* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CARDIAC EMERGENCIES
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
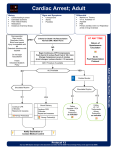
CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Anatomy of the Heart Muscular organ (fist size) Functions like a pump Protected by the ribs, sternum, and spine 4 chambers, right and left halves Supplied with blood by the coronary arteries Functions of the Heart Right atrium (receives O2 poor blood from veins) Right ventricle (pumps O2 poor blood to the lungs) Left atrium (receives O2 rich blood) Left ventricle (pumps O2 rich blood to the body) HEART ATTACK Coronary arteries fail to supply the heart muscle with O2 rich blood Muscle tissue starts to die (too much = heart stops pumping blood) Interrupts heart’s electrical system, causes irregular heartbeat Causes of Heart Attack Cardiovascular Disease (heart and blood vessels) 70 million Americans have it 1 million deaths Coronary Artery Disease Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Early tendencies….junk food and smoking Risk Factors Gender….males higher Family history of heart disease Smoking* Diets high in saturated fats* Obesity* High blood pressure* Lack of exercise* Cardiovascular Disease Cholesterol causes atherosclerosis S/S of Heart Attack Persistent chest pain or discomfort Difficulty breathing Changes in pulse rate Skin appearance Care for Heart Attack Summon EMS Convince victim to stop activity and rest Help victim rest comfortably SAMPLE History Comfort the victim Monitor Vitals Be prepared for CPR CARDIAC ARREST Heart stops beating or beats too weakly to circulate blood Breathing stops—clinical death Organs no longer receiving O2 rich blood 300,000 deaths prior to reaching hospital Causes of Cardiac Arrest *Cardiovascular disease* Drowning Suffocation Certain drugs Severe injuries to the chest Severe blood loss Electrocution Stroke Stroke STROKE A stroke is an interruption of the blood supply to any part of the brain. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack." Alternative Names Cerebrovascular disease; CVA; Cerebral infarction; Cerebral hemorrhage Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy HCM is the leading cause of sudden death in young people (1 in 500 people) Excessive thickening of heart muscle Anthony Bates Foundation Signs of Cardiac Arrest NO PULSE NO BREATHING Care for Cardiac Arrest Call CPR 911 and AED until ACLS equipment arrives Using an AED 1. 2. 3. 4. Confirm cardiac arrest (ABC’s) Do CPR until AED is ready Open the lid of the AED Attach the electrode pads to the chest 1. 5. 6. Dry and shave chest if necessary Let the AED analyze the rhythm Deliver a shock, if indicated Precautions….DO NOT: use alcohol pads to clean the chest touch victim while analyzing and defibrillating use in a moving vehicle, water, or on sheet metal use within 10 feet of cell phones use on children under the age of 8 use on someone wearing a nitroglycerine patch use near flammable materials Adult CPR Hand position Body position Compression depth….1.5-2 inches Compression rate….30 compressions in 20 seconds Cycle…30 compressions: 2 breaths ADULT CPR 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Check LOC Call 911 Open airway, check for breathing Give 2 slow breaths Check for circulation and severe bleeding Begin CPR by giving 30 compressions Then give 2 slow breaths Repeat cycles of 30 compressions and 2 breaths After 1 minute, re-check the pulse for 5 seconds Child CPR Hand position-1 hand Body position Compression depth…1-1.5 inches Compression rate…5 compressions in 3 seconds Cycle…30 compressions: 2 breath CHILD CPR 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Check LOC Call 911 Open airway and check for breathing Give 2 slow breaths Check for circulation and severe bleeding Begin CPR by giving 30 compressions Then give 2 breaths Repeat cycles of 30 compressions and 2 breaths After 1 minute, recheck pulse for 5 seconds INFANT CPR Hand position-nipple line, 2 fingers Body position Compression depth…1/2 to 1 inch Compression rate…5 compressions in about 3 seconds Cycle…5 compressions: 1 breath INFANT CPR 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Check LOC Call 911 Open airway and check for breathing Give 2 slow breaths Check for circulation and severe bleeding Begin CPR by giving 5 compressions Then give 1 breath Repeat cycles of 5 compressions and 1 breath After 1 minute, recheck pulse for 5 seconds When to stop CPR A person with higher training takes over EMS takes over Person’s heart starts beating The scene becomes unsafe An AED is being used If you are presented with a DNR order If you are too exhausted to continue