* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. drugs are used to treat arrhythmias
Survey
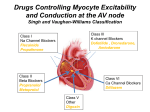
Document related concepts
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
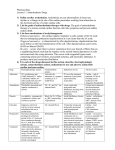
MED 268: Cardiac Drugs Lecture Worksheet #6: Antiarrhythmic Medications 1. ______________ drugs are used to treat arrhythmias; disturbances in the normal heart rhythm. 2. Antiarrhythmics are categorized into ______ classes; Class I, II, III and IV. 3. Class I antiarrhythmics, the largest group of antiarrhythmic drugs, consist of ________________ channel blockers. 4. ________________, an AV nodal-blocking agent used to treat PSVT is an antiarrhythmic not listed in the Class I category. 5. _________ ____ _____ antiarrhythmics are used to treat PVT, VT, A Fib, A flutter and PAT, by blocking sodium channels in the cell membrane during action potential. 6. ____________ ___ _____ antiarrhythmics work by blocking the rapid influx of sodium ions during the depolarization phase of the heart’s depolarization-repolarization cycle; effect the Purkinje fibers and myocardial cells in the ventricles so used to treat ventricular arrhythmias. 7. ________ __ ____ antiarrhythmics primarily slow conduction along the heart’s conduction system and used to treat life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias. 8. Adenosine ________________ the pacemaker activity of the SA node, reducing heart rate and the ability of the AV node to conduct form the atria to the ventricles. 9. Adenosine is especially effective against _______________ tachycardias that involve the AV node. 10. Adenosine is predominantly used to treat arrhythmias associated with accessory _____________ tracts, such as WPW. 11. ___________________ reaction to Adenosine includes facial flushing, shortness of breath, dyspnea, palpitations, and chest discomfort. 12. ___________ ___ ______________________________ are composed of beta-adrenergic antagonists, which are also known as beta-adrenergic blockers or beta blockers. 13. _________ _________________ block beta adrenergic receptor sites and the SA node firing is slowed. 14. Class II Antiarrhythmics reduce the __________________ of the heart’s contractions. 15. Class II antiarrhythmics slow ventricular rates in patients with __________ ______________, atrial fibrillation and PAT. 16. Class III antiarrhythmics are used for __________________________ arrhythmias. 17. _______________________ is the first-line drug of choice for ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. 18. Class IV antiarrhythmics inhibit _________________ ion influx across cardiac and smooth muscle cells, known as calcium channel blockers. 19. Class IV antiarrhythmics also ___________ coronary arteries and arterioles to relieve angina, lower blood pressure and ___________ normal sinus rhythm. 20. _______________ causes bradycardias because it blocks conduction through both the SA and AV node. 21. ___________________ and Diltiazem are examples of calcium channel blockers used to treat supraventricular arrhythmias 22. Amiodarone increases the risk of ________________ toxicity. 23. The effects of Warfarin are ________________ when taken with Amiodarone. 24. Beta blockers given with _________________ can cause hypotension, bradycardia, AV block, and asystole. 25. ___________________ (Inderal) is a common beta blocker used to reduce the strength of the heart’s contractions, thus reducing oxygen demand of the myocardium.