* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
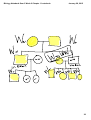
Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook # Date 1. 01/20/15 January 28, 2015 Table of Contents Title Chapter 11: Genetics Page # 1 i 1 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 SpiderMap Supporting Point 1 #2 int 1 # nt Supporting Point 1 jo a M Po Supporting Point 2 jor Supporting Point 3 Ma i o r P Supporting Point 2 Supporting Point 3 Main Idea 4 r P oin M Supporting Point 3 Supporting Point 2 ajo M ajo r P Supporting Point 2 Supporting Point 1 t # oin t # 3 Supporting Point 1 Supporting Point 3 2 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 01/26/15 January 28, 2015 Ch 11 35 Objective: Students will be able to infer which traits are inherited and differentiate between dominant and recessive alleles. Lab Section of Notebook "Making Babies" 3 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 05/15/12 Genetics Objective: January 28, 2015 75 Students will be able to infer which traits are inherited and differentiate between dominant and recessive alleles. Making Babies Pre-Lab Questions 1. What does a single side of a doublesided coin on disk represent? 2. What is the probability, in percent, that a single coin toss will result in heads? In tails? 3. Why is a coin toss a good way to represent allele combinations that occur in nature? 4. For the traits explore in this lab, do all heterozygous pairs of alleles produce an intermediate phenotype? 5. Can you accurately determine an organism's genotype by observing its phenotype? Explain your answer. 4 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 01/28/15 Genetics January 28, 2015 9 Objective: Students will be able to apply probability to predict the outcome of various genetic crosses. Mendel's Basic Principles (laws) Principle (Law) of Dominance: Some alleles are dominant, some are recessive. Law of Segregation: When gametes form, the alleles separate. Law of Independent Assortment: Each chromosome, and therefore alleles of the gene, separate independently from each other unless linked. gametes: sex cells eg: sperm, eggs, pollen allele: 1 form of a gene eg: H or h 5 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 01/28/15 January 28, 2015 10 Ch 11 Objective: Students will be able to set up Punnett Squares in order to predict the outcome of genetic crosses. Punnett Squares--Terminology Punnett Square: Tool used by scientists to predict the traits of an individual. Homozygous: 2 of the same alleles present dominant: alleles that show up ex: HH recessive: alleles that get covered up ex: hh Heterozygous: 2 different alleles present ex: Hh Genotype: genetic combination, or alleles present ex: Hh, HH, hh Phenotype: physical characteristics P1 Generation: parental generation ex: Hairy knuckles, hairless knuckles F1 Ge ner ati on: fir st fili al g ene rat ion Genotypic Ratio (geno): actual alleles (form of the genes) Phenotypic Ratio (pheno): physical characteristics F2 Ge ne ra tio n: se co nd fil ial ge ne ra tio n 6 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 05/21/12 January 28, 2015 77 Genetics Objective: Students will be able to apply probability to predict the outcome of various genetic crosses. Punnett Squares--Terminology alleles that show up ex: HH alleles that get covered up ex: hh Heterozygous: 2 different alleles present ex: Hh Genotype: genetic combination, or alleles present ex: Hh, HH, hh Phenotype: physical characteristics ex: Hairy knuckles, hairless knuckles 7 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 05/22/12 Genetics January 28, 2015 77 Punnett Squares--Practice Cross two rabbits, one is homozygous dominant for white fur, the other is heterozygous. W=white, w=brown. Genotype: Phenotype: Cross two pea plants, both heterozygous for Round pea shape. R=round, r=wrinkled. Genotype: Phenotype: Genotype: Phenotype: Genotype: Phenotype: Genotype: Phenotype: Genotype: Phenotype: Practice with Monohybrid Crosses 8 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 05/24/12 Genetics January 28, 2015 85 Determining the Number and Type of Gametes 9 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 10 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 05/25/12 January 28, 2015 Genetics 86 Dihybrid and Trihybrid Crosses 11 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 05/25/12 January 28, 2015 86 Genetics Dihybrid Crosses Cross one parent pea plant who is homozygous dominant for both green and tall with a parent who is homozygous recessive for both traits. G = green g = yellow T = tall t = short Mom = Dad = Cross = Cross one parent pea plant who is homozygous dominant for both green and tall with a parent who is heterozygous for both traits. G = green g = yellow T = tall t = short Mom = Dad = Cross = Cross two pea plants that are heterozygous for both