* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Arrays, Factors, and Number Theory
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
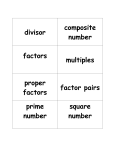
Arrays, Factors, and Number Theory Unit 2: Fun and Games Grade Level 6th grade Overview Students will work to find the arrays of numbers 1-20 and how factors and fact families are used to create the arrays. Students will also analyze number theory properties such as prime, composite, even, odd, and square numbers. Key Standards M6N1. Students will understand the meaning of the four arithmetic operations as related to positive rational numbers and will use these concepts to solve problems. a. Apply factors and multiples. M6P1. Students will solve problems (using appropriate technology). a. Build new mathematical knowledge through problem solving. b. Solve problems that arise in mathematics and in other contexts. c. Apply and adapt a variety if appropriate strategies to solve problems. d. Monitor and reflect on the process of mathematical problem solving. M6P2. Students will reason and evaluate mathematical arguments. c. Develop and evaluate mathematical arguments and proofs. d. Select and use various types of reasoning and methods of proof. M6P3. Students will communicate mathematically. a. Organize and consolidate their mathematical thinking through communication. b. Communicate their mathematical thinking coherently and clearly to peers teachers and others. c. Use the language of mathematics to express mathematical ideas precisely. M6P5. Students will represent mathematics in multiple ways. a. Create and use representations to organize, record, and communicate mathematical ideas. b. Select, apply and translate among mathematical representations to solve problems. c. Use representations to model and interpret physical, social, and mathematical phenomena. Possible Materials • • • • • • • • • 2 cm grid paper chart paper scissors ruler markers copy paper pencil rubric Arrays, Factors, and Number Theory checklist Task Create, draw, and shade all possible arrays for the numbers 1-20. a. Label all of the dimensions of the arrays, which are the factors of each number. b. Look for patterns in the arrangements, factors, or drawings. c. Describe the patterns or observations that help you “see” the factors, prime numbers, composite numbers and square numbers. d. In the numbers 1-20, label the prime, composite and square numbers. e. Describe all of the things you notice about the arrays and patterns, but especially discuss what you notice about the number 1. Sample Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. When or why would it be useful to know the factors of a number? When or why would it be useful to know the multiples of a number? What features does a number have if the number is prime? What role does the number 1 have when you are finding factors of any number? How are multiplication and division related? How are factors and multiples related to multiplication and division? How do I know if a number is even or odd? Composite or prime? Square? Sample Question Solutions 1. It is useful to know the factors of numbers because multiplication is the foundation of mathematics. 2. It is useful to know the multiples of a number when you are finding the least common multiple of a number. 3. One feature of a prime number is its factors are one and itself. 4. The number 1 is a factor of every number. 5. Multiplication and division are related because multiplication is the inverse of division and vice versa. 6. Factors and multiples are related in multiplication and division because factors are the fact families that are used to find the product or quotient. 7. A number is even if it is divisible by 2. An odd number is NOT divisible by 2. A composite number has more than 2 factors, and a prime number has only two factors, one and itself. 16 is a square number because its multiplier and multiplicand are 4. Example: 4 x 4 = 16. Assessment Ideas This task has a teacher-made assessment aligned to the standards as well as a checklist so that students know exactly what is expected of them. Example rubric and checklist included.