* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download parallel circuit +
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Residual-current device wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
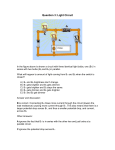
REMINDER: Complete the online attitude survey IMMEDIATELY if you have not already done so; it closes TODAY TODAY’S OUTCOMES: ELECTRICITY - Discuss the differences between series and parallel circuits - Introduce the concept of resistance - Conclude our hands-on study of electricity with construction of a complex circuit GRADING OF PARALLEL CIRCUITS 5 points: 5 points: 10. The circuit for the lights in a house resembles the circuit drawn at right. The bulbs are all in parallel. What are the advantages of wiring them this way, instead of putting them in series? 1) In a series circuit, if one electrical device (bulb) is turned off, ALL the devices (bulbs) go off, because the circuit is broken this would not be good in a house! 2) In a series circuit, the brightest of the bulbs depends on the number of bulbs, but in a parallel circuit the brightness stays the same .* * Brightness might change SLIGHTLY in a parallel circuit if there is a large change in the current drawn from the power source, but the change is generally small for a good battery or power source. 11. Terry claims there is another advantage: the additional light bulbs don’t cost anything to operate. He argues that the light bulbs are independent of each other, and so there is no way for the power company to know how many are turned on. Paula says there is a way for the power company to tell when a light bulb is turned on. Please explain who is right. Paula is correct - the power used is higher if more light bulbs are turned on. If more bulbs are lit, with the same brightness, then more current flows from the power source, and POWER increases with CURRENT. IMPORTANT: Current is the same at all points in a SERIES circuit; this is NOT true in a PARALLEL circuit. all CURRENT IN SERIES CIRCUITS bulbs(assume are identical) 3 volts D C 3 volts J A B E F H G Currents through A, B, C, and D are all equal Currents through E, F, G, H and J are all equal 1) Current is the same at all points in a SERIES circuit. Currents in the left diagram are GREATER THAN the currents in the right diagram 2) Adding more devices/bulbs in SERIES reduces the current. Bulbs dimmer in right diagram CURRENT IN PARALLEL CIRCUITS 3 volts 3 volts A D (assume all bulbs are identical) E J B F C G Bulbs are (almost) the same brightness in both diagrams H Currents through A, B, C, and D are NOT all equal The current splits at the green points ; so the current through A or D is the SUM of the currents through B and C Current A = Current D = Current B + Current C Currents through E, F, G, H and J are NOT all equal The current through E or J is the SUM of the currents through F, G, H Current E = Current J = Current F + Current G + Current H CURRENT IN PARALLEL CIRCUITS 3 volts 3 volts A D (assume all bulbs are identical) E J B F C G Bulbs are (almost) the same brightness in both diagrams H 1) Current is NOT the same at all points in a PARALLEL circuit, and is highest in the wires leading to and from the power source 2) Adding more devices/bulbs in PARALLEL increases the current at the power source. IS THERE A LIMIT TO HOW MANY DEVICES YOU CAN HOOK UP IN PARALLEL? No - but remember: The CURRENT near the power source keeps going up when you add more! CONSEQUENCES OF INCREASING THE CURRENT TOO HIGH: Power use goes up Too much power HEAT In a house, this blows a fuse or trips circuit breaker SIPHON ANALOGIES SERIES CIRCUIT = devices or bulbs + – PARALLEL CIRCUIT Flow rate highest nearest to source, before the tube branches off = devices or bulbs three outlets pull more water from the source than one + – 9. Susan made an extra bright flashlight. It has two batteries (like most flashlights) but three light bulbs. It gives off three times as much light, but the batteries don't last very long. Here is a diagram of Susan's flashlight. Explain how the concepts voltage, current, power, and energy are involved in this device; by the time you are done, you should have completely explained the sentence, " It gives off three times as much light, but the batteries don't last very long. " Adding extra bulbs in parallel to a common voltage increases the current drawn from the batteries, and thus the power used, which increases total brightness. A higher power flashlight increases the rate at which energy is used, depleting the batteries faster. WHAT YOU ARE EXPECTED TO KNOW: - How series and parallel circuits are different - What happens in a parallel circuit when more elements are added - Where the current is greatest in a parallel circuit and why TODAY IS THE LAST ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT LAB; MONDAY WE CONTINUE WITH NEXT UNIT TEST ON ELECTRICITY: OPEN NOTE NEXT FRIDAY 9/16/11 Study materials between now and then: 1) Reading assignment on electrical safety at end of today’s lab (read by Monday) 2) Test practice problems and review sheet (to be handed out Monday) TODAY’S OUTCOMES: ELECTRICITY - Discuss the differences between series and parallel circuits✓ - Introduce the concept of resistance - Conclude our hands-on study of electricity with construction of a complex circuit