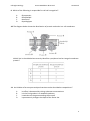
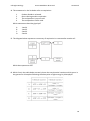
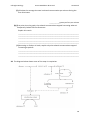
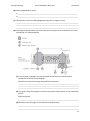
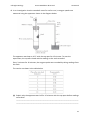
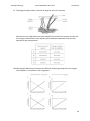
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 Homework Booklet [pdf 5MB]
Survey
Document related concepts
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Curriculum for Excellence Higher Biology Name: _________________________ Key Area 2.1. Metabolism pathways and their control 2.2. Cellular respiration 2.3. Metabolic rate 2.4. Metabolism in conformers and regulators 2.5. Metabolism and adverse conditions 2.6. Environmental control of metabolism 2.7. Genetic control of metabolism Feedback Mark CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Key Area 2.1 1. In the condition phenylketonuria (PKU), the human body is unable to A B C D synthesise phenylalanine from tyrosine secrete phenylalanine from cells absorb phenylalanine into the bloodstream convert phenylalanine to tyrosine. 2. The following sentences give information about the plasma membrane of beetroot cells. Underline one alternative in each pair to make the sentences correct. The plasma membrane contains (cellulose/protein) and (phospholipids/carbohydrates) and has a (fibrous/porous) nature. As a result, the membrane is (fully/selectively) permeable. 3. Membranes can form small compartments within cells. Small compartments have A B C D high surface to volume ratios and allow low concentrations of substrates inside high surface to volume ratios and allow high concentrations of substrates inside low surface to volume ratios and allow low concentrations of substrates inside low surface to volume ratios and allow high concentrations of substrates inside. 4. The sodium–potassium pump spans the plasma membrane. Various processes involved in the active transport of sodium and potassium ions take place either inside the cell (intracellular) or outside the cell (extracellular). Which line in the table correctly applies to the transport of potassium ions? 2 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 5. The graph below shows the effect of substrate concentration on the rate of an enzymecatalysed reaction. At which substrate concentration is the reaction rate equal to 75% of the maximum rate? A B C D 5 units 8 units 12 units 15 units 6. The reaction below is part of a metabolic pathway in cells. amino acids polypeptide Which line in the table below correctly identifies the type of reaction and whether it releases or takes up energy? 3 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 7. The graph below shows the mass of product resulting from an enzyme controlled reaction. What is the initial rate of reaction? A B C D 0·53 mg s−1 0·63 mg s−1 0·89 mg s−1 1·60 mg s−1 8. The table below shows the results of an investigation into the effects of varying substrate concentration on the activity of the enzyme phosphatase in the presence of inhibitors. The greater the absorbance the more active the enzyme. What valid conclusion can be drawn from the results? A B C D An increase in substrate concentration reduces the effect of all three inhibitors. All three inhibitors are competitive inhibitors. Inhibitor Z has least effect on enzyme activity. Inhibitor Y has least effect on enzyme activity. 4 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 9. Which of the following is responsible for cell-cell recognition? A B C D Glycoprotein Phospholipid Hormones Peptidoglycan 10. The diagram below shows the distribution of protein molecules in a cell membrane. Which line in the table below correctly identifies a peripheral and an integral membrane protein? 11. An inhibitor of an enzyme-catalysed reaction can be described as competitive if A B C D its effect is decreased by raising substrate concentrations it is the final product in a metabolic pathway it switches off the gene encoding the enzyme it permanently changes the shape of the active site. 5 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 12. Liver tissue contains an enzyme which breaks down alcohol. The graph below shows the effect of different concentrations of copper ions on the breakdown of alcohol by this enzyme over a 30 minute period. Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from the graph? A B C D 4·5 mM copper has no effect on enzyme activity. 2·5 mM copper halves the enzyme activity. 0·5 mM copper completely inhibits enzyme activity. Enzyme activity increases when copper concentration is increased from 1 mM to 2 mM. 13. The diagram below shows a metabolic pathway that is controlled by end product inhibition. For Substance 4 to bring about end product inhibition, which of the following will it interact with? A B C D Substance 1 Substance 3 Enzyme 1 Enzyme 3 6 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 14. The diagram below shows an enzyme-catalysed reaction. Which of the following correctly identifies molecule P? A B C D Substrate Activator Competitive inhibitor Non-competitive inhibitor 7 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 15. Phenylalanine and tyrosine are amino acids produced from the digestion of protein in the human diet. Once absorbed, they are involved in the metabolic pathway shown below. The condition phenylketonuria (PKU) can be caused by the absence of enzyme 1. (a) Describe what leads to the absence of enzyme 1 in this condition. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ (b) Explain why individuals with PKU still develop some pigment in their skin. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ (c) State the role of thyroxine in the human body. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 16. The diagram below shows a section of plasma membrane with proteins labelled A to E. (a) Identify which of the proteins A to E are integral membrane proteins. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (b) Which type of signalling molecule requires a receptor protein at the cell surface? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 8 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 17. Catechol oxidase is an enzyme found in apple tissue. It is involved in the reaction which produces the brown pigment that forms in cut or damaged apples. The effect of the concentration of lead ethanoate on this reaction was investigated. 