* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fraction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
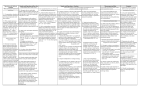
Chapter 2 Fractions Part 2 Day….. 1. Relating multiplication and division. 2. Dividing fractions by fractions, whole numbers, and mixed numbers 3. Creating real world problems involving the multiplication and division of fractions 4. Using models to solve problems involving the multiplication and division of fractions 5. Mid-unit recap Day 1 Bell Work Hakeem’s front porch measures 9 3/4 feet by 4 feet. Estimate the area of his front porch. Justify and illustrate your solution path. (Hint: Area = Length x Width) Vocabulary Denominator- the bottom number of a fraction (the whole) Equivalent- equal or the same Fraction- a number that represents part of a whole or part of a set Greatest Common Factor- the greatest of the common factors of two or more numbers Improper Fraction- a fraction with a numerator that is greater than or equal to the denominator Mixed Number- a number that has a whole number part and a fraction part Numerator- the top number of a fraction (the part) Product- the answer to a multiplication equation Quotient- the answer to a division equation Reciprocal – two numbers with a product of 1 (flipped upside down) Scaling- to increase or decrease a ratio Simplest Form- a fraction in which the GCF of the numerator and denominator is 1 Test Critiques Please your desk of everything except for a blue ink pen and your test. Today's Standard Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, create a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4) and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient; use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that (2/3) ÷ (3/4) = 8/9 because 3/4 of 8/9 is 2/3. (In general, (a/b) ÷ (c/d) = ad/bc.) How much chocolate will each person get if 3 people share 1/2 lb of chocolate equally? How many 3/4-cup servings are in 2/3 of a cup of yogurt? How wide is a rectangular strip of land with length 3/4 mi and area 1/2 square mi? Multiplying Fractions (Review) Essential Understanding: • To multiply a fraction by a fraction, you simply multiply the numerator by numerator, then the denominator by denominator. • To multiply a fraction by a whole number or a mixed number, you must first change the number to an improper fraction. Then, multiply numerator by numerator and denominator by denominator. • Write each product in simplest form. Examples: Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Exit Tickets Day 2 Bell Work Homework Critique Vocabulary Denominator- the bottom number of a fraction (the whole) Equivalent- equal or the same Fraction- a number that represents part of a whole or part of a set Greatest Common Factor- the greatest of the common factors of two or more numbers Improper Fraction- a fraction with a numerator that is greater than or equal to the denominator Mixed Number- a number that has a whole number part and a fraction part Numerator- the top number of a fraction (the part) Product- the answer to a multiplication equation Quotient- the answer to a division equation Reciprocal – two numbers with a product of 1 (flipped upside down) Scaling- to increase or decrease a ratio Simplest Form- a fraction in which the GCF of the numerator and denominator is 1 Today's Standard Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, create a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4) and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient; use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that (2/3) ÷ (3/4) = 8/9 because 3/4 of 8/9 is 2/3. (In general, (a/b) ÷ (c/d) = ad/bc.) How much chocolate will each person get if 3 people share 1/2 lb of chocolate equally? How many 3/4-cup servings are in 2/3 of a cup of yogurt? How wide is a rectangular strip of land with length 3/4 mi and area 1/2 square mi? Dividing Fractions Essential Understanding: There are two ways to divide fractions. One way is to create common denominators and divide. The second way is to find the reciprocal of the divisor, and multiply. •To divide fractions using common denominators… – You must first change all mixed numbers and/or whole numbers in to improper fractions. – Then, simply scale each fraction to the least common multiple to create common denominators. – Finally, divide the numerator of dividend (1st fraction) by the numerator of the divisor (2nd fraction) Examples: Dividing Fractions Essential Understanding: There are two ways to divide fractions. One way is to create common denominators and divide. The second way is to find the reciprocal of the divisor, and multiply. •To divide fractions using the reciprocal… –You must first change all mixed numbers and/or whole numbers in to improper fractions. – Next, find the reciprocal of the divisor. In other words, flip the second fraction. – Then, change the sign from division to multiplication. – Finally, multiply numerator by numerator and denominator by denominator. Examples: Think: Keep Change Flip Watch This • http://learnzillion.com/lessons/1323-solvedivision-of-fractions-problems-usingreciprocals Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Exit Tickets Day 3 Bell Work Sandy wants to split one-half of a pan of brownies between herself and three friends. How much of the pan of brownies will each person get? Homework Critique Vocabulary Denominator- the bottom number of a fraction (the whole) Equivalent- equal or the same Fraction- a number that represents part of a whole or part of a set Greatest Common