* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Test 1 - WordPress.com
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
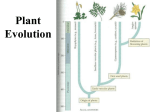
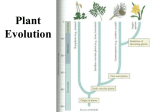
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Introduction, plant evolution and different plant groups – Test 1 1. Describe why plants are crucial in A) evolution and survival of other species B) maintaining a healthy environment and C) our efforts to combat climate change. 2. Indicate medicinal uses of phytochemicals from willow bark, sweet woodruff, tobacco, sweet wormwood and foxglove – website on slide. 3. Describe which groups of photosynthesizers are included in Cyanobacteria, Excavates, Chromalveolates and Archaeplastids. 4. Profile photosyhthetic pigments in Euglena, Phaeophytes, Chrysophytes, Bacillariophytes, Rhodophytes, Chloprophytes and Plantae. 5. Describe how certain Chromalveolates permanently remove C from the atmosphere. 6. Describe adaptation thru selection of phenotype, significance of environment in producing the/a phenotype, and fitness. 7. Discuss plant cladogram with 10 phyla referring to the times of evolution of major apomorphies (synapomorphies). 8. Define plant primary and secondary metabolism with examples in each, and discuss the significance of secondary metabolism for survival of plants. 9. Describe auto- and allopolyploidy in plants. Name some major crop species that are polyploids. 10. What is green revolution – discuss pros and cons. 11. Describe what ideal plant type is (in artificial selection and breeding for producing improved crop cultivars). What is HI – why is Dr. Norman Borlaug considered farther of Green revolution? 12. What are IRRI, CIMMYT and IPC? Where are they located? 13. What are Bryophytes, Cryptogams and Spermatophytes? 14. Discuss what adaptations (synapomorphies) made land plant evolution from Charophytes possible? 15. What are common characteristics of Phyla, Hepaticophyta, Bryophyta and Anthocerophyta? 16. What are differences in growth/body patterns of the three Bryophyte phyla? 17. What are gemmae, archegoniophore, antheridiophore, monoicous and dioicous? 18. Describe life cycles of Bryophytes and major parts of Bryophyte sporophytes. 19. What are Hydroids and Leptoids? How do small body size and lack of conducting tissues help Bryophyta phylum to survive in many habitats? 20. How do Anthocerophyta differ from other Bryophytes? 21. Characterize earliest - now extinct - vascular plants using Cooksonia as an example. What Bryophyte phylum is most closely related to vascular plants? 22. What is stele? Describe protostele and syphonostele? Describe endarch and exarch protostele. 23. Describe evolution of microphyll and megaphyll in vascular plant phylogeny. 24. What is strobilus, micro- megasporophyll, micro- megaspore, seta – describe using Lycopodium and Selaginella. 25. Describe Psylotum morphology and life cycle as a homosporous, and monoecious gametophytic example. 26. Describe Equisetum morphology. 27. Describe fern stem vascular cylinder as an example of an early siphonostele. 28. Describe fern life cycle as another homosporous, and monoecious gametophytic example. 29. Describe adaptive advantage that ovule offers in seed plants compared to nonseed plants with no ovule – refer to the start of sporophytic generation in alternation of generations. 30. Describe adaptive advantages that seed provides to spermatophytes compared to nonseed plants. 31. Describe morphological features of Cycads, Conifers, Ginkgo and Gnetos. 32. Describe morphological features of male and female pine cones. 33. Briefly describe major events in pine life cycle. Plant Evolution/Life Cycles 41. In the life cycle of a moss shown above: A. The gametophyte stage (A or B) _______________ B. The Sporophyte Stage (A or B) ______________ C. The stage which is dominant (Sporophyte or Gametophyte) ___________ D. What are parts of A and their functions. E. Is the sporophytes monoecious or dioecious? F. Is the gametophyte monoecious or dioecious? G. Is this life cycle homosporous or heterosporous? 42. Match the name to the number on the liverwort above A. Rhizoids ______________ B. Gemmae cups ______________ C. Sporophyte ______________ D. Antheridium ______________ E. Archegonium______________ F. Thallus ______________ G. Which stage is dominant in the Liverwort, sporophyte or gametophyte?__________ H. Is this life cycle homosporous or heterosporous? 