* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiac Emergencies
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
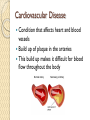
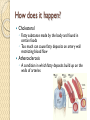
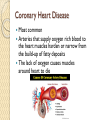
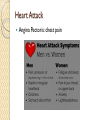
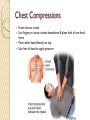
Cardiac Emergencies Chapter 7 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death for men & woman in the USA ~610,000 per year ◦ That’s 1 in every 4 deaths Cardiovascular Disease What puts you at higher risk? ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Diabetes Overweight Poor diet Physical inactivity Excessive alcohol use Cardiovascular Disease Condition that affects heart and blood vessels Build up of plaque in the arteries This build up makes it difficult for blood flow throughout the body How does it happen? Cholesterol ◦ Fatty substance made by the body and found in certain foods ◦ Too much can cause fatty deposits on artery wall restricting blood flow Atherosclerosis ◦ A condition in which fatty deposits build up on the walls of arteries Coronary Heart Disease Most common Arteries that supply oxygen rich blood to the heart muscles harden or narrow from the build-up of fatty deposits The lack of oxygen causes muscles around heart to die Cardiac Emergencies: Heart Attack Blood flow to some part of the heart muscle is compromised and the heart begins to die Heart will not be able to circulate blood effectively Heart Attack Angina Pectoris: chest pain Heart Attack: Care Send someone to call 9-1-1 Have victim stop what they are doing and rest Loosen any restrictive clothing Monitor victim closely until EMS arrives Be prepared to perform CPR or use Automated External Defibrillators (AED) if victim stops breathing Cardiac Emergencies: Cardiac Arrest Condition in which the heart stops beating Cardiac Arrest Heart stops beating Heart is beating too ineffectively to generate a pulse Causes: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Cardiovascular disease Drowning Suffocation Drugs Severe chest injuries Severe blood loss Stroke or other types of brain damage Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation CPR Cardio: Heart Pulmonary: Lungs CPR will artificially take over the function of the lungs & heart ◦ Can keep oxygenated blood flowing to the brain and other organs until advanced medical care can be given Increasing Chances of Survival Early recognition ◦ Calling 9-1-1 immediately Early CPR ◦ Keep oxygenated blood flowing Early defibrillation ◦ Electric shock that disrupts activity of the heart long enough to allow heart to spontaneously develop effective rhythm alone Early advanced medical care ◦ Getting victim to hospital quick CPR: Adult Showing no signs of life Check, Call, Care 2 rescue breaths, 30 chest compressions Chest Compressions Kneel next to victim Use fingers to locate victims breastbone & place heel of one hand there Place other hand directly on top Use heel of hand to apply pressure Chest Compressions Keep arms straight & lock elbows Compress only 1.5-2 inches Keep movements smoother, maintain a rhythm ◦ “One and two and three and four…” ◦ Bee Gees “Staying Alive” 30 chest compressions, 2 rescue breaths Children Infants Locate proper hand position; middle of chest like an adult Can use 1 hand technique with 1 hand on chest, 1 hand on forehead to maintain open airway Compress 1.5 inches 30 compressions to 2 breaths Imagine a line across the chest between nipples Pad of 2-3 fingers on that line; on sternum Compress ½-1 inch 30 compressions to 2 breaths CPR Children Infant CPR When to STOP Scene becomes unsafe Victim shows obvious signs of life AED is available and ready to use Another trained rescuer arrives and takes over You are too exhausted to continue