Factor- the greatest of the common factors of two or more numbers Improper Fraction- a fraction with a numerator that is greater than or equal to the denominator Mixed Number- a number that has a whole number part and a fraction part Numerator- the top number of a fraction (the part) Product- the answer to a multiplication equation Quotient- the answer to a division equation Reciprocal – two numbers with a product of 1 (flipped upside down) Scaling- to increase or decrease a ratio Simplest Form- a fraction in which the GCF of the numerator and denominator is 1 Today's Standard Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, create a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4) and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient; use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that (2/3) ÷ (3/4) = 8/9 because 3/4 of 8/9 is 2/3. (In general, (a/b) ÷ (c/d) = ad/bc.) How much chocolate will each person get if 3 people share 1/2 lb of chocolate equally? How many 3/4-cup servings are in 2/3 of a cup of yogurt? How wide is a rectangular strip of land with length 3/4 mi and area 1/2 square mi? Story Problems Group Work Activity • Your group will be given a recipe. • Your job is to create , model, and solve 2 story problems using your recipe. (1 must be multiplication and 1 must be division) • You must work your problems out and include a separate answer key. • We will use these problems in class tomorrow, be ready to share. Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Exit Tickets Day 4 Bell Work Create a story problem for 6÷¼= Illustrate the solution Homework Critique Vocabulary Denominator- the bottom number of a fraction (the whole) Equivalent- equal or the same Fraction- a number that represents part of a whole or part of a set Greatest Common Factor- the greatest of the common factors of two or more numbers Improper Fraction- a fraction with a numerator that is greater than or equal to the denominator Mixed Number- a number that has a whole number part and a fraction part Numerator- the top number of a fraction (the part) Product- the answer to a multiplication equation Quotient- the answer to a division equation Reciprocal – two numbers with a product of 1 (flipped upside down) Scaling- to increase or decrease a ratio Simplest Form- a fraction in which the GCF of the numerator and denominator is 1 Today's Standard Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, create a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4) and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient; use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that (2/3) ÷ (3/4) = 8/9 because 3/4 of 8/9 is 2/3. (In general, (a/b) ÷ (c/d) = ad/bc.) How much chocolate will each person get if 3 people share 1/2 lb of chocolate equally? How many 3/4-cup servings are in 2/3 of a cup of yogurt? How wide is a rectangular strip of land with length 3/4 mi and area 1/2 square mi? Fraction Models Essential Understandings: Fractions are numbers used to represent part of a whole or part of a set. •You can show/solve fraction equations using models. Example: ¼ divided by ½ But first, you must know how to model different types of fractions. •You can model a part of a whole by using a single figure. Example: •You can model part of a set using multiple figures. Example: Modeling Fraction Equations Essential Understandings: Fractions equation models can be used to solve/prove… •Addition Equations Example: •Subtraction Equations Example: •Multiplication Equations Example: •Division Equations Example: Watch This • http://learnzillion.com/lessons/212-multiplyfractions-by-whole-numbers-using-bar-models • http://learnzillion.com/lessons/199-dividewhole-numbers-by-unit-fractions-using-visualmodels • http://learnzillion.com/lessons/1383-solveword-problems-involving-division-of-mixednumbers-and-fractions-using-picture-models Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Exit Tickets Day 5 Quick Quiz Please clear your desk of everything except for a pencil and a piece of scratch paper. Homework Critique Vocabulary Denominator- the bottom number of a fraction (the whole) Equivalent- equal or the same Fraction- a number that represents part of a whole or part of a set Greatest Common Factor- the greatest of the common factors of two or more numbers Improper Fraction- a fraction with a numerator that is greater than or equal to the denominator Mixed Number- a number that has a whole number part and a fraction part Numerator- the top number of a fraction (the part) Product- the answer to a multiplication equation Quotient- the answer to a division equation Reciprocal – two numbers with a product of 1 (flipped upside down) Scaling- to increase or decrease a ratio Simplest Form- a fraction in which the GCF of the numerator and denominator is 1 Today's Standard Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, create a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4) and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient; use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that (2/3) ÷ (3/4) = 8/9 because 3/4 of 8/9 is 2/3. (In general, (a/b) ÷ (c/d) = ad/bc.) How much chocolate will each person get if 3 people share 1/2 lb of chocolate equally? How many 3/4-cup servings are in 2/3 of a cup of yogurt? How wide is a rectangular strip of land with length 3/4 mi and area 1/2 square mi? Chapter Review Math Time Technology: PowerSchool Practice Items Independent: Provided Page My Choice: Try Something New! Extension: Options have been posted. Wrap it Up • Review • Questions • Quiz