10 g of apple tissue was cut up, added to 10cm3 of distilled water and then liquidised and filtered. This produced an extract containing both catechol and catechol oxidase. Test tubes were set up as described in Table 1 and kept at 20 ºC in a water bath. Every 10 minutes, the tubes were placed in a colorimeter which measured how much brown pigment was present. The more brown pigment present the higher the colorimeter reading. The results are shown in Table 2. 9 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (a) (i) Identify two variables not already mentioned that would have to be kept constant. 1 ____________________________________________________________________ 2 ____________________________________________________________________ (ii) Describe how tube A acts as a control in this investigation. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (b) Explain why the initial colorimeter readings were not 0.0 units. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (c) The results for the extract with 0.1% lead ethanoate are shown in the graph below. Use information from Table 2 to complete the graph by: (i) adding the scale and label to each axis; (ii) presenting the results for the extract + 0.01% lead ethanoate solution and labelling the line. (d) State the effect of the concentration of lead ethanoate solution on the activity of catechol oxidase. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (e) The experiment was repeated with the 0.1% lead ethanoate solution at 60 °C. Predict the colorimeter reading at 10 minutes and justify your answer. Prediction _____________ units Justification _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 10 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 18. Cholesterol is an important component of cell membranes and a starter molecule in the formation of steroid hormones. (a) Give one role of cholesterol in cell membranes. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (b) When cholesterol accumulates in the wall of an artery, the plaque that forms reduces the internal diameter of the vessel. Plaque formation (atherosclerosis) is a major cause of heart disease. Statins are taken to reduce blood cholesterol and are one of the most commonly prescribed medications. Cholesterol is synthesised by cells in a sequence of steps starting with acetyl-CoA from the Krebs cycle. The step that limits the rate of production is near the start and is catalysed by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, as illustrated below. (i) In this pathway, a form of end-product inhibition occurs in which increasing cholesterol promotes the destruction of HMG-CoA reductase. Describe how end-product inhibition would be achieved if the enzyme was allosteric. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (ii) Statins are competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. Explain how they would reduce cholesterol formation. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 11 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (iii) The graph below shows results of an experiment done in 1976 on three forms of a substance, ML-236, extracted from a fungal culture. The experiment was assessing how well these substances inhibit cholesterol formation, the key requirement for a potential statin. Use data for 50% inhibition to compare the effectiveness of the three molecules as potential statins. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 19. Describe the control of enzyme activity by competitive and non-competitive inhibitors. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 12 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 20. Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rate of enzyme-catalysed reactions. The graph below shows the rates of the reaction for the enzyme penicillinase over a range of substrate concentrations. The substrate is penicillin. The Michaelis constant (Km) of an enzyme is the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half its maximum rate. (a) Calculate the Km of penicillinase assuming the graph shows that the maximum rate has been reached. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ (b) Explain why the Km of an enzyme increases when a competitive inhibitor is present. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ (c) The turnover number of an enzyme is the number of substrate molecules converted into product by an enzyme in one second when an enzyme is working at its maximum rate. The turnover number for penicillinase is 2000 per second. Calculate the time taken to catalyse the breakdown of one penicillin molecule. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 13 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 21. Write notes on: (a) structure of the plasma membrane; (b) function of the plasma membrane in active transport; (c) structure and function of the cell wall. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 14 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 22. Give an account of proteins in the following contexts: (a) membranes; (b) cell signalling; (c) cytoskeleton. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 15 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 23. Give an account of enzyme action and enzyme inhibition. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 16 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Key Area 2.2 1. Which of the following must be present in a living cell for glycolysis to occur? A B C D Glucose and ATP Pyruvic acid and oxygen Glucose and oxygen Pyruvic acid and ATP 2. Which of the following chemical changes in cells results in the synthesis of most ATP? A B C D Glucose to pyruvic acid Pyruvic acid to lactic acid Pyruvic acid to acetyl group Pyruvic acid to carbon dioxide and water 3. The processes in the list below occur in living cells. 1 2 3 4 NADP acts as a hydrogen acceptor. ATP is synthesised. Oxygen acts as a hydrogen acceptor. Carbon dioxide enters a cycle of reactions. Which line of the table below matches each process with the set of reactions in which it occurs? 17 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 4. The statements in the list below refer to respiration. 