* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Anatomy
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
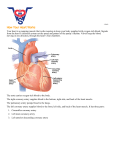
CARDIAC ANATOMY LEFT ATRIUM Left atrial appendage Left ventricle anterior wall Mitral valve Papillary muscles Left ventricle inferior wall MITRAL VALVE Pulmonary valve Anterior leaflet Right atrial appendage Posterior leaflet Infundibulum Tricuspid valve LEFT VENTRICLE OUTFLOW TRACT Sinotubular junction R Sinuses N ofLValsalva Ascending aorta Sinotubular junction Sinuses of Valsalva AORTIC VALVE Right ventricle outflow tract Right coronary cusp Right atrium Noncoronary cusp Left coronary cusp Left atrium PAPILLARY MUSCLES Anterolateral Right ventricle outflow tract Right ventricle Posteromedial Trabeculations Interventricular septum CHORDAE TENDINAE Papillary muscles Mitral valve LEFT VENTRICULAR WALLS Anterior wall Septal wall Lateral wall Inferior wall RIGHT ATRIAL APPENDAGE Right atrial appendage has a wide origin and a broad and triangular appearance. Lefttract atrial Right ventricle outflow appendage has a narrower origin and a tubular shape Pulmonary veins Superior caval vein Left atrial appendage CRISTA TERMINALIS The crista terminalis is Right ventricular free a wall ridge in the right atrium that separates Apex the two components of the right atrium, the sinus venosus (smooth Aortic valve muscles) and the atrium of the AV valve (pectinate muscles) Interatrial septum Mitral valve CORONARY SINUS Moderator band Posterior interventricular vein Right coronary artery The Thebesian Thebesian valve valve is a remnant of the right venous valve Inferior caval vein CS EUSTACHIAN VALVE Tricuspid anterosuperior leaflet The Eustachian valve is a fibromuscular web that attached to the opening of the inferior caval vein Tricuspid inferior leaflet Cavotricupid isthmus EV Inferior caval vein Superior caval vein RIGHT VENTRICULAR OUTFLOW TRACT Aortic valve Left atrium Mitral valve Right ventricular trabeculations Apex Crista supraventricularis MODERATOR BAND The moderator band is a muscular band that extends from the interventricular septum to the base of the anterior papillary muscle in the RV Pectinate muscles Chordae tendinae CONAL PAPILLARY MUSCLE Anterior descending artery Right coronary artery Foramen oval The right ventricle contains anterior and posterior papillary muscles and a smaller conal papillary muscle The conal papillary muscle arises from the septal band of the interventricular septum Circumflex artery RIGHT CORONARY ARTERY Aortic root Left ventricle CONUS ARTERY PDA AMB Acute marginal branch Right coronary artery The conus artery is the first branch of the right coronary artery in 50-60% of patients POSTERIOR DESCENDING ARTERY Circumflex artery Obtuse marginal branch The coronary artery that gives rise to the PDA and posterolateral branch is referred to as the dominant artery, with the RCA being dominant in Posterolateral artery approximately 70% of cases. LEFT CORONARY ARTERY LCA LCx RI LAD Right coronary artery In 15% of patients, a third branch (ramus Circumflex artery intermedius) arises at the division of the LCA, resulting in a trifurcation Anterior descending artery ANTERIOR DESCENDING ARTERY DIAGONAL BRANCHES Anterior descending artery SEPTAL BRANCHES Right coronary artery Anterior descending artery Left coronary artery CIRCUMFLEX ARTERY Left coronary artery LCA LAD OBTUSE MARGINAL BRANCH LCA The left circumflex artery courses in the left atrioventricular groove and gives off obtuse marginal branches to the lateral left ventricle LCx LAD SINOATRIAL NODAL ARTERY Right coronary artery Left circumflex artery Left coronary artery The sinoatrial nodal artery arises from the RCA in approximately 58% of patients; in the Ramus intermedius artery remaining patients it arises from the left circumflex artery Diagonal branches