* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physical Science Nuclear Decay: Alpha and Beta
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
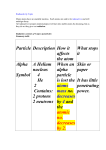
Physical Science Nuclear Decay: Alpha and Beta Particles Introduction There are over 100 different types of atoms. Some of these atoms are very unstable. Over time, the nucleus of an unstable atom will lose energy by emitting various particles spontaneously. This process is called nuclear decay. There are different types of nuclear decay, including alpha and beta decay. There are two different types of beta decay: beta minus (β–) decay and beta plus (β+) decay. Some scientists refer to beta minus decay simply as beta decay, for convenience. This activity only deals with this type of beta decay. In this activity, you will determine the differences in the charge and mass of alpha and beta minus (β–) particles and how their emission affects atoms. Analysis 1. Alpha Particles a. What is the mass number of an alpha particle? b. What is the identity of an alpha particle? c. What kind of charge does an alpha particle have? © 2014 Connections Education LLC. All rights reserved. 2. Beta Particles a. What is the mass number of the particle emitted from the nucleus during beta minus (β–) decay? b. What kind of charge does the particle emitted from the nucleus during beta minus (β–) decay have? c. What is another name for a beta minus (β–) particle? 3. Nuclear Decay a. What happens in the nucleus of an atom when an alpha particle is emitted? b. What happens in the nucleus of an atom when a beta particle is emitted? Drawing Conclusions 4. The helium used to fill birthday balloons doesn’t come out of the air, but from out of the ground. Some of the gas might escape from the ground into the atmosphere, but the majority of it is trapped in Earth’s crust. Based on what you have learned in today’s lab, give a reasonable explanation for the presence of helium gas in Earth’s crust. © 2014 Connections Education LLC. All rights reserved. 5. Why should it take significantly more energy to move a beam of alpha particles than a beam of beta minus (β–) particles? 6. What daughter product is produced when thallium–206, an isotope of thallium, undergoes beta minus (β–) decay? © 2014 Connections Education LLC. All rights reserved.