* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Help for Test
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Marine weather forecasting wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric convection wikipedia , lookup
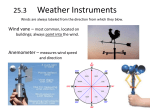
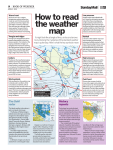
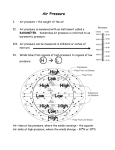
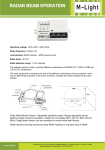
a. Define the term “atmospheric pressure” & describe the movement of air currents between areas of high & low pressure Atmospheric pressure: is the force per unit area due to the weight of the atmosphere (a layer of gases). These gases are kept in place by the force of gravity. measured in hectoPascals. Air moves from high air pressure to low air pressure. (breeze or wind) Typically, the air pressure varies from about 980 hPa to 1100 hPa- normal is 1006 hPa b. identify the distance between isobars on a weather map indicates the relative change in atmospheric pressure in an area. If the isobars are close together, this means that places that are not far apart experience a large difference in air pressure. As a result, the winds in this region will be strong. If the isobars are a long way away from each other, this means that the difference in air pressure between two places is not very large. As a result, the winds will be quite gentle. c. describe the relative pressures involved in the formation of tropical cyclones & tornadoes Cyclones & tornadoes are examples of extremely violent storms produced by large differences in air pressure. They are also known as typhoons or hurricanes, depending on where you live. The factors they have in common are: o They are formed when an area experiences extremely low air pressure o They are produced by extreme difference in air pressure o They often form over water & then move on to land The differences include: o Cyclones are longer in duration, have slower winds & are slower moving o Tornadoes are shorter in duration, have faster winds & are faster moving d. describe technological advances that contributed to increased understanding of meteorology Meteorology is the study of the weather & climate. There are several major aspects to it: o Measuring the characteristics of the weather o Predicting the weather o Researching ways to improve the measurement methods To predict the weather, meteorologists need to measure quantities like air pressure, humidity, temperature & wind speed & direction. They are measured in as many places as possible, as often as possible, normally a person is needed to make any measurement. These measurements then have to be interpreted to make predictions about the weather. The basic tools for measuring these characteristics include: e. describe the relationship between the monitoring of weather patterns by radar & laser light & the analysis of reflected wave patterns by computers Radar Use microwaves Waves reflect off clouds of rain The time taken for the pulse to return tells the operator how far the clouds are away The shapes of the waves tell us what they are showing o Longer wavelengths used to show water (liquid) o Shorter wavelengths show vapour (gas) Experienced operators can tell rain from hail & snow Doppler Radar Slightly different Used to measure the speed of air If wind is coming towards you it’s a different colour on the screen to wind moving away from you It works the same way in which a police radar The faster object is moving towards you the high frequency of the reflected wave Lidar (laser Light) Light detection & ranging Measures distance Measures speed Measures rotation Measures chemical composition & concentration Used to study atmosphere including pollutant & gas concentration f. explain why satellite photographs of cloud patterns have improved the reliability of interpretations of weather regularities & knowledge of global weather patterns Help to trace the life cycle of weather systems, better data about air pressure, cloud patterns & solar radiation estimates A new Japanese-built satellite, MTSAT-1R, has started snapping hourly photographs of weather fronts in the AsiaPacific region & is beaming them down to a base station at Cribb Point, near Hastings in Victoria. VIS Images Visual images Photographs from satellites Show cloud coverage IR Images Infared images Used to find out about temp of oceans & the atmosphere Radar Network Radio waves are sent form a radio dish Waves travel away from the dish & if they hit water or ice they are reflected back Computers measure the time they take to return & calculate the distance to them Computers then display the data on a colour coded map