43. In the Fern Life Cycle above: A. "A" Represents the (Gametophyte or Sporophyte) Stage _______________ B. "B" Represents the (Gametophyte or Sporophyte) Stage _______________ C. Is this life cycle homosporous or heterosporous? D. Is the sporophytes monoecious or dioecious? E. Is the gametophyte monoecious or dioecious? In the fern stage above, name the structure indicated by the letter F. A above _____________ G. B above _____________ H. C above ____________ I. D above ____________ J. Is the above the gametophyte or Sporophyte? ________________ K. Is the plant above haploid or diploid? _________________ The above is a life stage of a fern. L. Which number represents the roots? _______________________ M. Which number shows a fiddle-head? _______________________ N. Which number represents the rhizome? _______________________ O. Which number shows a frond? _______________________ P. Which number indicates a pinnae? _______________________ Q. Is the above plant a sporophyte or gametophyte? ______________________ R. Is the above plant diploid or haploid? _________________ 46. GYMNOSPERMS 1. In gymnosperms, which generation is the dominant generation? a. sporophyte b. gametophyte 2. In gymnosperms, the ______________is retained by the sporophyte generation. a. Megaspore b. Microspore c. Pollen d. Sporophyte 3. The term gymnosperm refers to a. naked seeds b. seeds enclosed in a fruit c. sperm enclosed in pollen d. sperm enclosed in a fruit 4. In gymnosperms, the ________gametophyte is distributed by air rather than requiring water for fertilization. a. Male b. Female 5. An evolutionary advantage of seeds is a. Provides food for the developing sporophyte b. Provides protection c. Allows for delayed germination until conditions are favorable d. All of the above 6. Seeds represent 3 generations. These area. Two gametophyte generations and a sporophyte generation b. Two sporophyte generations and a gametophyte generation c. Three gametophyte generations d. Three sporphyte generations 7. All seed plants are a. Heterosporus b. Homosporus c. Monoecious d. Dioecious 8. Integuments are sporophyte tissue that become the a. Seed b. Embryo c. Pollen d. Seed coat 9. The cones of gymnosperms are homologous to the __________of the seedless vascular plants a. Leaves b. Strobili c. Megasporangium d. Microsporangium 10. Pollen grains are reduced ___________ a. Sporangium b. Sporophylls c. Male gametophytes d. Female gametophytes 11. Ginko belongs to which division of gymnosperms? a. Ginkophyta b. Cycadophyta c. Coniferophyta d. Gnetophyta 12. Pines belong to a. Ginkophyta b. Cycadophyta c. Coniferophyta d. Gnetophyta 13. Gymnosperms such as pine produce a. Vast amounts of pollen b. Very little pollen c. Seeds in only a few weeks d. Pollen in megasporangia 14. How many species of Ginko are there world wide a. Only 1 b. Approximately 10 c. Several hundred d. Several thousand 15. The fossil record for Ginko suggests that Ginko a. Has evolved considerably in 80 million years b. Is virtually unchanged in 80 million years c. Has evolved from cycads d. Has evolved from ferns 16. Ginko is a. Monoecious b. Dioecious c. Vegetatively propagated - no sexual reproduction d. Very sensitive to air polution 17. Which of the following do NOT belong to Pinophyta? a. Hemlock b. Spruce c. Cypress d. Ephedra 18. Pollen grains are the _____________generation a. sporophyte b. gametophyte 19. In pines, the male gametophyte a. takes a few hours to fertilize the egg of the female gametophyte b. takes a few minutes to fertilize the egg of the female gametophyte c. takes several months to fertilize the egg of the female gametophyte 20. The archegonium of pine forms a. within the female gametophyte b. within the pollen tube c. within the microsporangium 21. The sporophyte embryo isa. diploid b. haploid 22. Gymnosperms produce _________of the worlds timber needs a. Very little b. Less than 30% c. About 50% d. About 75% PINE LIFE CYCLE 23. Structure number 1 is a a. Pollen grain b. Zygote c. Egg d. Megasporophyll e. Microsporophyll 24. Structure 2 is the a. Pollen grain b. Zygote c. Egg d. Megasporophyll e. Microsporophyll 25. Process number three is a. Mitosis b. Meiosis c. Fertilization d. Germination 26. Structure 4 represents the a. Male gametophyte b. Female gametophyte c. The embryo d. Megasporophyll e. Microsporophyll 27. Structure 5 represents a. Male gametophyte b. Female gametophyte c. The embryo d. Megasporophyll e. Microsporophyll 36. Structure 6 represents the a. zygote b. megaspore c. microspore d. Archogonia 38. The __________(number 10) is contained within the ____________ a. Embryo, female gametophyte b. Megaspores, Megasporangia c. Archegonia, female gametophyte d. Microspores, Microsporangia 39. Gnetophytes are unique among gymnosperms because a. they don't have cones b. they have double fertilization c. they have a short life cycle d. they are not photosynthetic