* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR COLLECTION OF THE BNP BLOOD
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
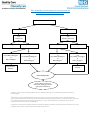
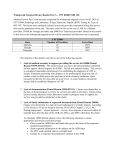
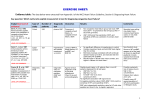
PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR COLLECTION OF THE BNP BLOOD TEST FOR UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL SOUTH MANCHESTER Please find attached guidelines for taking the B type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) blood sample for University Hospital South Manchester. B type Natriuretic Peptide is recommended by the NICE and ESC guidelines as part of the pathway for Heart Failure (HF) diagnosis. Heart failure is a complex clinical syndrome of symptoms and signs that suggest impairment of the heart as a pump supporting physiological circulation. It is caused by structural or functional abnormalities of the heart. The demonstration of objective evidence of these cardiac abnormalities is necessary for the diagnosis of heart failure to be made. The symptoms most commonly encountered are breathlessness (exertional dyspnoea, orthopnoea and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea) fatigue and ankle swelling. Signs in heart failure could be due to pulmonary and systemic congestion, the structural abnormalities causing heart failure, the structural abnormalities resulting from heart failure, or from complications of therapy. BNP guidance from NICE 2010 CG108 Chronic Heart Failure: Management of chronic heart failure in adults in primary and secondary care. Diagnosis: 1. Refer patients with suspected heart failure and previous myocardial infarction (MI) urgently, to have transthoracic Doppler 2D echocardiography and specialist assessment within 2 weeks. [new 2010]1 2. Measure serum natriuretic peptides (B-type natriuretic peptide [BNP] or N-terminal pro-Btype natriuretic peptide [NTproBNP]) in patients with suspected heart failure without previous MI. [new 2010]1 3. Because very high levels of serum natriuretic peptides carry a poor prognosis, refer patients with suspected heart failure and a BNP level above 400 pg/ml (116 pmol/litre) or an NTproBNP level above 2000 pg/ml (236 pmol/litre) urgently to have a transthoracic Doppler 2D echocardiography and specialist assessment within 2 weeks. [new 2010]1 4.Refer patients with suspect heart failure and a BNP level between 100 and 400 pg/ml or an NTproBNP level between 400 and 2000pg/ml to have a transthoracic Doppler 2D echocardiography and specialist assessment within 6 weeks [new 2010]1. 5. Consider a serum natriuretic peptide test (if not already performed) when heart failure is still suspected after transthoracic Doppler 2D echocardiography has shown a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. [new 2010]1. 1 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012 2 Suspected heart failure Acute onset Non-Acute onset ECG Chest X-ray ECG Possible chest x-ray Echocardiography Echo C BNP/NT-proBNP BNP/NT-proBNP ECG normal and NT-proBNP <300 pg/ml or BNP <100pg/ml ECG abnormal or NT-proBNP ≥ 300pg/ml b or BNP ≥100pg/ml b ECG abnormal or NT-proBNP ≥125pg/ml a or BNP ≥35pg/ml a Echocardiography ECG normal and NT-proBNP <125 pg/ml or BNP < 35 pg/ml Heart Failure Unlikely c Heart Failure Unlikely c Echocardiography If heart failure confirmed determine aetiology and start appropriate treatment a Exclusion cut off points for natriuretic peptides are chosen to minimise the false-negative rate while reducing unnecessary referrals for echocardiography. b Other causes of elevated natriuretic peptide levels in the acute setting are an acute coronary syndrome, atrial or ventricular arrhythmias, pulmonary embolism, and severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with elevated right heart pressures, renal failure and sepsis. Other causes of an elevated natriuretic level in the non-acute setting are: old age (>75 years), atrial arrhythmias, left ventricular hypertrophy, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic kidney disease. c Treatment may reduce natriuretic peptide concentration and natriuretic peptide concentration and natriuretic peptide concentrations may not be markedly elevated in patients with Heart failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction.2 2 For University Hospital South Manchester collection of BNP blood sample Be aware that: Obesity or treatment with diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, betablockers, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs) and aldosterone antagonists can reduce levels of serum natriuretic peptides. High levels of serum natriuretic peptides can have causes other than heart failure (for example, left ventricular hypertrophy, ischaemia, tachycardia, right ventricular overload, hypoxaemia [including pulmonary embolism], renal dysfunction [GFR <60ml/minute], sepsis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, age >70 years and cirrhosis of the liver). [new 2010]1. BNP Exhibits biological activity Biological half-life ranges from 13-20 minutes NTproBNP Exhibits no biological activity Biological half life ranges from 25-70 minutes Actively cleared via clearance receptors and to Cleared passively by organs with high a lesser extent by degradation. Also blood flow (kidneys, the liver and muscles) inactivated through kidneys Extracted renally and increased with renal Extracted renally (to similar extent) and dysfunction increased with renal dysfunction In vitro stability of BNP is assay dependent. Very stable at room temperature. Values are stable for around 4 hours at room temperature and should be measured as soon as possible after blood draw. LABORATORY INFORMATION AS PROVIDED BY UHSM EDTA plasma sample Results reported in ng/L Samples need to be received same day (see above on stability of BNP) Interpretative comments on all results Result BNP<100ng/L UHSM Lab Interpretation A diagnosis of heart failure is unlikely in an untreated patient Suggest refer for Echo and post Echo and specialist assessment if appropriate in <6 weeks Suggest refer for Echo and post Echo and specialist assessment if appropriate in <2 weeks BNP 100-400ng/L BNP >400ng/L 3 Contacts at University Hospital South Manchester Dr Graham Horsman Consultant Chemical Pathologist Biochemistry Department Wythenshawe Hospital 0161 291 2132 (Direct) 0161 291 2122 (Secretary) Dr Anne-Marie Kelly Consultant Chemical Pathologist Biochemistry Department Wythenshawe Hospital 0161 291 4791 (Direct) 0161 291 2122 (Secretary) Duty Biochemist Biochemistry Department Wythenshawe Hospital 0161 291 2136 References 1. NICE Clinical Guideline No 108. Chronic Heart Failure Guidelines 2. European Society of Cardiology for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012. 4