* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download what is electricity
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
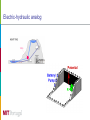
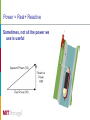
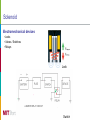
Electricity and Magnetism Carlos Silva October 21th 2009 WHAT IS ELECTRICITY An hydraulic system Electrical systems “are like” hydraulic systems • Analog systems (Electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, thermal..) • At the beginning, electricity was though to be some kind of fluid Electricity Definition Phenomena related to the presence and/or flow of electric charges Electric charge [Coloumb [C]) Property of subatomic particles that determines their interaction (electromagnetic) with other particles: • proton [+], • electron [-] Two particles with the same type of charge repel each other Two particles with opposite charges are attract each other Current and Voltage Current (Amperes [A]) Flow of electrons from a negative charge to a positive charge • However, the conventional current direction is said to be from + to – • 1 A= 1Cs-1 In a hydraulic circuit the current corresponds to the water low [liters] Voltage (Volt [V]) Electric potential difference between two points in a circuit • It indicates the capacity to produce work with the present charge • The potential itself is not important, the difference is • 1V = 1J/1C It a hydraulic system voltage corresponds to the water pressure [PSI] Resistance Definition The degree of opposition of an object when current passes though it • Measured in Ohm [Ω] • Depends of the length, cross-section and resistivity (and temperature) Resistor Is used to cause voltage drops in circuits (e.g. volume in a radio) Commercial resistor Ohm Law The resistance determines the amount of current for a given potential difference R V I Constriction Hydraulic analogue Electric-hydraulic analog Electric Energy and Power Energy (Joule [J]) Ability to do work • Property of a body • Can be expressed in several ways (thermal, kinetic, elastic, electric) Power (Watt [W] = J / s) Time rate at which work is done or energy is expended Electric Energy [Watt x hour] Potential energy associated with the charges within a system • Stored in Batteries Electric Power (Watt [W]) Energy transferred to a component in a circuit V2 P I V I R R 2 Batteries Definition Converts chemical energy to electrical energy • • • • Cathode (+) of one metal (Cu) - reduction Anode (-) of another metal (Zn) - oxidation Electrolyte (aqueous solution) External wire connecting electrodes 1. The electrodes react with the electrolyte, causing different potential between the electrodes (changes in electrons) 2. When a wire is connected, due to the potential difference, there is a electron flow (current) 3. The battery is exhausted when electrodes and electrolytes are stable, don’ react anymore Reaction : oxidation-reduction (e.g. corrosion) Capacity [Ah= 1C x 1s] Electric charge of the battery Direct current and alternate current Direct Current (DC) Unidirectional flow of charge • Battery • Dynamo • Rectification from Alternating Current (AC) Usually has a constant value Used for low voltages Alternating Current (AC) Electric flow of charge that changes cyclic • Alternators • Houses Usually is a sine wave High voltages VRMS V 2 Capacitors and Inductors Capacitor Device to store energy Filter signals Capacitance (C [F]) C Q V Inductor Tank Hydraulic analogue Symbol To resist changes in current Generates magnetic field Electromechanical devices (solenoids) Transformers Inductance (L [H]) Symbol Paddle Wheel Hydraulic analogue Semiconductors Diodes Conduce current only in one direction NP junction • Rectification • Switching (security) • Protection Symbol One-way valve Hydraulic analogue Transistors NPN or PNP junction • Amplification • Switching (security) • Logic components PNP Symbol Pressure valve Hydraulic analogue CIRCUITS Resistors Association Resistors Association • Series – same current • Parallel – same voltage R, RC and RLC R circuit Light lamp What is the current I in a 100W bulb light with 220 V (AC) circuit? RC circuit Charge Filters /Rectification How does this circuit work? Capacitor voltage RLC circuits Resonant circuit / harmonic oscillator Filter / Tunning Resistor voltage Rectification Circuit Half-wave rectifier Full-wave rectifier Full-wave rectifier plus filter Amplification Circuit Current amplification NPN transistor can be used to amplify 100 times the base current Radios (Transistors): • amplify low signal of radio waves Build your own radio! ELECTRIC POWER Power = Real+ Reactive Sometimes, not all the power we use is useful Power in AC (P=UI) Inductance and capacitance elements cause energy flow changes (AC) Capacitance introduces a 90º lead between current and voltage Inductance introduces a 90º lag between current and voltage C RC R L RL ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD Electric field Definition Forces acting around charges Water molecule Magnetic field Definition Forces acting on moving charges Usually connected to metals Earth magnetic field Magnetic field Maxwell’s laws Describe electric and magnetic fields Describe interactions and relationships between both fields Magnetic fields generate electric fields Electric fields generate magnetic fields Copper wire Hard disk (magnetic coating) Solenoid Electromechanical devices • Locks • Valves / Switches • Relays Lock Switch Electricity Generation - Induction Faraday law: A changing magnetic field passing though a conductor generates a current flow Generators The changing coal passing through a static magnetic field generates current flow Electricity Generation (AC) Alternator As the magnet moves near a wire it generates an electric current Electricity Generation (DC) Dynamo Commutation Always in the same direction (DC) Electrical Generation (Large scale) Three phase Three wiring conductors displaced by 120º Sum of currents is null at all times Special properties Hydroelectric power station