physics YEAr 12 4 The Standard Model Elementary particles See next page Formulae and data Booklet Formulae and data booklet 5 Physics year 12 Physical data Mean acceleration due to gravity on the Earth....... g = 9.80 m s-2 Mean acceleration due to gravity on the Moon...... gM = 1.62 m s-2 Mean radius of the Earth........................................ RE = 6.37 × 106 m Mass of the Earth................................................... ME = 5.97 × 1024 kg Mean radius of the Sun.......................................... RS = 6.96 × 108 m Mass of the Sun..................................................... MS = 1.99 × 1030 kg Mean radius of the Moon........................................ RM = 1.74 × 106 m Mass of the Moon................................................... MM = 7.35 × 1022 kg Mean Earth-Moon distance.................................... = 3.84 × 108 m Mean Earth-Sun distance....................................... = 1.50 × 1011 m Mass of electron .................................................... me = 9.11× 10-31 kg Mass of proton........................................................ mp = 1.67× 10-27 kg Tonne...................................................................... 1 t = 103 kg Physical constants Speed of light in vacuum or air............................... c = 3.00 × 108 m s-1 Electron charge...................................................... e =−1.60 × 10-19 C Planck constant...................................................... h = 6.63 × 10-34 J s Newtonian constant of gravitation.......................... G = 6.67 × 10-11 N m2 kg-2 Electron volt............................................................ 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J Electronic constant................................................. ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 F m-1 Magnetic constant.................................................. µ0 =4 Electromagnetic spectrum Note: shaded areas represent regions of overlap. See next page � × 10 –7 N A–2 = 1.26 × 10–6 N A–2 Physics YEAr 12 6 Formulae and data Booklet Prefixes of the metric system Factor Prefix Symbol Factor Prefix Symbol 1012 tera T 10-3 milli m 109 giga G 10-6 micro µ 106 mega M 10-9 nano n 103 kilo k 10-12 pico p Mathematical expressions Quadratic equations Given ax2 + bx + c = 0, x = −b ± √b2 − 4ac 2a Triangles The following expressions apply to the triangle ABC as shown: B c A a b c a b = = sin A sin B sin C a = √b2 + c2 − 2bc cos A See next page End of booklet C This page has been left blank intentionally ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Elementary particles Adapted from Standard Model image: MissMJ. (2006). File:Standard Model of Elementary Particles.svg. Retrieved June, 2016, from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Standard_Model_of_Elementary_ Particles.svg Used under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported licence. This document – apart from any third party copyright material contained in it – may be freely copied, or communicated on an intranet, for non-commercial purposes in educational institutions, provided that it is not changed and that the School Curriculum and Standards Authority is acknowledged as the copyright owner, and that the Authority’s moral rights are not infringed. Copying or communication for any other purpose can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with prior written permission of the School Curriculum and Standards Authority. Copying or communication of any third party copyright material can be done only within the terms of the Copyright Act 1968 or with permission of the copyright owners. Any content in this document that has been derived from the Australian Curriculum may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY) licence. Published by the School Curriculum and Standards Authority of Western Australia 303 Sevenoaks Street CANNINGTON WA 6107