1 2 3 4 Carbon dioxide is released. Occurs during aerobic respiration. The end product is pyruvic acid. The end product is lactic acid. Which statements describe glycolysis? A B C D 1 and 4 1 and 3 2 and 3 2 and 4 5. The diagram below represents a summary of respiration in a mammalian muscle cell. Which box represents ATP? 6. Which line in the table below correctly shows the two chemical reactions which occur in the grana of a chloroplast following the absorption of light energy by chlorophyll? 18 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 7. Which line in the table below correctly shows the number of molecules of ATP used and produced when one molecule of glucose undergoes glycolysis? 8. Which of the following produces water? A B C D Krebs cycle Glycolysis Photolysis Cytochrome system 9. The table below refers to processes in cellular respiration. Which line in the table below correctly identifies processes X, Y and Z? 19 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 10. The diagram below shows energy transfer within a cell. Which line in the table below identifies correctly compounds X and Y? 11. Which line in the table below shows correctly the sites of stages in aerobic respiration? 20 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 12. The diagram below shows the regeneration of ATP in a cell. The following statements relate to this diagram. 1 2 3 4 Reaction X releases energy for anabolic pathways. Reaction Y releases energy for anabolic pathways. Reaction X is catalysed by ATP synthase. Reaction Y is catalysed by ATP synthase. Which statements are correct? A B C D 1 and 3 1 and 4 2 and 3 2 and 4 13. An investigation was carried out into the uptake of sodium ions by animal cells. The graph below shows the rates of sodium ion uptake and breakdown of glucose at different concentrations of oxygen. How many units of sodium ions are taken up over a 5 minute period when the concentration of oxygen in solution is 2%? A B C D 80 100 400 500 21 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 14. The energy content of a glucose molecule is 2900 kilojoules. A glucose molecule entering aerobic respiration transfers 1160 kilojoules of the energy to ATP. What percentage of energy in glucose is transferred to ATP? A B C D 40 60 150 250 15. The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain of respiration is A B C D NADH water ATP oxygen 22 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 16. In an investigation into the effect of lead ion concentration on respiration in yeast, two flasks were set up as described below. The flasks were placed in a water bath at 20 °C for 10 minutes. After this time 2·5 cm3 of yeast suspension was added to each and oxygen sensors fitted as shown in the diagram below. The flasks were left for a further 10 minutes and then oxygen concentration was measured in each flask every 20 seconds for 2 minutes. The results are shown in the table below. (a) (i) Identify the independent variable in this investigation. ____________________________________________________________________ (ii) Identify one variable, not already mentioned, which would have to be kept constant so that valid conclusions could be drawn. ____________________________________________________________________ 23 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (ii) Explain why the flasks were left for 10 minutes before the yeast suspension was added. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ (iii) Explain why the flasks were left for a further 10 minutes after the yeast suspensions were added before measurement of oxygen concentrations were taken. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ (b) On the grid provided, draw a line graph to show the oxygen concentration in Flask A against time. Use an appropriate scale to fill most of the grid. (c) Using information from the table, state the effect of increasing lead ion concentration on the aerobic respiration of yeast. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 24 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (d) Bubbles of gas appeared in both flasks throughout the investigation. (i) Name this gas. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ (ii) Explain why this gas continued to be produced in Flask A at 120s. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 17. Cyanide is a poison that inhibits enzymes involved in aerobic respiration. The graph below shows how cyanide concentration affects the uptake of chloride ions by beetroot cells. The rates of chloride ion uptake are given as percentages of those obtained in a control experiment with no cyanide. 25 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (a) Predict the cyanide concentration at which chloride ion uptake would stop. ______________ units (b) The rate of chloride ion uptake by beetroot at 30 units of cyanide was 200 μg per hour. Calculate the rate of uptake in the control experiment. Space for calculation ___________________ μg per hour (c) The uptake of chloride ions occurs by active transport. Explain how the information given supports this statement. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 18. The diagram below shows an outline of respiration in yeast cells. (a) State the location of glycolysis in yeast cells. _______________________________________________________________________ 26 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (b) Name one substance, other than glucose, which must be present for glycolysis to occur. _______________________________________________________________________ (c) Name compounds R and S. R __________________________________________________________________ S __________________________________________________________________ (d) Explain why the further stages of respiration cannot occur in anaerobic conditions. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 19. In an investigation, yeast was grown in a glucose solution for 160 minutes in a sterilised fermenter. Temperature was kept constant and anaerobic conditions were maintained. The graph below shows the changes in concentration of ethanol in the fermenter during the period. (a) (i) Calculate the increase in concentration of ethanol between 60 and 140 minutes. ___________ grams per litre 27 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (ii) Calculate the average increase in ethanol concentration per minute during the first 40 minutes. ___________ grams per litre per minute (b) (i) At point A on the graph, the ethanol concentration stopped increasing when air temporarily leaked into the fermenter. Explain this result. