* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download this document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
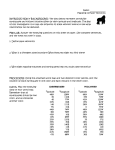
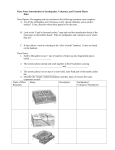
Name________________________ Date__________ Evidence for Plate Tectonics How do we know that the plates move? # 1 Evidence Supporting Continental Drift Although Wegener did not have the answer to how or why the plates were moving, he was able to compile evidence to show that the Earth is active. List the five pieces of evidence he used in his theory of Continental Drift. 1. ________________________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________________________________________ 4. ________________________________________________________________________________ 5. ________________________________________________________________________________ #2 Earthquake/Volcano Zones The most reliable clues to future quakes/volcanoes are the patterns of past earth movements. These allow geologists to suggest where earthquakes are most likely to strike. Areas most at risk of earthquakes can develop and implement strategies to minimize harm to people and property when the inevitable occurs. Geologists are still seeking a way to predict exactly when a quake will happen, so that people can be evacuated and valuable or dangerous substances can be secured. Directions: Plot the earthquakes and volcanoes on the attached map (next page). Study the maps of your data and provided data to understand where and why most earthquakes occur. Study the global distribution and depth of large earthquakes. Then answer the questions that follow. 1. Notice that earthquakes are mainly concentrated in narrow bands. Explain why. 2. Which parts of the United States have the most frequent earthquakes? 3. Look again at the map, and see that earthquakes can begin close to the Earth's surface or deep inside the crust. Geologists classify earthquakes as shallow (those that start 70 kilometers or less underground), deep (earthquakes beginning 300 km or more below the surface), and intermediate (quakes between 70 and 300 km). Earthquakes can only start within the solid rock of the lithospheric plates, not in the soft mantle below. a. Shallow earthquakes occur at all plate boundaries, and even in the middle of plates. Deep earthquakes only occur at some plate boundaries - why? b. Why might the depth of an earthquake be related to the amount of damage it causes? Name________________________ Date__________ Use two different colored pencils to signify earthquakes and volcanoes. Name________________________ Date__________ #3 Movement of Plates (example: Hot Spots) According to the theory of plate tectonics, the Earth’s lithosphere, or outermost layer consisting of the crust and part of the mantle, is made of interlocking pieces, much like the cracked shell of a hard-boiled egg. The pieces of the lithosphere are known as lithospheric plates. The plates float across the surface of the hot, soft, flexible layer of mantle that lies beneath them. (Scientists call this underlying layer the asthenosphere.) Most of the Earth’s volcanoes are found at the boundaries of plates. But a few volcanoes are found, surprisingly, in the center of the plates. Such volcanoes are thought to be caused by “hot spots” located deep within the Earth – perhaps in the lower parts of the mantle or even in the core itself. Superheated molten material rises from a hot spot and “burns through” the plate, creating a volcano. Because hot spots are stationary, a chain of volcanic islands may be formed as an oceanic plate moves over a hot spot. (*See the diagram below). By determining when the islands in the chain were formed, it is possible to calculate how fast the plate is moving over the hot spot. In this activity, you will determine how fast the Pacific plate is moving over the hot spot that formed the Hawaiian chain of volcanoes, which extends 3500 km northwesterly across the floor of the Pacific Ocean. The following diagram illustrates the eight main Hawaiian Islands. Approximate age is given for the larger islands. Name________________________ Date__________ Directions: 1. Using the scale shown on the diagram, determine the distance between the five major islands and enter you answers in the appropriate spaces in Data Table 1. Measure the distance between the dots placed at the center of the major islands. 2. Convert each distance from kilometers to centimeters by multiplying the value in kilometers by 100,000. Enter the new data in the appropriate spaces in Data Table 1. 3. Calculate the approximate age differences between the islands and enter the data in Data Table 1. Data Table 1 Islands Distance Between the Two Islands (km) (cm) Difference in Approximate Ages of the Two Islands (Years) Hawaii and Maui Maui and Molokai Molokai and Oahu Oahu and Kauai 4. Using the following formula, calculate the approximate speed at which the crustal plate was moving between the time that each of the islands formed. Enter your data in Data Table 2. Speed of crustal movement (cm/year) = Data Table 2 Islands Hawaii and Maui Maui and Molokai Molokai and Oahu Oahu and Kauai Distance between the two isalnds (in cm) Difference in approximate ages of the two islands (in years) Speed of Crustal Movement 5. Using the speeds from Data Table 2, calculate the average speed of crustal movement. Average speed = _____________________________ cm/yr 6. a. In which direction was the crustal plate apparently moving when the Hawaiian Islands were formed? __________________________________________________________________________________ b. Explain how you know. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 7. a. According to your data, did the crustal plate always move at the same speed? __________________________________________________________________________________ b. Explain how you know. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Name________________________ Date__________ #4 Ocean Floor/Geographical Features Divergent Boundaries: Label the parts Describe the process of sea-floor spreading: __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Convergent Boundaries: Describe the ocean floor features seen at an oceanic-continental plate: _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Which plate is subducted? ___________________________________ Describe the ocean floor features seen at an oceanic-oceanic plate: _________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ Which plate is subducted? ____________________________________ Describe the ocean floor features seen at an continental-continental plate: __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Which plate is subducted? ____________________________________ Transform Boundaries: Describe what happens at a transform boundary and how it is different from divergent and convergent: __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Name________________________ Date__________