* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
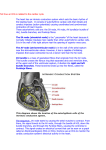
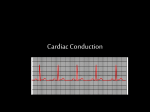
Electricity Of The Heart ABBAS SHAREEF Introduction – Cardiac Conduction The heart has a specialized cardiac conduction system which spreads to all parts of the myocardium Depolarization – Change in membrane potential from a more negative state to a more positive state Repolarization – change in membrane potential from a positive state to a more negative state Introduction – Sequence Of Heart Contraction Atrial Systole, contraction of the atria Atrial Systole is followed by ventricular systole, contraction of the ventricles During diastole all four chambers are relaxed Structures that make up conduction system: sinoatrial node(SA node), internodal atrial pathways, the atrioventricular node, the bundle of His, its branches, and the Purkinje system. Introduction Due to its rapid discharge, the SA Node is the normal cardiac pacemaker. Its rate of discharge determines the rate at which the heart beats. Impulse from SA node pass through atrial pathways to and through the AV node, to the bundle of His, through the branches of the bundle of His via Purkinje system to the ventricular muscle. Locations The SA Node is located at the junction of superior vena cava with the right atrium The AV node is located in the right posterior portion of the interatrial septum Bundle Of His runs from the AV Node to fascicular branches which leads to Purkinje Fibers Purkinje Fibers are located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart Path Of Conduction Spread Of Cardiac Excitation Depolarization initiated in SA node and converges onto AV Node (Atrial Depolarization). Time Length – completed in .1 s Conduction in AV Node is slow, which causes a delay of .1 s (AV nodal delay), before excitation spreads to the ventricles. From the top of the septum, a wave of depolarization spreads to the purkinje fibers from .08 - .1 s. Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram Electro – electricity Cardio – heart Gram – Record Electrocardiogram is a record of electricity of the heart. Waves Of Electrocardiogram The normal ECG shows 5 waves named as P,Q,R,S,T The P wave represents the impulse from the SA node sweeping over the atria (atrial depolarization) The QRS complex represents the spread of impulse from the AV node to Av bundle (bundle of His) and purkinje fibers(ventricular depolarization) The T wave represents relaxation of the muscles (ventricular repolarization) Clinical Relevance Complete Third Degree Heartblock – occurs when conduction from atria to the ventricles is completely interrupted and ventricles beat at a low rate (idioventricular rhythm) Causes of Third Degree Heartblock – disease of the AV node or in conducting system below the node(infranodal block) In patients with AV nodal block the nodal tissue becomes the pacemaker and the rate of idioventricular rhythm is approximately 45 beats/min. Clincal Revelance Increased Automaticity – present when His-Purkinje fibers or the myocardial fibers discharge spontaneously If an ectopic focus discharges once, this results in a beat that occurs before the expected next normal beat which interupts the normal cardiac rhythm (extrasystole or premature beat). If the focus discharges repetitively at a higher rate than that of SA node, it produces rapid, regular tachycardia. Clinical Revelance Atrial Arrhytmias - Excitation spreading from an independent focus in atria stimulates AV node prematurely and is conducted to the ventricles. The P waves of atrial extrasystoles are abnormal, which may depolarize the SA node, which must repolarize and then depolarize to the next level before it can initiate the next normal beat. Results in a pause between normal beats preceding the extrasystole Results in low cardiac output and symptoms are of heart failure appear Clinical Revelance – Long QT Syndrome Patients in whom QT interval is prolonged, cardiac repolarization is irregular increases incidence of ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death increases Caused by number of different drugs, electrolyte abnormalities, and by myocardial ischemia PHSYIOLOGY IS FUN!!!!!