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (ii) Assuming no further air leaks, explain why the ethanol concentration stopped increasing at point B. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 20. The diagram below shows some of the steps in respiration. 28 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (a) Complete the table below by naming substances W, X and Y. (b) State the number of carbon atoms present in a molecule of substance Z. _______________________________________________________________________ 21. Yeast cells were grown in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions and the volume of carbon dioxide produced was measured. The results are shown in the graph below. (a) At which time is there the greatest difference between the volumes of carbon dioxide produced in aerobic and anaerobic conditions? Tick (✓) the correct box. 29 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (b) Calculate the average rate of carbon dioxide production per hour over the first 6 hours in aerobic conditions. Space for calculation __________ cm3 per hour 22. The diagram below shows parts of two stages in the aerobic respiration of glucose. (a) Name stages X and Y. X __________________________________________________________________ Y __________________________________________________________________ 30 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (b) Name compounds P and Q. P __________________________________________________________________ Q __________________________________________________________________ (c) Describe the role of the dehydrogenase enzymes in stages X and Y. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (d) The diagram below shows part of the electron transport chain attached to the inner membrane of a mitochondrion. (i) In this system, hydrogen ions are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane as shown in the diagram. Describe the source of energy required for this process. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (ii) The return flow of hydrogen ions drives enzyme X which results in the production of ATP. Name enzyme X. ___________________________________________________________________ (iii) State the role of oxygen in the electron transport chain. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 31 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 23. Give an account of the structure of a mitochondrion and the role of the cytochrome system in respiration. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 32 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 24. Give an account of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle in cells. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 33 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Key Area 2.3 1. The graphs below show the results of an experiment into the effect of aerobic and anaerobic conditions on the uptake of calcium and magnesium ions by pond algae. Which of the following is a valid conclusion that can be drawn from the results? A B C D At 120 minutes in aerobic conditions the uptake of calcium ions is greater than that of magnesium ions. At 60 minutes in anaerobic conditions there was a greater uptake of calcium ions compared with magnesium ions. Over the 120 minutes in aerobic conditions the average rate of uptake of calcium ions is greater than that of magnesium ions. At 60 minutes in anaerobic conditions there was a greater uptake of magnesium ions compared with calcium ions. 2. The table below shows the mass of water gained and lost by a small mammal over a 24hour period. What percentage of water gained comes from metabolic water? A B C D 9% 45% 54% 90% 34 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 3. The graph below shows the effect of the carbon dioxide concentration of inhaled air on the breathing rate of an individual. If the volume of one breath is 0·5 litre, what volume of air will be breathed in one minute when the CO2 concentration is 4%? A B C D 6 litres 9 litres 18 litres 36 litres 4. An investigation was carried out into the uptake of sodium ions by animal cells. The graph below shows the rates of sodium ion uptake and breakdown of glucose at different concentrations of oxygen. 35 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework How many units of sodium ions are taken up over a 5 minute period when the concentration of oxygen in solution is 2%? A B C D 80 100 400 500 5. The graph below shows the effect of air temperature on the metabolic rate of two different animals. Which line in the table below identifies correctly the temperatures at which oxygen consumption will be greatest in the tissues of each animal? 36 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 6. In an investigation into the metabolic rate of a snail at rest, its oxygen uptake was measured using the apparatus shown in the diagram below. The apparatus was kept at 10 °C with the tap open for 15 minutes. To start the experiment, the tap was closed and the reading on the scale recorded. Every 2 minutes for 10 minutes, the oxygen uptake was recorded by taking readings from the scale. The results are shown in the table below. (a) Explain why the apparatus was left for 15 minutes with the tap open before readings were taken. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 37 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (b) Describe a suitable control for this investigation. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (c) Identify the dependent variable in this investigation. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (d) To increase the reliability of results, the experiment was repeated several times. Identify one variable, not already mentioned, that would have to be kept the same each time to ensure that the procedure was valid. