* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 03 Motor Symptoms PD SLIDES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
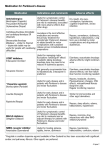
Management of Parkinson‟s disease Treatment of motor symptoms Learning Objectives • List the common medications used to treat the motor symptoms of Parkinson‟s disease and the adverse effects associated with their use • Demonstrate an understanding of the treatment pathways for early and advanced disease • Describe the role of non-pharmacological and complementary treatment in disease management Pharmacological treatment • Aim to improve motor and non-motor symptoms • Individually tailor medication • Medication aims to: – increase level of available dopamine in the brain – stimulate parts of the brain where dopamine works – block the action of other chemicals that affect dopamine • As disease progresses number of medications needed will increase and adjustments become more common When to start drug treatment • Based on: – age of patient – severity of symptoms – likelihood of adherence – cognitive impairment – co-morbidities – patient wishes Levodopa Low levels of dopamine makes movement difficult Levodopa is converted into dopamine in the brain and gut Levodopa increases the level of dopamine in the brain allowing movement to be restored. 5 Levodopa – dosing and dose forms Form Immediate release Name Sinemet, Madopar, Kinson, Levo/Carbidopa Controlled release (CR) Sinemet CR Dispersible tablets Madopar Rapid Gel (intestinal) Duodopa Combined with COMT Stalevo Levodopa – adverse effects Adverse effects How to combat them Nausea and vomiting May require an antiemetic e.g domperidone (Motilium) Constipation Alteration to diet; laxative use Hypotension ( low blood pressure) Stand up and change position slowly to avoid falling Increased lethargy Involvement in a balanced activity/rest program Nightmares/hallucinations/ confusion May require some medication adjustment Dyskinesia (involuntary movements) usually associated with long term use May require some medication adjustment and/or additional medication Prolonged use of levodopa Fluctuations Dyskinesias • • • • Wearing OFF Delayed ON ON-OFF swings Freezing • Involuntary erratic movements affecting the face, arms, legs and trunk Dopamine agonists Dopamine agonists Apomine (apomorphine hydrochloride) Cabaser; Bergoline (cabergoline) Neupro (rotigotine) Permax (pergolide mesylate) Parlodel ; Kripton (bromocriptine mesylate) Sifrol (pramipexole) Action Mimic the action of Dopamine in the brain making movement easier Use Early stages of PD – Monotherapy as less likely to cause dyskinesias than Levodopa Later stages of PD - Additional treatment with levodopa Dosage forms Extended release tablets, transdermal patch, subcutaneous injection or continuous subcutaneous infusion Adverse effects Nausea, hallucinations, sedation, light headedness, compulsive behaviours MAO-B inhibitors MAO-B inhibitors Selegiline hydrochloride (Selgene, Eldepryl ) Action Inhibits enzyme responsible for dopamine metabolism, leading to elevated dopamine levels in the brain Use Early stage of PD - delay the need for levodopa although rarely used alone Later stage of PD - to boost the effects of levodopa and prevent “wearing off” Dosage form tablet Adverse effects Insomnia, hallucinations and jitteriness COMT inhibitors COMT inhibitors Entacapone (Comtan )– taken with Levodopa Levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone (Stalevo) Action Increases amount of Levodopa entering the brain by preventing metabolism in the periphery Use Given with Levodopa; helps with the problem of „wearing off‟. Dosage form Tablet 200mg Adverse effects Vivid dreams, hallucinations, sleep disturbances, daytime drowsiness, headaches and dyskinesias; discolouration of body fluids (bright yellow/orange) and diarrhoea Anticholinergics Anticholinergics Benzhexol hydrochloride (Artane) Benztropine mesylate (Cogentin) Biperiden hydrochloride (Akineton) Orphenadrine (Norflex) Action Correct the imbalance between two neurotransmitters in the brain, dopamine and acetylcholine Use Useful in the treatment of tremor but may also address bradykinesia, rigidity and sialorrhea in the younger people with PD Dosage form Tablet Adverse effects Dry mouth, urinary retention, blurred vision and confusion (especially in the older people with PD) Amantadine Amantadine Amantadine hydrochloride (Symmetrel ) Action Increases dopamine release and blocks cholinergic receptors Use Used as an additional treatment to levodopa; useful in reducing dyskinesias (abnormal movements) Dosage form Capsules Adverse effects Insomnia, confusion and a mottled rash on the lower limbs. Long term treatment of PD Early PD • Diagnosis • Monotherapy based on patient factors i.e. Dopamine agonist Therapy adjustments • Addition of levodopa therapy to enhance symptom control • Adjunctive therapy with MAO-inhibitor Advanced PD • Treatment of non-motor symptoms • COMTinhibitor added to reduce levodopa motor complications 14 Complementary treatment • • • • • Creatinine Vitamins C and E Vitamin D Vitamins B6,B12 and folate Coenzyme Q10 Non-drug treatments • • • • Regular exercise Balanced diet Speech therapy Intervention by occupational therapists • Education and counselling Surgical options • Thalamotomy • Pallidotomy • Deep brain stimulation What a patient needs to know • • • • • What the medication is for? What benefits should be expected? Possible side effects and their management Drug interactions Detailed drug record Case study • Admitted to ACF – Sinemet 275mg tds • Poorly controlled PD; hallucinations; falls • PD was reviewed by neurologist • Sinemet reduced to 62.5mg tds with the use of the controlled release formulation at night. Summary • All patients with PD will ultimately require pharmacotherapy • Aim of treatment of motor symptoms is to restore dopamine levels • Treatment choice will depend on age, symptoms, comorbidities and patient wishes • As disease progresses the number of medications and adjustments required will increase • It is extremely important that medications are managed well and given on time to reduce motor symptoms 20