* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell characteristics
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
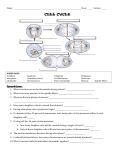
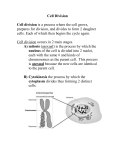
The cell cycle is defined as the series of changes that a cell undergoes from time it forms until it divides. - Interphase used to be considered a time of rest; but it is a very active period. During this time, cell grows, and maintains its routine functions. Interphase is divided into phases based on the sequence of activities: • S phase- DNA replicates • G1 and G2 phase –cell growth and DNA is packed. Mitosis is the cell division of somatic cells and produces two identical daughter cells. These new cells are identical, each of them have 46 chromosomes. Two main parts in mitosis • 1- Karyokinesis- Nucleus divides • 2-Cytokinesis-Cytoplasm divides Mitosis Stages: • Prophase- Condensation of chromatin fibers forming chromosomes. x Each chromosome consist of two identical structures called chromatids that are attached together at the center by the centromere Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the chomosomes so that a fiber accompanying on chromatid attaches to one centromere and the fiber accompanying to the otherchromatid attaches to its centromere. The chromosomes move along the spindle fibers and align in the middle. Metaphase plate The centromeres of the chromatids separate and these identical chromatids are now considered individual chromosomes. The separated chromosomes move in opposite directions. The spindle fibers shorten and pull their attached chromosomes toward the centrioles at opposite sides of cell. The final stage of mitosis begins when the chromosomes complete their migration toward the centiroles. A nuclear envelope forms around each chromosome set, and nucleioi becomes visible. It is the cytoplasmic division The cytoplasmic division starts during the anaphase. The cell membrane starts to constrict around the middle. The ring of spindles pinches and separtates the two newly formed nuclei and half of organelles go into different cells. The newly formed cells may have different size and number of organelles but the same number of chromosomes. How often a cell divides depends on the type of cell. Skin cells, liver cells, and blood forming cells divide constantly. A physical basis for mitotic clock is the DNA at the tip of chromosome. Other external factors that control mitosis are the kinases ( proteins) and cyclins , hormones and growth factors. Internal factors that control the mitosis are the surface area ratio between cell and membrane and the cell size. Other external factors are availability Too frequency mitosis crates a disorganized mass called TUMOR Two types of tumors: 1. Bening: It remains in place like a lump,eventually interfering with the functions of the tissue. 2. Malignant: or cancerous tumor may resemble a crab. Cancer cells if not stopped, they metastatize to other sites. Two major types of genes cause cancer. • Oncogenes: activates other genes that cause cell division • Tumor suppresor genes: hold mitosis Cells that retain the ability to divide themselves allow for continual growth and renewal. Stem Cell- divides mitotically to yield either two daughter cells as themselves or one daughter cell that is a stem cell and another partially specialized. The partially specialized cell is termed progenitor cell. Stem cells and progenitor cells are described in terms of their potential,according to the fates of their daughter cells. • 1- totipotent- can give rise to every cell type. • 2- pluripotent- their daughter cells can follow different pathways.