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (e) On the grid below, draw a line graph to show the reading on the scale against time, choosing appropriate scales so that the graph fills most of the grid. 38 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (f) The mass of the snail was 5·0 g. Use results in the table to calculate the rate of oxygen uptake by the snail over the 10 minute period. ________________ cm3 oxygen per minute per gram of snail (g) Predict the effect of an increase in temperature to 15 °C on the oxygen uptake by the snail and justify your answer. Prediction _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Justification _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (h) Explain how the respiration of the snail and the presence of the solution in the test tube results in the movement of the coloured liquid on the scale. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 7. The following diagrams represent the structures of fish, mammal and amphibian hearts. 39 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (a) Complete the table below by inserting the correct letters, animal group and type of circulation. Heart Animal Group Type of circulation (single, incomplete double or complete double) single mammal S (b) Add arrows in the vessels X, Y and Z on the diagrams to indicate the direction of flow of blood within them. (c) Explain how heart R is better adapted than heart S to allow a high metabolic rate in the cells which it supplies with blood. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 8. The graph shows the rate of potassium ion uptake by human liver cells in different oxygen concentrations at 30 °C. 40 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (a) When the oxygen concentration is 1%, how many units of potassium would a cell take up in one hour? ________________ units per hour (b) Suggest a reason why the graph levels off at oxygen concentrations above 3·5%. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (c) When the experiment was repeated at 20 °C, the potassium ion uptake decreased. Explain this observation. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 41 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Key Area 2.4 and 2.5 1. The drinking rate and concentrations of sodium and chloride ions in blood were measured over a six hour period after a salmon was transferred from freshwater to sea water. The results are shown in the graph below. Which line in the table correctly shows the results after three hours? 42 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 2. Which line in the table below shows features likely to be found in a plant and in a small mammal both adapted to life in hot desert conditions? 3. The statements below describe methods of maintaining a water balance in fish. 1 2 3 4 Salts actively absorbed by chloride secretory cells Salts actively secreted by chloride secretory cells Low rate of kidney filtration High rate of kidney filtration Which of these are used by freshwater bony fish? A B C D 1 and 3 only 2 and 4 only 1 and 4 only 2 and 3 only 4. Which line in the table below shows correctly the main source of body heat and the method of controlling body temperature in an ectotherm? 43 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 5. The graph below shows the relationship between air temperature and the body temperature of two animal species X and Y. Which line in the table below correctly describes species X and Y? 6. The figure below shows the general relationships between the internal environment and variation in the external environment of four animals. Which animal could occupy the widest range of habitats? 44 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 7. The graphs below show how environmental changes can affect the internal conditions in aquatic organisms W, X, Y and Z. Which line in the table correctly identifies the osmoconformer and the homeotherm? 8. Animals may interact with their environment by conformation or regulation. Each statement below applies to one of these interactions. 1 2 3 4 A wide range of habitats can be occupied A restricted range of habitats can be occupied There is a high energy cost There is no energy cost Which statements apply to conformation? A B C D 1 and 4 1 and 3 2 and 4 2 and 3 45 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 9. The diagram below shows a section through the skin of a mammal. Which line in the table below correctly identifies the state of the erector muscle and the change in blood flow in the capillary which would be expected if the skin was exposed to low temperature? 10. Which graph below best illustrates the effect of increasing temperature on oxygen consumption in a conformer and a regulator? 46 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 11. In an investigation, 50 salmon were kept in a tank of fresh water for four days, then transferred to a tank of salt water for a further six days. Each day, their gills were examined and the average diameter of chloride secretory cells was recorded. The results are shown in the table below. (a) In the following sentence, underline one alternative in each pair to make the sentence correct. On day 3 the salmon are (hypertonic / hypotonic) to their surroundings and their chloride secretory cells actively transport salts (into / out of) the salmon. (b) Describe the effect of salt water on the average diameter of the chloride secretory cells between day 5 and day 10. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (c) Following the investigation, the fish were returned to fresh water. In the table below, tick one box in each row to show how this change affects kidney function. 47 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 12. The diagram shows an outline of the control of body temperature in a mammal. (a) (i) State the exact location of the temperature monitoring centre. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (ii) The skin has effectors which are involved in corrective mechanisms A and B. State how messages are sent from the temperature monitoring centre to the skin. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (iii) Give one example of a corrective mechanism B and explain how it would return the body temperature to normal. Example ___________________________________________________ Explanation ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ (iv) Explain why maintaining body temperature within tolerable limits is important to the metabolism of mammals. