* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Preventing Cardiovascular Disease
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
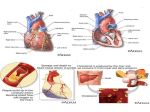
Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S.— 42% of all deaths Approximately 1.5 million heart attacks occur each year—500,000 are fatal About 50% of people who have heart attacks wait 2 hours before seeking medical attention Circulation The primary function of circulation is to provide a constant supply of blood and nutrients to cells while removing their waste products Blood is so important to the heart that every muscle fiber is supplied by at least one capillary Cardiovascular Disease (1) Coronary heart disease (coronary artery disease; CAD) is diagnosed when any artery is narrowed by 60% or more A myocardial infarction (heart attack; death of the heart muscle) occurs when blood flow to the heart muscle is disrupted Most heart attacks occur after age 65, but the process begins as early as adolescence Myocardial Infarction The medical term for heart attack is myocardial infarction (MI) Up to one third of all heart attacks are silent—without obvious signs or symptoms Silent ischemia, reduced blood flow, can initiate heart attacks without warning Most heart attacks are obvious Cardiovascular Disease (2) Heart disease is an acquired disease that is preventable Americans as young as 18 have obstructions in their coronary arteries caused by atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis, characterized by plaque beneath artery linings, is responsible for 80% of CAD deaths in the U.S. Brain Attack (Stroke) Brain attacks are caused by a thrombus or an embolus (70% to 80%) or a cerebral hemorrhage Brain cells die, causing loss of function of some parts of the body Brain attacks have the same risk factors and prevention factors as heart disease Unchangeable Risk Factors for Heart Disease (AHA) Age—80% of fatal heart attacks occur after age 65 Male gender—Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both males and females » Females have a lower rate than males » Rate is increasing among females, particularly those who smoke and use oral contraceptives Heredity and Race—A tendency toward heart disease appears to be hereditary Changeable Risk Factors Cholesterol (1) A certain amount of cholesterol is necessary for good health The best way to lower serum (blood) cholesterol is to reduce intake of saturated fat Saturated fat increases the liver’s production of cholesterol Changeable Risk Factors Cholesterol (2) Cholesterol is a steroid that does not dissolve in blood, so it is transported to cells by protein packages Low-density lipoproteins (LDL), the primary transporters of cholesterol, are the most capable of producing atherosclerosis People with low blood levels of LDL (less than 100 mg/dl) rarely have heart attacks Changeable Risk Factors Blood Pressure (1) Blood pressure is the force exerted against artery walls as blood travels through the circulatory system High blood pressure (hypertension) has no signs or symptoms High BP= 140/90 mmHg Changeable Risk Factors Blood Pressure (2) Long-term uncontrolled hypertension increases the work of the heart, causes it to hypertrophy, and leads to congestive heart failure Hypertension damages the arteries, accelerates atherosclerosis, and is the most important risk factor for brain attacks Changeable Risk Factors Tobacco Cigarette smoking may be the most harmful of the preventable risk factors for chronic illness and premature death These illnesses include chronic bronchitis, emphysema, strokes, and 87% of all lung cancers Passive smoking, inhaling the smoke of others, causes the deaths of 38,000 to 43,000 nonsmokers annually Changeable Risk Factors Physical Inactivity Physical inactivity increases the risk of coronary heart disease by 1.5 to 2.4 times The greatest health benefits are gained when people expend 1500 to 2000 calories (walk 15 to 20 miles) per week Exercise for health does not have to be as strenuous as exercise for physical fitness Changeable Risk Factors Physical Inactivity Physical activity is any physical movement that results in energy expenditure—walking, mowing the lawn, vacuuming “Every U.S. adult should accumulate 30 minutes or more of moderate intensity physical activity on most, preferably all, days of the week.” (ACSM/CDC statement) Changeable Risk Factors Obesity Obesity contributes to about 300,000 deaths per year Fat that accumulates in the upper half of the body (central abdominal obesity) is significantly more likely to contribute to heart disease A 5% to 10% weight loss that is maintained can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease Changeable Risk Factors Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes is a metabolic disorder in which the body cannot properly use sugar (glucose) as fuel Type II (90% of all diabetes) occurs in older, overweight, sedentary adults Diabetes increases the risk of coronary artery disease 2 to 3 times in men and 3 to 7 times in women Changeable Risk Factors Stress Stress elevates heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and blood sugar levels, activates the immune response, and causes other physiological changes Chronic (long-term) distress significantly strains the body Prevention of Heart Disease Prevention includes: Regular exercise Optimal body weight Sound nutritional practices Nonuse of tobacco and other drugs Nonuse or moderate use of alcohol Dealing constructively with stress Periodic medical examinations Diagnostic Techniques Medical examination and patient history Exercise stress tests Thallium treadmill test Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Medical Treatment Low-dose aspirin therapy Coronary artery bypass surgery Balloon angioplasty Coronary stent Artificial valves Left ventricular assist devices Heart transplants