* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Air Movement
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
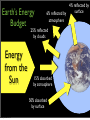
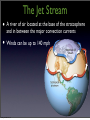
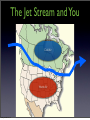
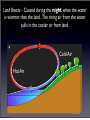
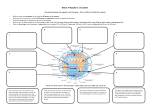
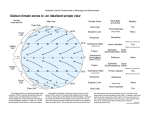
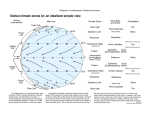
Air Movement I’m angry because this isn’t really how wind forms! Friday, October 28, 11 What you should know so far. • What gases make up the atmosphere • The five layers of the atmosphere • Their location and important facts (flip book) • Function of the ozone layer • Atmospheric Pressure (Density) • Energy transfer • Convection, Conduction and Radiation • The Water Cycle Friday, October 28, 11 What causes wind? Friday, October 28, 11 Uneven heating of Earth’s surface causes wind. Indirect Light Direct Light Friday, October 28, 11 Earth’s Energy Budget 4% reflected by surface 6% reflected by atmosphere 25% reflected by clouds Energy from the Sun 15% absorbed by atmosphere 50% absorbed by surface Friday, October 28, 11 Global Convection Currents Remember: Hot Air Rises and Cold Air Sinks Polar Cell Polar Front Ferrel Cell Horse Latitudes Hadley Cell The Doldrums Hadley Cell Horse Latitudes Ferrel Cell Polar Front Polar Cell Friday, October 28, 11 Definitions to Know • Polar Cells - Convection current that circulates in near the poles. Between o 60 and o 90 latitude. • Polar Front - Division between a polar cell and ferrel cell. Know for a sharp change in temperature. • Ferrel Cells - Convection cell that circulates between o 30 and Friday, October 28, 11 o 60 latitude. Definitions to Know • Horse Latitudes - Division between Ferrel and Hadley cells. Air is Dry, Most deserts found here. • Hadley Cells - Convection current found between the equator and 30o latitude. • Doldrums - Division between the two Hadley cells. Known for having little to no wind present and lots of rain. Sailors really don’t like it there. Friday, October 28, 11 But Earth’s isn’t motionless right? It’s rotating! Friday, October 28, 11 The Coriolis Effect • The curved motion of wind caused by Earth’s rotation • Think of it like throwing a ball to a friend on a merry go round NOTE: Winds are named based on the direction they are coming from. Friday, October 28, 11 The Jet Stream • A river of air located at the base of the stratosphere and in between the major convection currents • Winds can be up to 140 mph Friday, October 28, 11 The Jet Stream and You Cold Air Warm Air Friday, October 28, 11 Let’s get a little more local • Local Winds - Small wind systems that determine local weather • Caused by the uneven heating of surfaces • Most apparent near bodies of water Friday, October 28, 11 Sea Breeze - Caused during the day when the land is warmer than the water. The rising air on land pulls in the cooler air from the water. Hot Air Cold Air Friday, October 28, 11 Land Breeze - Caused during the night when the water is warmer than the land. The rising air from the water pulls in the cooler air from land. Cold Air Hot Air Friday, October 28, 11