* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychotherapies Notes - San Elijo Elementary School
Gestalt therapy wikipedia , lookup
Primal therapy wikipedia , lookup
Albert Ellis wikipedia , lookup
Professional practice of behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Methods of neuro-linguistic programming wikipedia , lookup
Dance therapy wikipedia , lookup
Intensive short-term dynamic psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Chelation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dodo bird verdict wikipedia , lookup
Behaviour therapy wikipedia , lookup
Conversion therapy wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
The Radical Therapist wikipedia , lookup
Emotionally focused therapy wikipedia , lookup
Relationship counseling wikipedia , lookup
Reality therapy wikipedia , lookup
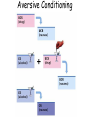
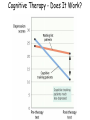
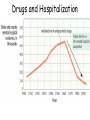
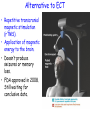
Psychological Therapies Psychotherapy • An interaction between a trained therapist and someone suffering from psychological difficulties. Eclectic Approach • Therapy where the therapist combines techniques from different schools of psychology. Kind of like a buffet. Psychoanalysis • Freud's therapy. • Use free association, hypnosis and dream interpretation to gain insight into the client’s unconscious. Psychoanalytic Methods • Psychotherapists use their techniques to overcome resistance (the blocking from consciousness of anxiety-laden material) by the client. •The psychoanalyst wants you to become aware of the resistance and together interpret it’s underlying meaning to gain self-insight. Transference • In psychoanalysis, the patient transfers to the analyst emotions linked with other relationships. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b02H0dW2xf8 Humanistic Therapy • Focuses on people’s potential for selffulfillment (selfactualization). • Focuses on the present and future. • Focuses on conscious thoughts (not unconscious ones). • Take responsibility for you actions. Client (Person) Centered Therapy • Developed by Carl Rogers. • Therapist should use genuineness, acceptance and empathy to show unconditional positive regard towards their clients. • Most widely used Humanistic technique. Active Listening • Central to Roger’s client-centered therapy. • Empathetic listening where the listener echoes, restates and clarifies. Behavior Therapies • Therapy that applies learning principles to the elimination of unwanted behaviors. •The behaviors are the problems - so we must change the behaviors. Classical Conditioning Techniques Counterconditioning: • A behavioral therapy that conditions new responses to stimuli that trigger unwanted behaviors. Two Types: Exposure Therapies & Aversive Conditioning 1. Exposure Therapies • Systematic desensitization is a type of counterconditioning that associates a pleasant relaxed state with gradually increasing anxiety-triggering stimuli. (i.e. phobias) How would I use systematic desensitization to reduce my fear of old women? Systematic Desensitization uses… progressive relaxation versus Flooding which… exposes you to an anxiety-provoking situation at the highest level of fear all at once. Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy 2. Aversive Conditioning • A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state with an unwanted behavior. How would putting peppers on the fingernails of a nail biter effect their behavior? Aversive Conditioning Operant Conditioning Token Economy: an operant conditioning procedure that rewards a desired behavior. A patient exchanges a token of some sort (earned by exhibiting the desired behavior) for various privileges or treats. Cognitive Therapy Aaron Beck’s Cognitive Therapy • Noticed that depressed people were similar in the way they viewed the world. • Used cognitive therapy get people to take off the “dark sunglasses” in which they view their surroundings Cognitive Therapy • Cognitive therapists try to teach people new, more constructive ways of thinking. Is .300 a good or bad batting average? Cognitive Therapy Albert Ellis & Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT) • Focuses on uncovering irrational beliefs which may lead to unhealthy negative emotions and replacing them with more productive rational alternatives. Stress Inoculation Training • Teaches people to restructure their thinking in stressful situations. • Basically changing your self-talk. • Like when you’re nervous and negative before a big exam. Cognitive Therapy - Does It Work? Group & Family Therapies Biomedical Therapies Therapies aimed at the altering the body chemistry. Psychopharmacology • The study of the effects of drugs on mind and behavior. Drugs and Hospitalization Emptying of Mental Hospitals Testing New Drugs • When a new drug is released there is always too much enthusiasm. •Must use a double-blind procedure to combat placebo and experimental effects. Types of drugs include: Antipsychotic Drugs • Medicines used to treat psychosis - typically in schizophrenia and bipolar patients. • Thorazine although effective often has powerful side effects. • Tardive dyskinesia – neurotoxic effect involving involuntary movements of the facial muscles, tongue, and limbs. Antianxiety Drugs • Anxiolytic drugs like Valium, Librium, and Xanax. • Like alcohol, they depress nervous system activity. • Most widely abused drugs. Antidepressant Drugs • Lift you up out of depression. • Most increase the availability of norepinephrine or serotonin. • Prozac, Paxil & Zoloft are known as SSRI’s (selective-serotoninreuptake-inhibitors). They block serotonin reuptake. • Lithium is an effective mood stabilizer used by those with bipolar disorder. Prozac, Paxil & Zoloft Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) • Biomedical therapy for severely depressed patients in which a brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient causing a mild seizure. • Usually produces temporary memory loss. • But has been very effective of temporarily ridding people of suicidal thoughts. Alternative to ECT • Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). • Application of magnetic energy to the brain. • Doesn’t produce seizures or memory loss. • FDA approved in 2008. Still waiting for conclusive data. Psychosurgery • Egas Moniz developed the lobotomy and it became very popular in the 1940’s and 50’s. • Surgery that removes or destroys frontal lobe brain tissue in an effort to change behavior. • Ice pick like instrument through the eye sockets cutting the links between the frontal lobes and the emotional control centers. Lobotomy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_0aNILW6ILk