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (b) Mammals obtain most of their heat from their metabolism. Give the term which describes animals that obtain most of their body heat from their surroundings. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 48 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 13. The list below shows conditions which must be maintained within tolerable limits in the human body. A B C blood glucose concentration blood water concentration body temperature (a) Use all the letters from the list to complete the table below to show where each condition is monitored. (b) The liver contains a reservoir of stored carbohydrate. Name two hormones which can cause the breakdown of this carbohydrate to increase the concentration of glucose in the blood. 1 2 _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ (c) An increase in blood water concentration causes a reduction in the level of ADH in the bloodstream. Describe the effect of this reduction on the kidney tubules. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (d) (i) When body temperature falls below normal, the blood vessels in the skin respond. State how the blood vessels in the skin respond and explain how this helps return body temperature to normal. Blood vessel response _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ Explanation _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ (ii) What term is used to describe animals which derive most of their body heat from their own metabolism? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 49 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 14. Animals that live under polar sea-ice benefit from adaptations that allow them to survive changes in the salinity of their immediate environment as the ice freezes and thaws. The crustacean Gammarus wilkitzkii is a dominant species of the Arctic ice community. During the summer, as sea-ice melts, this species experiences low salinity and during sea‑ice growth in the winter it is exposed to high salinity. Figure 1 shows the rate of oxygen consumption of this animal when transferred to water of varying salinity. Figure 2 shows ion concentrations in its body fluids at the higher salinities. (a) Refer to Figure 1. Explain how the data suggest that Gammarus wilkitzkii is a regulator in salinities up to 2·5%. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (b) Refer to Figure 2. (i) What term is used to describe an organism that shows this type of physiological response? _______________________________________________________________ 50 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (ii) Increasing concentrations of ions in body fluids lower the temperature at which these fluids will freeze. Suggest how the response shown in Figure 2 would aid the survival of G. wilkitzkii during winter. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ (c) Another crustacean, Parathemisto libellula, is unable to tolerate or resist salinity variations. How would this affect the habitat range that it could occupy? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 15. The table below refers to environmental problems that salt water bony fish and desert rats have in osmoregulation and adaptations that these animals use to maintain their water balance. Complete the table by giving an environmental problem faced by salt water bony fish and adding one adaptation to each empty box. 51 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 16. The diagram below represents a section through the skin of a mammal. (a) Select one structure labelled in the diagram and explain how it responds to a decrease in temperature to bring about a correction in body temperature. Structure ___________________________________________________ Explanation ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ (b) (i) Explain the importance of thermoregulation to mammals. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (ii) Reptiles have behavioural adaptations to help them to thermoregulate. Give one example of this. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (c) Name one external abiotic factor, other than temperature, which can affect the ability of an organism to maintain its metabolic rate. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 52 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 17. Write notes on maintaining a water balance under the following headings: (a) osmoregulation in salt water bony fish; (b) water conservation in the desert rat. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 53 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework 18. Write notes on the following : (a) endotherms and ectotherms; (b) temperature regulation in mammals. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 54 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Key Area 2.6 1. The diagram below shows an image of a bacterial cell that has been magnified 1500 times. What is the actual length of the cell in micrometres (μm)? A B C D 2. 0·003 3·000 6750 6·750 The graph below shows a typical growth pattern for micro-organisms in culture. At which point on the graph are most enzymes being induced to metabolise available substrates? 3. Which line in the table below correctly represents the organelles in a prokaryotic cell? 55 CfE Higher Biology 4. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework The following diagram shows a bacterial cell. The length of this cell in millimetres (mm) is A B C D 5. 800 80 0·008 0·0008 Complete the following sentences by underlining one of the alternatives in each pair. Regeneration involves development of cells with specialised functions from (differentiated / undifferentiated) cells through the switching on or off of particular (hormones / genes). Mammals have (limited / extensive) powers of regeneration. 56 CfE Higher Biology 6. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework A growth curve in a culture of bacteria is shown in the diagram below. (a) In culturing bacteria it is important to control the pH of the culture medium. Describe how the pH of a culture medium can be controlled. