* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stroke Event in Complete Heart Block and Sinus Node Dysfunction
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
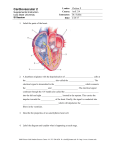
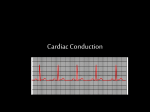
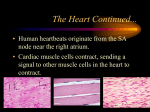
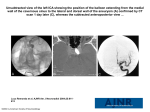
Stroke Event in Complete Heart Block and Sinus Node Dysfunction : A Rare and Unusual Case Report Arrhythmia is the term used for an irregularity or rapidity of the heart beat or an abnormal heart rhythm. There are two types of common arrhythmia, bradyarrhythmia and tachyarrhythmia. Based on the location, bradyarrhythmia divide to 3 types : sinus bradycardia and sick sinus syndrome (SA node), conduction blocks and junctional escape rhythm (AV node), and ventricular escape rhythm (ventricles). Sinus node dysfunction (SND) refers to abnormalities in sinus node impulse formation and propagation. Dysfunction of the sinus node or failure to conduct electrical impulses through the AV node and conducting bundles may cause marked slowing of the heartbeat, a bradycardia of 32 - 40 beat per minute. Sinus node dysfunction is referred to as sick sinus syndrome when it is accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness or syncope. Complete heart block is complete failure of conduction between the atria and ventricles. In adults, the most common causes are acute myocardial infarction and chronic degeneration of the conduction pathways with advanced age. As a result of the slow rate, patients frequently experience light-headedness or syncope. Arrhythmia may increase the risk of conditions such as stroke and heart failure. And stroke due to arrhythmia ist most often caused by atrial fibrillation. In this case, the patient had a stroke clinically without atrial fibrillation. He had complete heart block and sinus node dysfunction. Keywords : Stroke, Complete Heart Block, Sinus Node Dysfunction Case History : A-44 years old Male carried by his family to Emergency Room with unconsciousness suddenly after dinner. He had vomitting while on the trip to the hospital. There were no diabetes mellitus type II, hypertension, and heart disease before. He was only a smoker. On physical examination, a low heart rate 38 beat per minute and hemiplegi on his left extremity were found. The laboratorium examination showed there was only increasing of CKMB 54 but normal value of serial troponin I 0,00. From the electrocardiogram, a complete heart block with there was only three of P wave at 6 seconds record and left bundle branch block. There was no abnormality in head CT Scan. Patient decided to implant of temporary pacemaker (TPM), which was set on heart rate 80, treshold 0.5 mA, and output 1mA. After that, echocardiogram was performed and showed dilatation of left ventrikel with ejection fraction 48%, and hypokinetic of partial inferior wall. Patient decided to angiography coronary and his result was normal. 3 Days after implant of TPM, there was no progression of his heart rate and decided to implant of permanent pacemaker (PPM). 9 Days after implant of PPM, patient can be outpatient without complaint and his left superior extremity can be lifted by himself but his inferior extremity can not be moved. Now his mobility with a stick and he still continue control for his PPM. When reprogram of his PPM performed, there were still sinus node dysfunction and AV node dysfunction. Discussion