* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4 Decisions Driving Growth - Croydon Health Services NHS Trust
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
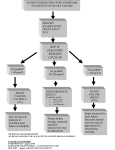
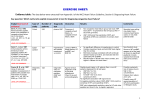
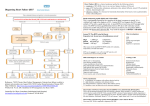
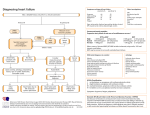
Diagnosing Heart Failure Sanjay Kumar Lead Consultant Cardiologist Grace Williams Lead Heart Failure Specialist Nurse Croydon Health Services NHS Trust © your company name. All rights reserved. Overview • Role of BNP • Role of Echo • One Stop Heart Failure Clinic • When to refer to secondary care Role of BNP “Rule-out” test for HF Diagnosis: • typical history • physical signs • evidence of an underlying cause (12 lead ECG, CXR, echo) B-Natriuretic peptides: • Released by stretched ventricular myocytes • Homeostatic mechanism - decrease SVR, cause natriuresis (sodium and water loss) • N-terminal (NT-)proBNP has long half-life (good diagnostic test), but 100% renal clearance (high in CKD) In patients presenting with SOB, for diagnosis of HF: • 90% negative predictive value at cut-off BNP<100ng/l • High BNP>500ng/l has 90% positive predictive value • Intermediate levels - consider other causes e.g. AF, valves, ACHD, IHD (especially with LV dysfunction), cor pulmonale, pulmonary HT, renal failure Role of BNP “Rule-out” test for HF • “Negative” BNP in an untreated patient makes a diagnosis of heart failure unlikely (high negative predictive value) • Elevated BNP does not distinguish between heart failure due to left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVSD) and heart failure with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (HeFPEF). Role of BNP Like cardiac enzymes, BNP levels are dynamic Fall with… Rise with… • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Obesity Diuretic therapy, ACE inhibitors, ARBs Aldosterone antagonists Beta-blockers Left ventricular hypertrophy Cardiac ischaemia Tachycardia High right ventricular pre-load Hypoxaemia [including PE] Renal dysfunction [GFR <60 ml/min] Sepsis COPD Diabetes, Old age Hepatic cirrhosis Role of BNP NICE CG108 (2010) Management of CHF in adults in primary and secondary care Key priorities for implementation • Measure serum natriuretic peptides (B-type natriuretic peptide [BNP] or N-terminal pro-B- type natriuretic peptide [NTproBNP]) in patients with suspected heart failure without previous MI. • Because very high levels of serum natriuretic peptides carry a poor prognosis, refer patients with suspected heart failure and a BNP level above 400 pg/ml (116 pmol/litre) or an NTproBNP level above 2000 pg/ml (236 pmol/litre) urgently, to have transthoracic Doppler 2D echocardiography and specialist assessment within 2 weeks. Role of BNP NICE CG108 (2010) Management of CHF in adults in primary and secondary care Key priorities for implementation • Refer patients with suspected heart failure and previous myocardial infarction (MI) urgently - echo and specialist assessment within 2 weeks. • Measure serum natriuretic peptides (BNP or NTproBNP) for suspected heart failure without previous MI. • If BNP levels are “high” (BNP >400 pg/ml (116 pmol/l) or NTproBNP >2000 pg/ml (236 pmol/l)) – echo and specialist assessment within 2 weeks. • If BNP levels are “intermediate” (BNP 100-400 pg/ml (29–116 pmol/l) or NTproBNP 400-2000 pg/ml (47–236 pmol/l) – echo and specialist assessment within 6 weeks. Role of Echocardiography Cause of clinical syndrome...including non-cardiac causes Determines which treatments to offer Role of Echocardiography LVSD or HeFPEF? Implications for prognosis and treatment options Evidence of old MI LV hypertrophy? specific patterns e.g. ASH or apical HCM? Valvular heart disease – primary cause of HF? or a consequence of adverse remodelling? Right ventricular involvement (excludes hypertensive myopathy)? Pericardial disease e.g. constriction, effusion? Restrictive myopathy? Pulmonary hypertension? Direct Access Echocardiography • http://www.cress.bics.nhs.uk/health-professionals/referral-supportdirectory/c/direct-access-echocardiography Community One-stop Heart Failure Clinic • • Echocardiogram performed on the day of the consultation, so diagnosis confirmed or refuted immediately http://www.cress.bics.nhs.uk/health-professionals/referral-supportdirectory/c/cardiology-services/ Heart Failure • An integrated approach to provision of services is fundamental to the delivery of high-quality care to adults with chronic heart failure. • Croydon Clinical Commissioning Group • Pathway diagnosing Heart Failure Community One-Stop Heart Failure Clinic • Rapid access (within 2 weeks for high-risk patients, within 6 weeks for others) • Specialist review by Cardiologist and Heart Failure Nurse, with echo at the same appointment, thereby providing early confirmation of diagnosis • Follow-on diagnostics/ specialist treatments planned • Specific management plan communicated to GP • Medicine optimisation, patient education, empowerment to enable self-management provided by HFSN • OSHFC referral form available via CReSS (Croydon Referral Support Service) • http://www.cress.bics.nhs.uk/health-professionals/referralsupport-directory/c/cardiology-services/ One Stop HF Clinic • 2 clinics per week in community locations (Tuesday at Purley Hospital, Thursday at Shirley Clinic) • Currently being led by Dr Silvia Gianstefani (Consultant Cardiologist in Imaging) • Locum dedicated Heart Failure Consultant starting 3rd August 2015 – Dr Brian Noronha – to be followed by substantive appointment • • • • • • • • • • • • HF Coding Congestive heart failure G580 Heart Failure G58 Right heart failure G580-2 Acute congestive heart failure G5800 Acute heart failure G582 Congestive heart failure due to valvular disease G5804 Heart Failure with preserved ejection fraction G583 Left ventricular failure G581 Echocardiogram shows left ventricular systolic dysfunction 585f Echocardiogram shows left ventricular diastolic dysfunction 585g Chronic Cor Pulmonale G41z-1 Preserved LV G583 Nice Quality statement 5 • People with chronic heart failure are offered personalised information, education, support and opportunities for discussion throughout their care to help them understand their condition and be involved in its management, if they wish. Role of HF Nurse in OSHFC • Provide British Heart Foundation booklet , Traffic light’s management tool, Personal management plan, contact details • Follow up post OSHFC includes - Medication titration to target/optimal doses, Symptom monitoring • …….then transfer care back to GP with long term management plan and open re-referral (self or GP) if HF symptoms deteriorate……… How to refer to the IHFNS • http://www.cress.bics.nhs.uk/healthprofessionals/referral-supportdirectory/c/integrated-heart-failure-nursespecialist-service/ Cardiology Advice Service • Cardiology advice Service available Monday to Friday except Wednesdays • Would prefer information via email on [email protected] but fax is acceptable • http://www.cress.bics.nhs.uk/healthprofessionals/referral-supportdirectory/c/cardiology-services/ When to refer to secondary care • GP Traffic Lights • NICE QS statement 9, monitoring stable chronic heart failure, 2011 • http://www.cress.bics.nhs.uk/healthprofessionals/referral-supportdirectory/c/integrated-heart-failure-nursespecialist-service/ GP Re-Referral Information to the Integrated Heart Failure Nurse Service GREEN ZONE Symptoms well controlled Manage patient in the General Practice Stable Heart Failure • No increased shortness of breath • No increased swelling of feet, ankles legs or stomach • No chest pain • No weight gain of more than 2-3 pounds (1Kg) in 2-3 days, (it may change by 1 to 2 lbs on some days). Continue on daily weights and 1.5Litre/24Hr fluid restriction Ensure patient has 6 monthly reviews which should include repeat blood test including Renal function, FBc, LFTs, TFTs, Weight/Fluid status, Sitting and Standing Blood Pressure and Pulse. (HF Quality Standards 9, 2011) YELLOW ZONE Exacerbation of Heart Failure: Change in NYHA Status Contact HF nurse to discuss concerns on 020 8274 6416 or 020 8401 3000 bleep 772 • Increased shortness of breath • Weight gain over last 2-3 days - ask patient to continue daily weights. • More swelling of feet, ankles, legs or stomach • Fatigue Consider using Trigger Tool for EoL (See attached) • Has a productive cough with frothy white sputum • Postural drop • Loss of appetite/cachexia • Have diarrhoea &vomiting – In view of dehydration • Orthopnoea and Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea Please ensure the patient has had up-to-date renal function and check vital signs. Please consider increase in diuretic therapy for symptom management. RED ZONE Consider need for hospital admission Acute Exacerbation of Heart Failure: Change in NYHA Status Or Advance Care Planning Resus status GSF register CMC register Referal Palliative Care/HF Nurse ©Specialist your companyService name. All for symptom rights reserved. management • Breathlessness at rest • Struggling to breathe - Orthopnoea and Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea • Increased fluid overload • Palpitations • Faint /Syncope Title of your presentation HFNS Contact details We are available Monday – Friday, 09.00hrs – 17.00hrs Lennard Road Office Telephone: 020 8274 6416 or 6152 Fax: 020 8274 6174 Croydon University Hospital Telephone: 020 8401 3000 Ext. 4413 Contact via switchboard 020 8401 3000, bleep 772 Cardiology Dept. Contact details • Telephone: 0208 401 3000 ext. 4487 • Fax: 0208 401 3022 © your company name. All rights reserved. Title of your presentation Reference • http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/qs9/chapter /List-of-statements