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (b) (i) Name each of the phases of growth indicated by letters on the graph. W _________________________________________________________ X _________________________________________________________ Y _________________________________________________________ Z _________________________________________________________ (ii) Give the letter which indicates a region of the graph in which most enzymes are being induced to metabolise the available substrate. Letter _________________________________________________________ (iii) Give one reason for the decrease in number of cells at phase Z. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 7. Many enzymes used in biotechnology are produced industrially by fermentation using naturally occurring micro-organisms. (a) Name one industrially produced enzyme and the micro-organism used in the fermentation. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 57 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (b) (i) Describe two conditions that need to be controlled during the fermentation process used to produce enzymes. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (ii) Give one method used in the recovery of enzymes from the fermentation culture. ___________________________________________________________________ (c) Explain what is meant when an industrial enzyme is described as a secondary metabolite. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 8. To make yoghurt, milk is pasteurised and then inoculated with bacteria that allow fermentation to occur. Two species commonly used together in the inoculum are Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. (a) What is the purpose of pasteurisation? _____________________________________________________________________ (b) The fermentation is a two-stage process. (i) State the chemical conversion taking place in the first stage. ___________________________________________________________________ (ii) What is the role of the second stage? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 58 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (c) The graph shows the growth of L. bulgaricus and S. thermophilus in both pure and mixed culture. (i) Calculate the reduction in growth of L. bulgaricus at 8 hours as a result of being in the mixed culture. (ii) Scientists have suggested that S. thermophilus receives a growth promoting substance in this mixed culture. How do the data support that conclusion? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 59 CfE Higher Biology 9. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Describe how the growth rate constant of a bacterial culture can be determined. What is its relevance when culturing bacteria for enzyme production? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 60 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Key Area 2.7 1. The following steps are involved in the process of genetic engineering. 1 2 3 4 Insertion of a plasmid into a bacterial host cell. Use of an enzyme to cut out the desired gene from a chromosome. Insertion of the desired gene into the bacterial plasmid. Use of an enzyme to open a bacterial plasmid. What is the correct sequence of these steps? A B C D 2. 4123 2431 4312 2341 The table below contains descriptions of terms used to illustrate the control of lactose metabolism in the bacterium Esherichia coli. Which line in the table contains terms which correctly match the descriptions given? 3. According to the Jacob-Monod hypothesis, a regulator gene is responsible for A B C D coding for the production of an inducer molecule switching on an operator coding for the production of a repressor molecule switching on a structural gene. 61 CfE Higher Biology 4. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework The flow chart below represents the programming of E. coli bacteria to produce human insulin. Which line in the table below identifies correctly the stages at which an endonuclease and a ligase are used? 5. Using recombinant DNA technology, the bacterium E. coli can be modified so that it can produce human insulin. The following steps are involved. 1 2 3 4 Culture large quantities of E. coli in nutrient medium. Insert human insulin gene into E. coli plasmid DNA. Cut insulin gene from human chromosome using enzymes. Extract insulin from culture medium. The correct order of these steps is A B C D 3, 2, 1, 4 3, 1, 2, 4 1, 4, 3, 2 1, 2, 3, 4. 62 CfE Higher Biology 6. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework The gene encoding a protein was removed from the human genome and transferred into two different recipient cells by different methods as shown in the table below. The protein was functional only when produced in yeast cells. The most likely reason for this was because the A B C D 7. bacterial plasmids did not contain marker genes protein produced in bacteria had an incorrect amino acid sequence bacterial plasmids did not contain self-replication genes protein produced in bacteria was not folded correctly. The diagram below shows the restriction enzyme sites in a plasmid that carries the genes for resistance to the antibiotics ampicillin and tetracycline. Which line in the table below identifies correctly the antibiotic resistance that would remain when a gene is inserted at these restriction enzyme sites? 63 CfE Higher Biology 8. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Diagram A shows a bacterial plasmid containing genes for resistance to the antibiotics tetracycline and ampicillin. Diagram B shows this plasmid after it had been genetically engineered by inserting a human blood-clotting gene. (a) Give a technique which could be used to locate the position of the blood-clotting gene on a human chromosome. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (b) Two different enzymes are used to produce the genetically engineered plasmid. Complete the table to show the function of each enzyme. (c) The genetically engineered plasmids were inserted into bacteria. Using information from the diagrams, explain why these bacteria were not resistant to tetracycline. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 64 CfE Higher Biology 9. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework In an experiment to investigate the Jacob-Monod hypothesis of lactose metabolism in E. coli, flasks were set up as shown in the diagram below. E. coli breaks down lactose using the enzyme β–galactosidase as shown. (a) (i) β –galactosidase was produced in Flask 1. Describe events which led to the production of this enzyme. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (ii) β –galactosidase was not produced in Flask 2. Explain the advantage to E. coli of not producing the enzyme in this case. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (b) ONPG is a colourless substance which is converted to a yellow product by β – galactosidase. Use this information to describe how ONPG could be used to show that E. coli only produced β –galactosidase in the presence of lactose. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 65 CfE Higher Biology 10. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework In the control of lactose metabolism in Escherichia coli (E. coli), lactose acts as an inducer of the enzyme β-galactosidase. The graph shows changes in concentrations of lactose and β-galactosidase after lactose was added to an E. coli culture growing in a container. (a) Describe how the graph supports the statement that β-galactosidase breaks down lactose. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (b) The statements in the table refer to times X, Y and Z on the graph. Complete the table by writing true or false in each of the spaces provided. 66 CfE Higher Biology 11. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Diagram 1 below shows a plasmid that contains two genes for antibiotic resistance. Diagram 2 shows the same plasmid after modification by the insertion of a gene from another organism. (a) Two different enzymes are required to produce the modified plasmid. Complete the table below by: (i) (ii) (iii) naming the enzyme which cuts plasmids at specific restriction sites; naming the second enzyme required to modify plasmids; describing the function of the second enzyme. (b) Bacteria took up the modified plasmids. Explain why these bacteria will not have resistance to antibiotic Y. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 67 CfE Higher Biology 12. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Escherichia coli is a species of bacteria found in the lower intestines of humans. Sections of the DNA of two strains of E. coli are shown below. Gene B codes for a protein known as Shiga toxin which can cause serious food poisoning in humans. (a) The gene for Shiga toxin has been acquired by E. coli 0157H7. Give two methods by which the bacterial strain could have acquired this gene. 1 _______________________________________________________________ 2 _______________________________________________________________ (b) E. coli K12 is routinely used in recombinant DNA technology. Explain why E. coli K12 is used whereas E. coli 0157H7 is not. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (c) Bacteria are used in recombinant DNA technology. Explain why animal DNA which has been transferred to bacteria may produce proteins which are not functional. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 68 CfE Higher Biology 13. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework Transgenic plants can be produced using genetically engineered plasmids. The plasmids are obtained from bacteria that naturally infect plant cells. A modified plasmid is shown in the diagram below. Bacterial cells containing the modified plasmid are incubated with plant cells. The plant cells are then cultured in a growth medium containing kanamycin. (a) What is meant by the term transgenic? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (b) Name the bacterial source of these plasmids. _____________________________________________________________________ (c) Explain the role of kanamycin in the production of transgenic plants. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (d) Give one example of the use of this transgenic technology _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ 69 CfE Higher Biology 14. Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework The Jacob-Monod hypothesis describes lactose metabolism in the bacterium Escherichia coli. Lactose acts as an inducer of the enzyme β-galactosidase in the bacterium. This enzyme breaks down lactose as shown. An investigation of this reaction in E. coli at 25 °C was carried out as described below. • 100cm3 of gel beads coated with E. coli were placed into each of seven identical funnels fitted with outlet taps. • 100cm3 of solution containing 2 grams of lactose was poured into each funnel. • At each time shown in the table, the solution from one of the funnels was collected. • The mass of lactose in each solution was measured. The results are shown in the table below. (a) Identify one variable, not already mentioned, that should have been controlled to ensure that the experimental procedure was valid. __________________________________________________________________ 70 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (b) A control experiment would be needed for each funnel. Describe such a control and explain its purpose in the investigation. Description ________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Purpose _________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (c) On the grid provided below, draw a line graph to show the mass of lactose in the solution collected against time. Use an appropriate scale to fill most of the grid. (d) Calculate the average mass of lactose broken down per minute in funnel 5. Space for calculation ____________ g per minute 71 CfE Higher Biology Unit 2 Metabolism & Survival Homework (e) Use the information given to explain why E. coli had not broken down any lactose in the first 10 minutes. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (f) State one advantage to E. coli of controlling lactose metabolism as described by the Jacob-Monod hypothesis. __________________________________________________________________ 15. The diagram below shows information relating to the Jacob–Monod hypothesis of the control of gene action in the bacterium Escherichia coli. (a) Name gene 1 __________________________________________________________________ (b) Name the substance which acts as the inducer. __________________________________________________________________ (c) Describe the sequence of events that occurs in the absence of the inducer. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ (d) Explain why it is important for E. coli to control gene action. __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 72