traits. G = green g = yellow T = tall t = short Mom = Dad = Cross = Phenotype: 12 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 13 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 Journals 05/21/12 # 64 JQ: Use the letters T or t to write the following genotypes: (1)homozygous dominant, (2) homozygous recessive, (3) heterozygous. A: 05/22/12 # 65 JQ: If you were told to cross two parents both heterozygous for Hairy knuckles, what would their genotypes be? A: 05/23/12 # 66 JQ: Use a Punnett Square to cross WW x ww. Where W=Widow's Peak. A: 05/24/12 # 67 JQ: Use a Punnett Square to cross HhxHh; H=Hitchiker's thumb. A: 05/25/12 # 68 JQ: HhRrSS--how many possible gametes are there? What are they? A: 14 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 Journals 05/29/12 # 69 JQ: TtBBTr--How many possible gametes are there? What are they? A: 05/30/12 # 70 JQ: What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous? A: 05/31/12 # 71 JQ: If a flower self-pollinates, will its kids look the same as the flower? Explain. A: 06/01/12 # 72 JQ: What will the phenotype be if the genotype is Wwff where W=widow's peak and F=Freckles across the nose? A: 06/02/12 # 73 JQ: What will the phenotype be if the genotype is Wwff where W=Widow‛s Peak and F=Free Earlobes? A: 15 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 06/04/12 Human Heredity January 28, 2015 90 Objective: Students will be able to make and analyze karyotypes. 16 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 03/12/14 Ch 11 January 28, 2015 35 Objective: Students will be able to identify and describe inheritance patterns that are different from simple dominance in order to apply genetic principles to all organisms. Mendel's Input Genes are the unit of inheritance, passed from parents to offspring (1 form of a gene is an allele) Principle of Dominance Some alleles are dominant, others are recessive Principle of Segregation Adults have 2 copies of each gene (1 from each parent) that segregate from each other when gametes are formed. Principle of Independent Assortment Genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes. What Mendel Never Knew 17 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 18 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 Journal Questions 03/10/14: Cross 2 fruit flies who are both heterozygous for 2 traits: red eyes and curled wings if R=Red, r=white; C=normal, c=curled wings. 03/11/14: RrCc x rrcc 19 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 2 01/21/15 Ch 11: Genetics Objective: Students will be able to describe the structures that sort independently and explain linkage. Linkage HW: Modified Outline 11-2 Protocol: Procedure: Materials: 20 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 21 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 03/17/14 Ch 14 January 28, 2015 52 Objective: Students will be able to make and analyze karyotypes in order to explain chromosome abnormalities. 22 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 03/21/14 Ch 14 Human Heredity January 28, 2015 90 Objective: Students will be able to make and analyze karyotypes. 23 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 Karyotype examples 24 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 03/25/14 Human Genetics January 28, 2015 127 Reading the Future? Analyzing Chromosomes and Explaining the Consequences Notes Advice/Options Information HW: TYPED final draft of the letter to parents due TOMORROW 25 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 03/25/14 Human Genetics January 28, 2015 126 Reading the Future? Analyzing Chromosomes and Explaining the Consequences Notes Smear 1 Smear 2 Aberration Patau syndrome, trisomy 13 Edwards syndrome, trisomy 18 Smear 3 Down's syndrome, trisomy 21 Smear 4 criduchat, deletion in 5 Smear 5 Jacobs, XYY Smear 6 Turner's syndrome, X0 Smear 7 Klinefelter's syndrome, XXY Smear 8 Triple X, XXX Smear 9 Philadelphia translocation, 9 to 22 translocation 26 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 06/07/12 January 28, 2015 Human Heredity 90 Objective: Students will be able to use and construct pedigrees to study human traits. Pedigree: Tool scientists use to study traits in families. Scientists observe families for a particular trait and record the presence or absence of that trait. They then draw a diagram to show the relationships between members of the family and who has that trait. 27 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook 05/19/11 January 28, 2015 127 Genetics Objective: Students will be able to use and construct pedigrees to study human traits. Example Pedigree Married Female Male Children Presence of the trait 28 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 29 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 30 Biology Notebook Sem 2 Week 2 Chapter 11.notebook January 28, 2015 31