* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7.1 Polygons and Exploring Interior Angles of Polygons Warm Up
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
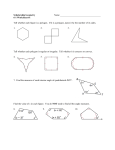
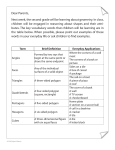
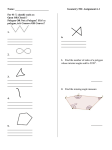
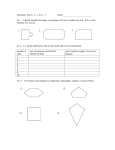
7.1 Polygons and Exploring Interior Angles of Polygons Warm Up Given A (4,-5) and B (-2, 7) find the following: 1.Midpoint of AB 2. AB (the distance) Evaluate each expression for n = 6. 3. (n – 4) 12 4. (n – 3) 90 Solve for a. 5. 12a + 4a + 9a = 100 7.1 Polygons and Exploring Interior Angles of Polygons Objective: Identify, name, and describe polygons. A polygon is a plane figure that is formed by two or more segments such that each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint. Each segment of a polygon is called a side. Any point where two sides meet is called a vertex. (The plural of vertex is vertices.) Two consecutive sides of a polygon form an interior angle. You can name a polygon by listing its vertices consecutively. For example, PQRST or QRSTP, etc. Examples: State whether each figure is a polygon. If it is not, explain why. 1. 2. 3. 4. Check for understanding: Fill in the blanks below to show your understanding of the parts of a polygon. a. Name a vertex. ____________ b. Name the polygon. ____________ c. Name a side. ____________ d. Name an interior angle. ____________ e. Name a diagonal. ____________ Polygons are also named by the number of sides they have. Number of Sides Type of Polygon Number of Sides Type of Polygon 3 Triangle 8 Octagon 4 Quadrilateral 9 Nonagon 5 Pentagon 10 Decagon 6 Hexagon 12 Dodecagon 7 Heptagon n n-gon A polygon is convex if no line that contains a side of the polygon contains a point in the interior of the polygon. A polygon that is not convex is called nonconvex or concave. Convex polygon Concave polygon Examples: Identify the type of polygon and state whether it is convex or concave. 5. 6. 7. A polygon is equilateral if all of its sides are congruent. A polygon is equiangular if all of its interior angles are congruent. A polygon is regular if it is equilateral and equiangular. Examples: Decide whether the polygon is equilateral, equiangular, regular, or neither. 8. 9. 10. Check for understanding 2. Draw a regular polygon. Then draw an irregular polygon with the same number of sides. A diagonal of a polygon is segment that joins two nonconsecutive vertices. For example, Polygon ABCDEF has 3 diagonals from point B: BD, BE, BF. Theorem 7.1: Sum of the Interior Angles of a Polygon The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon is equal to the difference of the number of sides of the polygon and 2, multiplied by 180. Sum of the interior angles = (n-2)∙180 720° = (6-2)∙180 Examples: Use the information in the diagram to solve for x. 14. What is the sum of the angles of an octagon? 15. If the figure is a regular octagon, what is the measure of each angle?