* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download C 6
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Yang–Mills theory wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
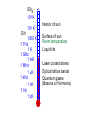
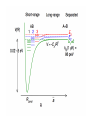
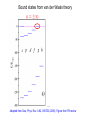
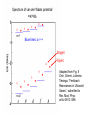
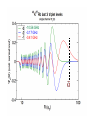
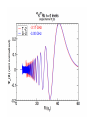
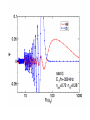
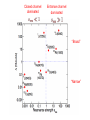
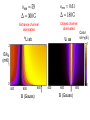
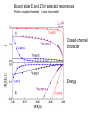
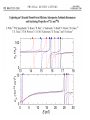
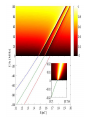
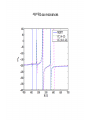
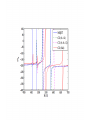
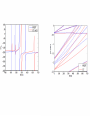
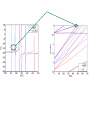
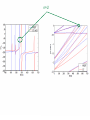
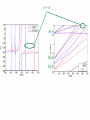
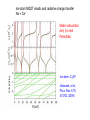
EuroQUAM satellite meeting, University of Durham, April 18, 2009 Understanding Feshbach molecules with long range quantum defect theory Paul S. Julienne Joint Quantum Institute, NIST and The University of Maryland Collaborators (theory) Tom Hanna, Eite Tiesinga (NIST) Thanks also to Bo Gao (U. of Toledo) and Cheng Chin (U. Chicago) J. K. Freericks (Georgetown U.), M. Maśka (U. Silesia), R. Lemański (Wroclaw) Outline 1. Sone general considerations 2. The significance of the long-range potential 0812.1486, Feshbach review 0902.1727, Book chapter 0903.0884, MQDT treatment LiK, KRb 3. Long-range potential + quantum defect theory for atom-atom collisions Can we get simple, practical models? E/kB 109 K 106 K E/h 1000 K 1 THz 1K 1 GHz 1 mK 1 MHz 1 K 1 kHz 1 nK 1 Hz 1 pK Interior of sun Surface of sun Room temperature Liquid He Laser cooled atoms Optical lattice bands Quantum gases (Bosons or Fermions) Ultracold polar molecules are now with us 3. Population transfer STIRAP 1. Atom preparation 100 kHz 100 THz 2. Atom Association weakly bound pair Kohler et al, Rev. Mod. Phys. 4. Polar molecules 78, 1311 (2006) Dipolar gases, lattices Chin, et al, arXiv: 0812.1496 Short range Long range Separated atoms A+B AB 1 eV 10-10 eV (1 K) 10-4 eV (E) scattering phase Y _ a (E) bound state phase (Ei)=n at eigenvalue -C6/R6 “Core” independent of E ≈ 0 Analytic long-range theory (B. Gao) Properties of separated species “simple” Resonance scattering S-matrix theory of molecular collisions F. H. Mies, J. Chem. Phys. 51, 787, 798 (1969) where 3 2 where h 1 3 T QT 2 k T B QT = translational partition function T = thermal de Broglie wavelength of pair Replace Phase Time Dynamics Space scale density for elastic collisions Bound states from van der Waals theory Adapted from Gao, Phys. Rev. A 62, 050702 (2000); Figure from FB review Spectrum of van der Waals potential 40K87Rb Blue lines: a = ∞ Singlet Triplet Adapted from Fig. 8 Chin, Grimm, Julienne, Tiesinga, “Feshbach Resonances in Ultracold Gases”, submitted to Rev. Mod. Phys. arXiv:0813.1496 -10.56 GHz -3.17 GHz -0.41 GHz -3.17 GHz -3.00 GHz Goal: Simple, reliable model for classification and calculation * Now: Full quantum dynamics with CC calculations All degrees of freedom with real potentials Exact, but not simple * vdW-MQDT: Reduction to a simpler representation Parameterized by C6 van der Waals coefficient reduced mass abg “background” scattering length resonance width B0 singularity in a(B) magnetic moment difference vdW Energy scale Use vdW solutions for MQDT analysis Analytic properties of (R,E) across thresholds (E) and between short and long range (R) Generalized Multichannel Quantum Defect Theory (MQDT): F. H. Mies, J. Chem. Phys. 80, 2514 (1984) F. H. Mies and P. S. Julienne, J. Chem. Phys. 80, 2526 (1984) Ultracold: Eindhoven (Verhaar group), JILA (Greene, Bohn) P. S. Julienne and F. H. Mies, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 6, 2257 (1989) F. H. Mies and M. Raoult, Phys. Rev. A 62, 012708 (2000) P. S. Julienne and B. Gao, in Atomic Physics 20, ed. by C. Roos, H. Haffner, and R. Blatt (2006) (physics/0609013) Analytic solutions for -C6/R6 van der Waals potential B. Gao, Phys. Rev. A 58, 1728, 4222 (1998) Also 1999, 2000, 2001, 2004, 2005 Solely a function of C6, reduced mass , and scattering length a For coupled channels case Given the reference the single-channel functions: for scattering (E>0) (E), C(E), tan (E) and bound states (E<0) (E) From vdW theory, given C6, , a MQDT theory (1984) gives coupled channels S-matrix and bound states. Assume a single isolated resonance weakly coupled to the continuum Yc,bg <<1, Ycc = -Ybg,bg = 0 Bound states Scattering states Classification of resonances by strength, arXiv:0812.1496 Resonance strength See Kohler et al, Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 1311 (2006) For magnetically tunable resonances: Bound state E=0 shifts to Bound state norm Z as E → 0 Closed channel dominated Entrance channel dominated “Broad” “Narrow” Closed channel dominated Entrance channel dominated 6Li 7Li ab aa Color: sin2(E) 1 2 E/kB (mK) 1 0 400 600 B (Gauss) 800 400 600 B (Gauss) 800 0 Two-channel “box” model Corresponds to vdW MQDT when “box” width is chosen to be Bound state equation for level with binding energy with Bound state E and Z for selected resonances Points: coupled channels Lines: box model Closed-channel character Energy Can we get simple models for bound and scattering states? Use vdW solutions for MQDT treatment Ingredients: Atomic hyperfine/Zeeman properties Atomic-molecule basis set frame transformation Van der Waals coefficient C6 S, T scattering lengths 3 AND ONLY 3 free parameters arXiv: 0903.0884 Fit 9 s-wave measured resonances in 6Li40K from E. Wille, F. M. Spiegelhalder, G. Kerner, D. Naik, A. Trenkwalder, G. Hendl, F. Schreck, R. Grimm, T. G. Tiecke, J. T. M. Walraven, et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 053201 (2008). To about 2 per cent accuracy (3 G) 40K87Rb aa resonances n=-2 n = -3 A(-1) B(-2) D(-3) Ion-atom MQDT elastic and radiative charge transfer Na + Ca+ Model calculation only (no real Potentials) Ion-atom -C4/R4: Idziaszek, et al., Phys. Rev. A 79, 010702 (2009) “Universal” van der Waals inelasticity Chemistry Long range Asymptotic Reflect A+B Lost Cold species prepared Scatter off long-range potential Assume unit probability of inelastic event at small R Transmit Reflect “Universal” van der Waals model Applied to RbCs molecular quenching by Hudson, Gilfoy, Kotochigova, Sage, and De Mille, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 203201 (2008)