* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download mukesh-kumar-all-india-institute-of-medical
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
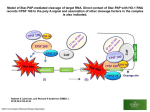
Membrane fusion mediated cytosolic drug delivery through scFv targeted Sendai viral envelopes Mukesh Kumar Research Associate 1. National Brain Research Centre, Manesar, Haryana 2. All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi Human Placental Alkaline Phosphatase (PAP) » PAP is an isozyme of alkaline phosphatase » 513 amino acid peripheral membrane glycoprotein anchored to the outer surface of plasma membrane via a phosphatidylinositol linkage. PAP Phosphatidyl Inositol Anchor » Dimer of two identical subunits with molecular weight of 64kDa each. 2 » Expression » is restricted to the second and third-trimester of human placenta. It is a marker for placental cells as well as for tumors of reproductive organs like ovarian tumor, seminomas, and cervical tumors. Nearly universally seen in germ cell tumors. Characteristics:- Increased heat stability, differential inhibition by various uncompetitive inhibitors like L-Phenylalanine, L-Leucine, peptides like L-Phe- Gly-Gly. 3 Features that make it an attractive immunotherapeuic target • Cell surface localization • Clathrin mediated endocytosis • Low shedding into circulation • Ectopic expression in various malignancies viz. choriocarcinoma, germ cells(>80%), seminomas, uterus and ovary, breast, colon, head and neck 4 Human Alkaline Phosphatases Subunit mol. wt. Tissue nonSpecific (TNAP) 69 kDa Subunit association Dimer dimer Heat lability Labile 70oC; 5min Homology with PAP 60% 90% Urea inhibition 2mol/L 70% 40% Levamisole inhibition 10 µmol/L 50% insensitive insensitive Amino – acid / peptide inhibiton L-Homoarginine L-Phe L-Phe, L-Leu, L-Phe-gly-gly Intestinal (IAP) 68 kDa Placental ( PAP) 64 kDa dimer 70oC; 30 min 25% Alkaline Phosphatase Isozymes PAP • L-Phe • L-Phe-gly-gly BONE INTESTINAL • L-Homo THESE INHIBITORS ARE : (i) Isozyme specific (ii) Bind to defined sites on the molecule • L-Phe Phagemid Filamentous Phage Bio-panning from Human Phage Display Antibody Library Tomlinson’s human antibody library was used for selection. Bio-panning »TG1 (E.coli) - “Suppressor strain”- recognizes stop codon (TAG) as glutamate- surface display of scFv » HB2151(E.coli) - “Non-suppressor” strain- recognize amber stop codon-for soluble expression of scFv. Selection of PAP binding monoclonal phage scFv PLAP IAP BAP Phage Helper Absorbance(492nm) 2 1.6 1.2 0.8 0.4 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 Phage Helper Enzyme(ug) PEG precipitated monoclonal phage ELISA . Cross- reactivity profile of P4C8 in presence of varying amounts of PAP/IAP/BAP. P4C8 is showing good binding to PAP consistently. P4C8 shows maximum inhibition in binding to PAP in the presence of 1.5µg of free PAP Soluble expression and binding of scFv 2 M 1.75 HB2151 28kD Absorbance(492nm) P1 P1 P4 P3 C6 C8 C8 C27 1.5 1.25 1 0.75 0.5 0.25 0 SDS-PAGE of soluble expression of clones showing 29kD protein neat periplasm Binding of dialyzed soluble scFvs of monoclonals on PAP coated plate Binding of soluble scFv of P4C8 to PAP is maximum Cellular Internalization Three strategic categories to enhance endosomal escape :(i) Molecular ferries (ii) Leakage-inducing molecules (iii)Physico-chemical techniques Enveloped viral fusion Sascha Martens & Harvey T. McMahon (July 2008) The hemifusion model for bilayer fusion. SENDAI, A PARAMYXOVIRIDAE ( HEMOLYTIC VIRUS FAMILY ) Enveloped animal virus, containing single stranded RNA as genetic material. Discovered in early fifties in “Sendai” Japan, also known as “HVJ” It requires physiological pH and temperature to enter/infect host cells. Mechanisms of entry fairly resolved. However, the exact role of HN help to F-protein in membrane fusion is yet to be deciphered. It is highly expected to be non-pathogenic for human. F-protein Its a glycoprotein which mediates pH-independent fusion of viral envelope with the plasma membrane of host cell. Synthesized as inactive precursor F0 (60 kD)– proteolytic cleavage – F-protein - (disulfide-linked F1 (45kD) and F2 (15 kD) poly peptide) Fusion peptide – Hydrophobic stretch of 20-25 amino acid at N-terminus of F1 –essential for biological activity of the protein 15 Preparation of Drug loaded Virosomes Ramani et. al . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 11886-11890, September 1998 16 Cloning Strategy of scFv with F-protein fragment Chimeric scFv has been used with F-protein for virosome reconstitution. Choice of Cell Lines and Controls HeLa cells - have PAP; Controls – Heat inactivated CscFv-F-virosome F-virosome alone CscFv-F-virosome at 10°C SaOs cells - BAP only, no PAP SaOs transfected with PAP - have PAP with BAP CHO - no PAP Octadecyl rhodamine B chloride (R18) Detection of Membrane Fusion Pictorial representation of a lipid-mixing assay based on fluorescence self-quenching. 18 Fold expression PAP Expression Analysis of Transfected SaOs-2 Real-Time analysis of PAP expression in transiently transfected SaOs-2 cell line. ~42 fold increase in the PAP RNA level was observed. Flow-cytometer analysis of the PAP transfected SaOs cells. PAP expressed on the surface of the cells were detected with anti-PAP monoclonal as a primary Ab and anti-mouse alexa 596 as secondary Ab. 14% PAP transfected cells were positively stained for PAP. Fusion Kinetics of scFv Engineered Virosome with Cell Lines HeLa cells SaOs-2 SaOs (T) CHO - Natural expression of PAP on surface - No PAP but BAP expression on surface - PAP transfected SaOs - No expression of PAP on surface Kinetics of scFv-F-virosome fusion with different cell lines. Dequenched fluorescence of R-18 shows that the initial membrane fusion is scFv dependent. FITC-lysozyme delivery by scFv-F-virosome HC = Heat treatment to virosomes abrogates fusion mediated delivery of the cargo without affecting scFv mediated endocytosis. C = Virosome without scFv. Fusion mediated cytosolic delivery of FITC-Lysozyme and fluorescence, Quantification by ImageJ, CTCF = Corrected Total Cell Fluorescence Doxorubicin delivery by scFv-F-virosome HC = Heat treatment to virosomes abrogates fusion mediated delivery of the cargo without affecting scFv mediated endocytosis. Fusion mediated cytosolic delivery of doxorubicin and fluorescence quantification by ImageJ, CTCF = Corrected Total Cell Fluorescence Cell Survival Analysis after Virosome Mediated Doxorubicin Treatment P<0.0014 P<0.001 P<0.069 P<0.0037 P<0.074 HeLA (HC) - Heat Control HeLa (control)- HeLa with F-virosome, no scFv SaOs(UT) - Untransfected SaOs SaOs(T) - PAP Transfected SaOs CHO – Negative control Trypan blue exclusion assay for cell survival after Doxorubicin packaged virosomal delivery. (significance level of P-value is <0.05) Significant reduction in HeLa cells and PLAP transfected SaOs cells viability Effect of Endocytotic Inhibitor on Cellular Internalization Delivery of FITC-lysozyme to PAP expressing HeLa cells by immunovirosome with or without cytochalasin B (10µM). In presence of cytochalasinB (cyto(+)), the cargo is delivered by membrane fusion mediated pathway. Localization of Intracellular RITC-lysozyme Delivered by Immuno-virosome Yellow fluorescence indicates endocytotic route of internalization. Reduced yellow fluorescence in panel A in comparison to Panel B but no such change in red fluorescence confirms membrane fusion mediated cytosolic delivery by Immuno-virosome. Live cell confocal microscopy for intracellular localization of RITC-lysozyme in HeLa cells in presence and absence of cytochalasinB (10µM). Lysotracker dye was used for tracking endocytotic route of internalization. HC – Heat control in terms of endocytotic route of entry. Efficacy of scFv-F-virosome Efficacy of CscFv-F-virosome for RITC-lysozyme delivery to HeLa cells. Cells without primary antibody against PAP (H17E2) were negative control. App. 68% PAP positive cells were also positive for RITC-lysozyme . Graphical presentation of the modality scFv targeted Sendai viral membrane efficiently delivers the payload in cytosol via membrane fusion mediated process. Chimeric scFv- scFv fused with trans-membrane and cytosolic region of F-protein with a linker in between. PAP- Placental Alkaline Phosphatase Conclusions scFv anchored on the virosome surface helps in binding of the virosome specifically to PAP expressing cells and subsequent membrane fusion is mediated by F-protein. Most of the cargo (FITC-lysozyme/ doxorubicin) is delivered directly to the cytosol. Enhancement to endosomal escape may result in less immunogenicity of the developed modality. The data is under review for publication. Acknowledgement Dr. Subrata Sinha, Director, National Brain Research Centre, Manesar, Haryana Dr. P. Chattopadhyay, Professor, Department of Biochemistry, AIIMS, N. Delhi Dr. D. P. Sarkar, Professor, Department of Biochemistry, South Campus, University of Delhi Dr. Kunzang chosdol, Additional Professor, Department of Biochemistry, AIIMS, N. Delhi Prashant Mani, Department of Biochemistry, South Campus, University of Delhi Lab members and staff of the Department of Biochemistry, AIIMS, New Delhi Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and ICMR for funding UGC for fellowship Deglycosylated immunovirosome did not fuse with hepatic cells but retained its fusion ability with HeLa cells expressing PAP with greater intensity than the virosomes without PNGase treatment